
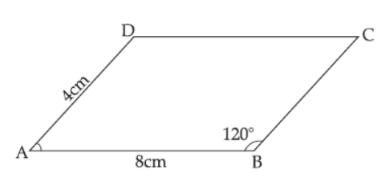
ABCD is a parallelogram with AB=8cm, AD=4cm, \[\angle B=120{}^\circ \]
(a) What is $\angle $A?
(b) What is the perpendicular distance from D to AB?
(c) What is the area of ABCD?

Answer
621.3k+ views
Hint: Use the property of parallelogram that opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal. Then use the property that the sum of all angles of a quadrilateral is \[360{}^\circ \] . For the second part, use cosine of angle A found from the first part to find perpendicular distance. For the third part, use the formula for Area of parallelogram = Length of base \[\times \] Height .
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given that ABCD is a parallelogram with AB=8cm, AD=4cm, \[\angle B=120{}^\circ \]
We need to find the following
(a) $\angle $A
(b) the perpendicular distance from D to AB
(c) the area of ABCD
Let us first solve (a).
We know that the opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal.
Using this, \[\angle B=\angle D=120{}^\circ \]
And, \[\angle A=\angle C\]
Also, we know that the sum of all angles of a quadrilateral is \[360{}^\circ \] .
\[\angle A+\angle B+\angle C+\angle D=360{}^\circ \]
Substituting the relations between the angles in this equation, we will get the following:
\[2\angle A+2\angle B=360{}^\circ \]
\[2\angle A+2\times 120{}^\circ =360{}^\circ \]
\[2\angle A+240{}^\circ =360{}^\circ \]
\[2\angle A=120{}^\circ \]
So, \[\angle A=60{}^\circ \]
Now, let us solve (b)
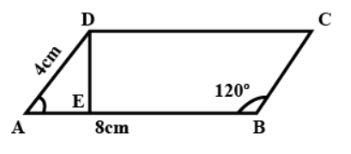
For this, draw DE as perpendicular from D to AB as shown in the figure.
We need to find the length of DE.
Now, we found in the previous part that \[\angle A=60{}^\circ \]
We also know that \[\sin 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\]
So, \[\sin \angle A=\dfrac{DE}{AD}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\]
\[\sin \angle A=\dfrac{DE}{4}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\]
This gives us: \[DE=2\sqrt{3}\] cm
So, the perpendicular distance from D to AB is \[2\sqrt{3}\] cm.
Now, we will solve (c).
We need to find the area of ABCD.
We know that:
Area of parallelogram = Length of base \[\times \] Height
Here, we have length of base, AB = 8 cm
Height, DE = \[2\sqrt{3}\] cm
Putting these values in the formula, we will get the following:
Area of ABCD = Length of AB \[\times \] Length of DE
Area of ABCD = \[8\times 2\sqrt{3}\] \[=16\sqrt{3}c{{m}^{2}}\]
So, Area of ABCD is \[16\sqrt{3}c{{m}^{2}}\]
Note: You have to remember the various geometrical properties to solve this kind of question. For example, in this question too, you need to use the properties like opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal and that the sum of all angles of a quadrilateral is \[360{}^\circ \]
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given that ABCD is a parallelogram with AB=8cm, AD=4cm, \[\angle B=120{}^\circ \]
We need to find the following
(a) $\angle $A
(b) the perpendicular distance from D to AB
(c) the area of ABCD
Let us first solve (a).
We know that the opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal.
Using this, \[\angle B=\angle D=120{}^\circ \]
And, \[\angle A=\angle C\]
Also, we know that the sum of all angles of a quadrilateral is \[360{}^\circ \] .
\[\angle A+\angle B+\angle C+\angle D=360{}^\circ \]
Substituting the relations between the angles in this equation, we will get the following:
\[2\angle A+2\angle B=360{}^\circ \]
\[2\angle A+2\times 120{}^\circ =360{}^\circ \]
\[2\angle A+240{}^\circ =360{}^\circ \]
\[2\angle A=120{}^\circ \]
So, \[\angle A=60{}^\circ \]
Now, let us solve (b)
For this, draw DE as perpendicular from D to AB as shown in the figure.
We need to find the length of DE.

Now, we found in the previous part that \[\angle A=60{}^\circ \]
We also know that \[\sin 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\]
So, \[\sin \angle A=\dfrac{DE}{AD}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\]
\[\sin \angle A=\dfrac{DE}{4}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\]
This gives us: \[DE=2\sqrt{3}\] cm
So, the perpendicular distance from D to AB is \[2\sqrt{3}\] cm.
Now, we will solve (c).
We need to find the area of ABCD.
We know that:
Area of parallelogram = Length of base \[\times \] Height
Here, we have length of base, AB = 8 cm
Height, DE = \[2\sqrt{3}\] cm
Putting these values in the formula, we will get the following:
Area of ABCD = Length of AB \[\times \] Length of DE
Area of ABCD = \[8\times 2\sqrt{3}\] \[=16\sqrt{3}c{{m}^{2}}\]
So, Area of ABCD is \[16\sqrt{3}c{{m}^{2}}\]
Note: You have to remember the various geometrical properties to solve this kind of question. For example, in this question too, you need to use the properties like opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal and that the sum of all angles of a quadrilateral is \[360{}^\circ \]
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Find the greatest fivedigit number which is a perfect class 9 maths CBSE

Find the mode and median of the data 13 16 12 14 1-class-9-maths-CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Find the sum of series 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + + 100 class 9 maths CBSE




