
Account for the following:
(a)Gabriel phthalimide synthesis is not preferred for preparing aromatic primary amines.
(b) On reaction with benzene sulphonyl chloride, primary amine yields product soluble in alkali whereas second amine yield product insoluble in alkali.
Answer
576.6k+ views
Hint: The aromatic compound prefers to form electrophile. The phthalimide gives nucleophilic substitution with alkyl halide. The product of reaction of benzene sulphonyl chloride with primary amine has hydrogen attached with nitrogen atom. The product of reaction of benzene sulphonyl chloride with secondary amine has no hydrogen attached with nitrogen atom.
Complete step by step answer:
(a) Gabriel’s Phthalimide synthesis is used for the conversion of primary alkyl halide into a primary amine.
The reaction is as follows:
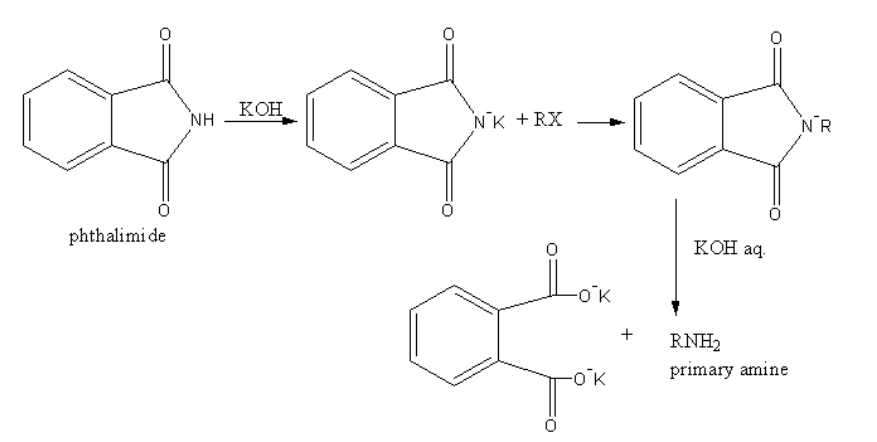
In Gabriel phthalimide synthesis, the nucleophile phthalimide ion attacks on the primary alkyl halide. So, an electrophilic alkyl centre is created on primary alkyl halide. Aromatic amine prefer the electrophilic substitution reaction. Because aromatic halides show resonance due to resonance they are stable. The nucleophilic substitution destabilizes the resonance of the aromatic compounds.
Therefore, due to lack of reactivity of aromatic amines towards nucleophilic substitution, the Gabriel phthalimide synthesis is not preferred for preparing aromatic primary amines.
(b) The reaction of benzene sulphonyl chloride with primary amine is as follows:
The reaction of benzene sulphonyl chloride with primary amine yields N-alkyl benzene sulphonamide.
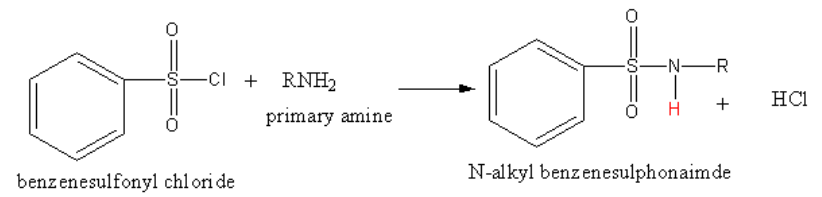
The product N-alkyl benzene sulphonamide has acidic hydrogen. The hydrogen (shown in red colour) is very acidic due to presence of strong electron-withdrawing sulphonyl group. So, the product N-alkyl benzene sulphonamide forms hydrogen bonding with alkali (polar solvents) and hence soluble in alkali.
The reaction of benzene sulphonyl chloride with secondary amine is as follows:
The reaction of benzene sulphonyl chloride with secondary amine yields N, N-alkyl benzene sulphonamide.
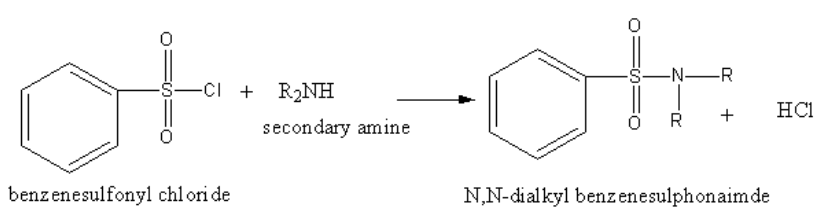
The product N,N-alkyl benzene sulphonamide has no acidic hydrogen. So, the product N-alkyl benzene sulphonamide cannot form hydrogen bonding with alkali and hence insoluble in alkali.
Note:
The reagent used in Gabriel’s Phthalimide synthesis potassium Phthalimide. Gabriel phthalimide synthesis nucleophilic substitution reaction. The general reaction shown by aromatic compounds is electrophilic substitution reaction. Due to the unsaturated electron density the aromatic compounds work as nucleophiles. The reaction of benzene sulphonyl chloride with amines is known as the Hinesburg test. The tertiary amine does not give the Hinesburg test. Because in case of tertiary amine it has no hydrogen attached with nitrogen.
Complete step by step answer:
(a) Gabriel’s Phthalimide synthesis is used for the conversion of primary alkyl halide into a primary amine.
The reaction is as follows:

In Gabriel phthalimide synthesis, the nucleophile phthalimide ion attacks on the primary alkyl halide. So, an electrophilic alkyl centre is created on primary alkyl halide. Aromatic amine prefer the electrophilic substitution reaction. Because aromatic halides show resonance due to resonance they are stable. The nucleophilic substitution destabilizes the resonance of the aromatic compounds.
Therefore, due to lack of reactivity of aromatic amines towards nucleophilic substitution, the Gabriel phthalimide synthesis is not preferred for preparing aromatic primary amines.
(b) The reaction of benzene sulphonyl chloride with primary amine is as follows:
The reaction of benzene sulphonyl chloride with primary amine yields N-alkyl benzene sulphonamide.

The product N-alkyl benzene sulphonamide has acidic hydrogen. The hydrogen (shown in red colour) is very acidic due to presence of strong electron-withdrawing sulphonyl group. So, the product N-alkyl benzene sulphonamide forms hydrogen bonding with alkali (polar solvents) and hence soluble in alkali.
The reaction of benzene sulphonyl chloride with secondary amine is as follows:
The reaction of benzene sulphonyl chloride with secondary amine yields N, N-alkyl benzene sulphonamide.

The product N,N-alkyl benzene sulphonamide has no acidic hydrogen. So, the product N-alkyl benzene sulphonamide cannot form hydrogen bonding with alkali and hence insoluble in alkali.
Note:
The reagent used in Gabriel’s Phthalimide synthesis potassium Phthalimide. Gabriel phthalimide synthesis nucleophilic substitution reaction. The general reaction shown by aromatic compounds is electrophilic substitution reaction. Due to the unsaturated electron density the aromatic compounds work as nucleophiles. The reaction of benzene sulphonyl chloride with amines is known as the Hinesburg test. The tertiary amine does not give the Hinesburg test. Because in case of tertiary amine it has no hydrogen attached with nitrogen.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




