
How is a Wavefront different from a Ray?
Answer
504.6k+ views
Hint: Wavefront is defined as the locus of all the points with a constant phase. The ray on the other hand on the wavefront is normal to the wavefront. Ray represents the direction of propagation of the wave through which travels.
Complete answer:
Wavefront is the set of all locations in a medium where the wave is at the same phase. This could be where all the crests are, where all the troughs are, or any phase in between. Wavefronts are useful for showing how waves are useful for showing how waves move in two dimensions. The length between two lines on a wavefront is exactly one wavelength.
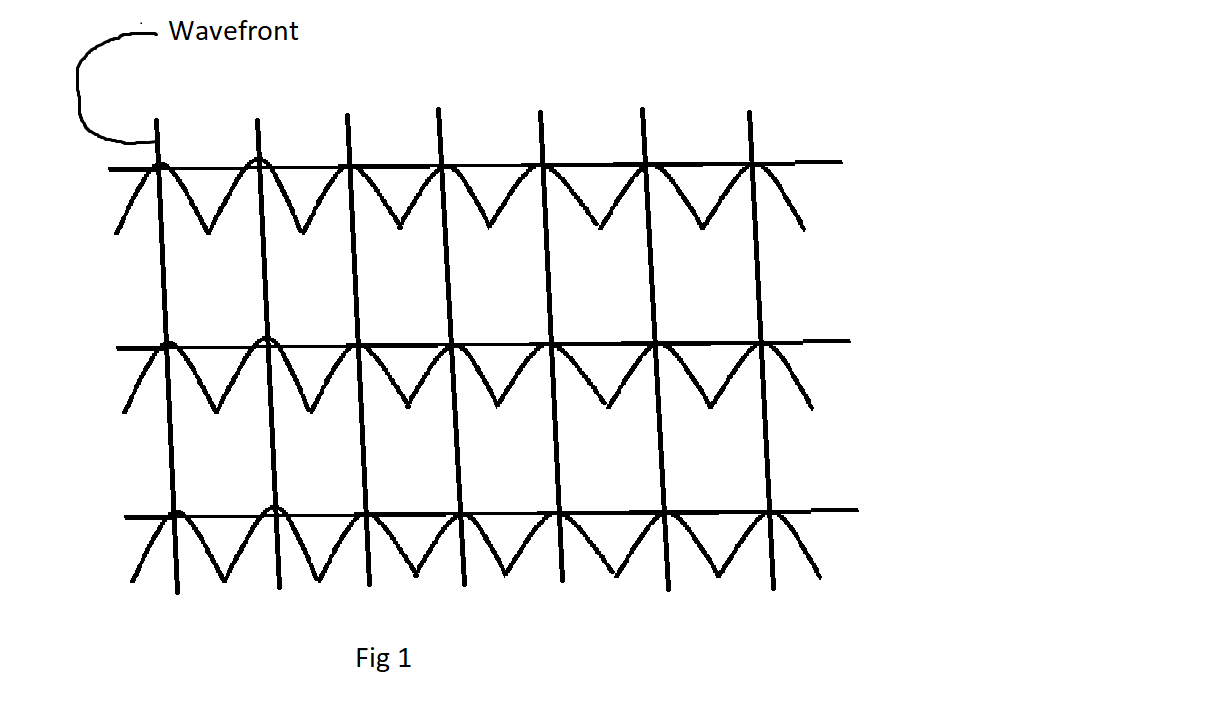
The above diagram represents the wavefront.
Suppose if we take only the wavefront we can use it to represent rays.
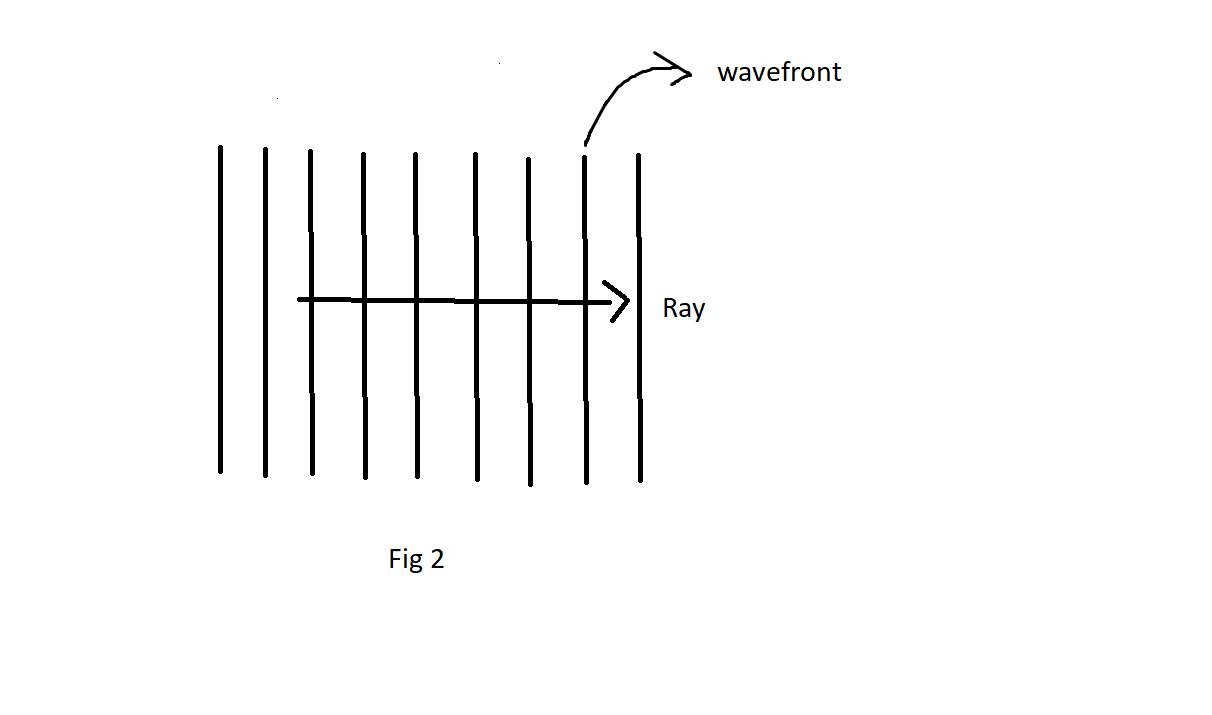
Here the water waves travel from left to right. The ray is something that shows the direction of the water waves. Rays are always normal to the wavefront.
Thus we can summarize that the wavefront is the surface of the constant phase and the ray indicates the direction of the propagation.
Note:
There are three different types of the wavefront.
Plane wavefront: Plane wavefront has a constant wave phase along a planar surface or the wavefront.
Spherical wavefront: A spherical wavefront is the front of a propagating wave that has the shape of the ball
Cylindrical wavefront: This wavefront appears when the source of waves is a line source.
Wavefront’s shape always depends on the source. A wavefront from a point source is spherical or circular while an extended large source has a plane or flat wavefront.
Complete answer:
Wavefront is the set of all locations in a medium where the wave is at the same phase. This could be where all the crests are, where all the troughs are, or any phase in between. Wavefronts are useful for showing how waves are useful for showing how waves move in two dimensions. The length between two lines on a wavefront is exactly one wavelength.

The above diagram represents the wavefront.
Suppose if we take only the wavefront we can use it to represent rays.

Here the water waves travel from left to right. The ray is something that shows the direction of the water waves. Rays are always normal to the wavefront.
Thus we can summarize that the wavefront is the surface of the constant phase and the ray indicates the direction of the propagation.
Note:
There are three different types of the wavefront.
Plane wavefront: Plane wavefront has a constant wave phase along a planar surface or the wavefront.
Spherical wavefront: A spherical wavefront is the front of a propagating wave that has the shape of the ball
Cylindrical wavefront: This wavefront appears when the source of waves is a line source.
Wavefront’s shape always depends on the source. A wavefront from a point source is spherical or circular while an extended large source has a plane or flat wavefront.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




