
A uniform electric field of \[100V{{m}^{-1}}\] is directed at ${{30}^{\circ }}$ with the positive x - axis as shown in fig. Find the potential difference, $VBA$ if OA=2m and OB=4m.
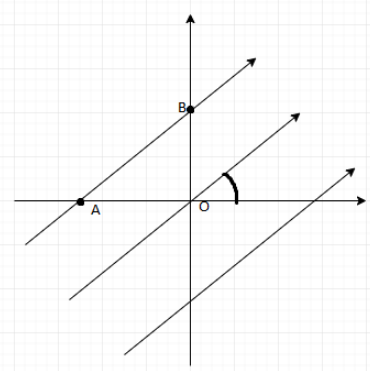

Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: We can find more information from the given figure by forming an equipotential surface that is perpendicular to the given electric field.
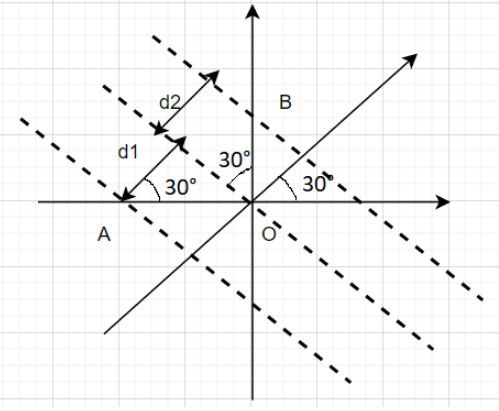
This forms two small right triangles within the figure. When we use its sides and angles, we can continue the calculation to find the potential difference.
Formulas used:
$V=E\times d$
where $V$ is the potential at a point, $E$ is the electric field and $d$ is the distance of separation.
Complete step by step answer:
From the modified figure,
\[{V_B}-{V_A}=100(\sqrt{3}+2)V\]
\[{d_1}=AO cos{{30}^{\circ }}\\
\Rightarrow {d_1} =\dfrac{2\sqrt{3}}{2}
\Rightarrow {d_1} =\sqrt{3}m\]
\[\Rightarrow {d_2}=BOsin{{30}^{\circ }}\\
\Rightarrow {d_2} =4\times \dfrac{1}{2}\\
\Rightarrow {d_2} =2m\]
\[{V_A}-{V_0}=E {d_1}\\
\therefore{V_A}-{V_0}=100\sqrt{3}V\]
We’re given that A lies on the X axis. However it can be moved forward along the equipotential surface lines and can be aligned with B to make our calculations easier. Hence, potential difference between initial point A and final point B in the same electric field E is given by
\[{V_A}-{V_B}=E({d_1}+{d_2})=100(\sqrt{3}+2)V\] or \[{V_B} - {V_A} =100(\sqrt{3}+2)V\]
Note:Equipotential surfaces are always created perpendicular to the field and they never intersect. For a point charge, these are concentric circles and for a uniform electric field, the equipotential surfaces are planes normal to the x-axis. The potential is constant inside a hollow charged spherical conductor . This can be treated as equipotential volume. No external work is required to move a charge from the centre to the surface. For an isolated point charge, the equipotential surface is a sphere. i.e. concentric spheres around the point charge are different equipotential surfaces.

This forms two small right triangles within the figure. When we use its sides and angles, we can continue the calculation to find the potential difference.
Formulas used:
$V=E\times d$
where $V$ is the potential at a point, $E$ is the electric field and $d$ is the distance of separation.
Complete step by step answer:
From the modified figure,
\[{V_B}-{V_A}=100(\sqrt{3}+2)V\]
\[{d_1}=AO cos{{30}^{\circ }}\\
\Rightarrow {d_1} =\dfrac{2\sqrt{3}}{2}
\Rightarrow {d_1} =\sqrt{3}m\]
\[\Rightarrow {d_2}=BOsin{{30}^{\circ }}\\
\Rightarrow {d_2} =4\times \dfrac{1}{2}\\
\Rightarrow {d_2} =2m\]
\[{V_A}-{V_0}=E {d_1}\\
\therefore{V_A}-{V_0}=100\sqrt{3}V\]
We’re given that A lies on the X axis. However it can be moved forward along the equipotential surface lines and can be aligned with B to make our calculations easier. Hence, potential difference between initial point A and final point B in the same electric field E is given by
\[{V_A}-{V_B}=E({d_1}+{d_2})=100(\sqrt{3}+2)V\] or \[{V_B} - {V_A} =100(\sqrt{3}+2)V\]
Note:Equipotential surfaces are always created perpendicular to the field and they never intersect. For a point charge, these are concentric circles and for a uniform electric field, the equipotential surfaces are planes normal to the x-axis. The potential is constant inside a hollow charged spherical conductor . This can be treated as equipotential volume. No external work is required to move a charge from the centre to the surface. For an isolated point charge, the equipotential surface is a sphere. i.e. concentric spheres around the point charge are different equipotential surfaces.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




