
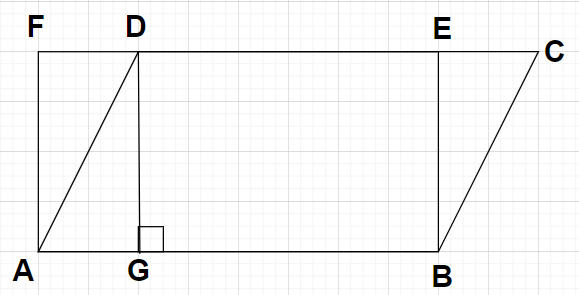
ABCD is a parallelogram and ABEF is a rectangle and DG is perpendicular on AB.
Prove that
$\left( {\text{i}} \right)$ ar(ABCD) = ar(ABEF)
$\left( {{\text{ii}}} \right)$ ar(ABCD) = AB$ \times $DG

Answer
622.8k+ views
Hint: Here, we will proceed by using the concept that a rectangle is a special case of parallelogram having pairs of opposite sides equal. After that we will apply the concept that the areas of the two parallelograms having equal height and between the same parallels are always equal.
Complete step-by-step answer:
As shown in the figure, ABCD is a parallelogram with side AB parallel to side CD and side BC parallel to AD.
Also given that ABEF is a rectangle with AB = EF and BE = AF
$\left( {\text{i}} \right)$ To prove: ar(ABCD) = ar(ABEF)
Rectangle is also a parallelogram having the pair of opposite sides equal. So, ABEF is also a parallelogram.
As we know that the areas of the two parallelograms having equal height and between the same parallels are always equal.
Since, the height of both the parallelograms i.e., ABCD and ABEF are equal and they are between the same parallels i.e., AB and FC. So, the areas of both these parallelograms will be equal.
Therefore, Area of ABCD = Area of ABEF i.e., ar(ABCD) = ar(ABEF) $ \to \left( 1 \right)$
The above equation is the same equation which we needed to prove.
$\left( {{\text{ii}}} \right)$ To prove: ar(ABCD) = AB$ \times $DG
As we know that the area of any rectangle is given by
Area of the rectangle = (Length of the rectangle)$ \times $(Breadth of the rectangle)
Using the above formula, we have
Area of rectangle ABEF = (AB)$ \times $(BE) $ \to \left( 2 \right)$
Clearly from the figure, we can write
BE = DG$ \to \left( 3 \right)$
Using equations (1) and (3) in equation (2), we get
ar(ABCD) = AB$ \times $DG
The above equation is the same equation which we needed to prove.
Note: In this particular problem, in parallelogram ABCD, AB$\parallel $FC and in rectangle ABEF, again AB$\parallel $FC. Also, the interior angles of rectangle ABEF at the vertices are all equal to ${90^0}$ and also, DG is a perpendicular to the length AB so $\angle {\text{DGE}} = {90^0}$, that’s why we have written that the side BE is equal to side DG i.e., BE = DG.
Complete step-by-step answer:
As shown in the figure, ABCD is a parallelogram with side AB parallel to side CD and side BC parallel to AD.
Also given that ABEF is a rectangle with AB = EF and BE = AF
$\left( {\text{i}} \right)$ To prove: ar(ABCD) = ar(ABEF)
Rectangle is also a parallelogram having the pair of opposite sides equal. So, ABEF is also a parallelogram.
As we know that the areas of the two parallelograms having equal height and between the same parallels are always equal.
Since, the height of both the parallelograms i.e., ABCD and ABEF are equal and they are between the same parallels i.e., AB and FC. So, the areas of both these parallelograms will be equal.
Therefore, Area of ABCD = Area of ABEF i.e., ar(ABCD) = ar(ABEF) $ \to \left( 1 \right)$
The above equation is the same equation which we needed to prove.
$\left( {{\text{ii}}} \right)$ To prove: ar(ABCD) = AB$ \times $DG
As we know that the area of any rectangle is given by
Area of the rectangle = (Length of the rectangle)$ \times $(Breadth of the rectangle)
Using the above formula, we have
Area of rectangle ABEF = (AB)$ \times $(BE) $ \to \left( 2 \right)$
Clearly from the figure, we can write
BE = DG$ \to \left( 3 \right)$
Using equations (1) and (3) in equation (2), we get
ar(ABCD) = AB$ \times $DG
The above equation is the same equation which we needed to prove.
Note: In this particular problem, in parallelogram ABCD, AB$\parallel $FC and in rectangle ABEF, again AB$\parallel $FC. Also, the interior angles of rectangle ABEF at the vertices are all equal to ${90^0}$ and also, DG is a perpendicular to the length AB so $\angle {\text{DGE}} = {90^0}$, that’s why we have written that the side BE is equal to side DG i.e., BE = DG.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

What is the color of ferrous sulphate crystals? How does this color change after heating? Name the products formed on strongly heating ferrous sulphate crystals. What type of chemical reaction occurs in this type of change.

What is the Full Form of ICSE / ISC ?

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Explain the importance of pH in everyday life class 9 chemistry CBSE




