
How is a voltmeter connected in the circuit to measure the potential difference between two points?
Answer
606k+ views
Hint: A voltmeter is a device that measures the potential difference across two points in the circuit. Think if we want to measure the potential difference across a component or any two points in the circuit then whether we should connect the voltmeter in series in parallel across these two points.
Complete step by step answer:
A voltmeter is a device that measures the potential difference across two points in the circuit. It is connected in parallel to the two points in the circuit. It must be connected in parallel and not to be connected in series because we want to measure the potential difference across two difference points. If we connect a voltmeter in series, it will measure a potential difference of 0 volts. In other words, we short the terminal of the voltmeter.
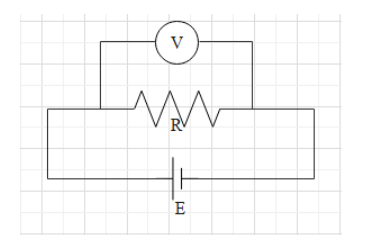
Additional Information: Let us understand the mechanism or setup of a voltmeter.
A voltmeter consists of a galvanometer. A galvanometer is a device that detects current. However, a galvanometer has very less tolerance to current. The maximum amount of current that a galvanometer can allow to pass through is denoted as ${{i}_{g}}$.
A large resistance is connected to the galvanometer in series.
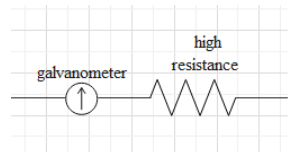
This is because the current is inversely proportional to the resistance. Since the galvanometer can accept a little current, a large resistance in series will increase the net resistance of the device and thus a very little amount of current will flow through the device when connected in parallel in the circuit.
Note: When we connect the voltmeter in the circuit, its job is to measure the voltage across a component without alternating or participating in the circuit. This means that no current must pass through the voltmeter.
Therefore, the large resistance that is connected in series with the galvanometer must be infinite.
However, this is an ideal case. First of all, we cannot have an infinitely large resistance. Second, to any measure the voltage the device needs some amount of current.
Hence, in real life the reading of a voltmeter isn’t accurate. But we try to make it accurate.
Complete step by step answer:
A voltmeter is a device that measures the potential difference across two points in the circuit. It is connected in parallel to the two points in the circuit. It must be connected in parallel and not to be connected in series because we want to measure the potential difference across two difference points. If we connect a voltmeter in series, it will measure a potential difference of 0 volts. In other words, we short the terminal of the voltmeter.

Additional Information: Let us understand the mechanism or setup of a voltmeter.
A voltmeter consists of a galvanometer. A galvanometer is a device that detects current. However, a galvanometer has very less tolerance to current. The maximum amount of current that a galvanometer can allow to pass through is denoted as ${{i}_{g}}$.
A large resistance is connected to the galvanometer in series.

This is because the current is inversely proportional to the resistance. Since the galvanometer can accept a little current, a large resistance in series will increase the net resistance of the device and thus a very little amount of current will flow through the device when connected in parallel in the circuit.
Note: When we connect the voltmeter in the circuit, its job is to measure the voltage across a component without alternating or participating in the circuit. This means that no current must pass through the voltmeter.
Therefore, the large resistance that is connected in series with the galvanometer must be infinite.
However, this is an ideal case. First of all, we cannot have an infinitely large resistance. Second, to any measure the voltage the device needs some amount of current.
Hence, in real life the reading of a voltmeter isn’t accurate. But we try to make it accurate.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE




