
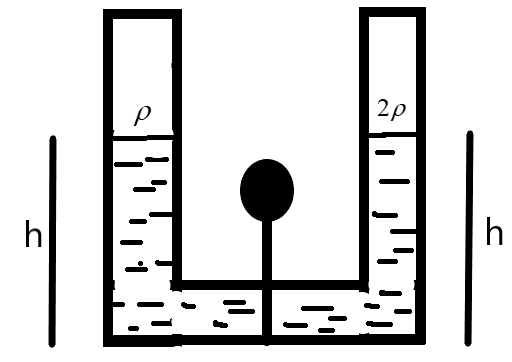
A tube as shown below with constant cross-section throughout is filled with tube liquids for density \[\rho \text{ and 2}\rho \] separated by a line-plug. What happens to the height in each of the columns when this plug is removed?

Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: We should understand the pressure difference due to the density difference in the two media separated by the plug. The density difference will change the height of the liquid column on the two sides of the tube which can be found from this information.
Complete answer:
We are given a U-shaped tube as shown in the figure.
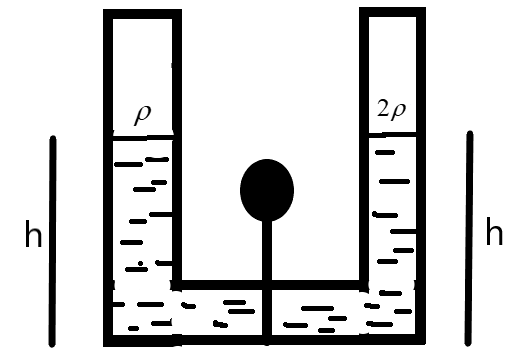
The two liquids of densities \[\rho \text{ and 2}\rho \] are at an equal height ‘h’ divided by the plug as shown. Let \[{{\rho }_{0}}\] be the atmospheric pressure acting as the tube is kept open. The pressure on the left-side can be defined as –
\[{{P}_{1}}={{\rho }_{0}}-\rho gh\]
The right-side can be defined as –
\[{{P}_{2}}={{\rho }_{0}}-2\rho gh\]
The pressures at the same height are equal. This gives –
\[{{P}_{1}}={{P}_{2}}\]
This is the situation when the height is the same.
Now, let us consider the condition when the plug is removed. In this case, there will be a pressure difference as the height attained will vary, such that –
\[\begin{align}
& {{P}_{1}}=\rho g{{h}_{1}} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }{{h}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{P}_{1}}}{\rho g} \\
& {{P}_{2}}=2\rho g{{h}_{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }{{h}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{P}_{2}}}{2\rho g} \\
\end{align}\]\
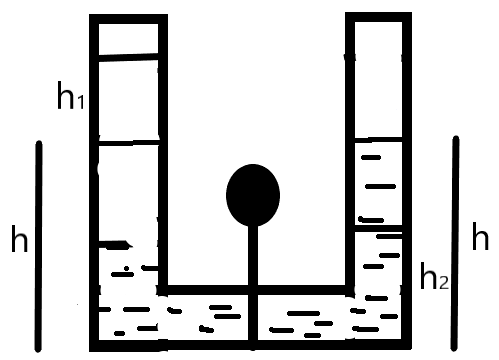
From the above relation we can understand that the height of the liquid column is inversely proportional to the density of the liquid.
Also, the height has a constraint –
\[\Rightarrow 2h={{h}_{2}}+{{h}_{1}}\]
But,
\[\rho \propto \dfrac{1}{h}\]
This implies that the heights are related by the ratio –
\[{{h}_{1}}:{{h}_{2}}\text{ }\Rightarrow \text{ }\dfrac{1}{\rho }:\dfrac{1}{2\rho }=2:1\]
The heights are related in the ratio 2:1.
Note:
The height achieved by a liquid in the column is inversely proportional to the density of the medium. The surface tension is neglected in this case or assumed to have equal values. The height of the liquid in left-side will be higher than the initial height.
Complete answer:
We are given a U-shaped tube as shown in the figure.

The two liquids of densities \[\rho \text{ and 2}\rho \] are at an equal height ‘h’ divided by the plug as shown. Let \[{{\rho }_{0}}\] be the atmospheric pressure acting as the tube is kept open. The pressure on the left-side can be defined as –
\[{{P}_{1}}={{\rho }_{0}}-\rho gh\]
The right-side can be defined as –
\[{{P}_{2}}={{\rho }_{0}}-2\rho gh\]
The pressures at the same height are equal. This gives –
\[{{P}_{1}}={{P}_{2}}\]
This is the situation when the height is the same.
Now, let us consider the condition when the plug is removed. In this case, there will be a pressure difference as the height attained will vary, such that –
\[\begin{align}
& {{P}_{1}}=\rho g{{h}_{1}} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }{{h}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{P}_{1}}}{\rho g} \\
& {{P}_{2}}=2\rho g{{h}_{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }{{h}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{P}_{2}}}{2\rho g} \\
\end{align}\]\

From the above relation we can understand that the height of the liquid column is inversely proportional to the density of the liquid.
Also, the height has a constraint –
\[\Rightarrow 2h={{h}_{2}}+{{h}_{1}}\]
But,
\[\rho \propto \dfrac{1}{h}\]
This implies that the heights are related by the ratio –
\[{{h}_{1}}:{{h}_{2}}\text{ }\Rightarrow \text{ }\dfrac{1}{\rho }:\dfrac{1}{2\rho }=2:1\]
The heights are related in the ratio 2:1.
Note:
The height achieved by a liquid in the column is inversely proportional to the density of the medium. The surface tension is neglected in this case or assumed to have equal values. The height of the liquid in left-side will be higher than the initial height.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

What is the difference between biodegradable and nonbiodegradable class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE

Bond order ofO2 O2+ O2 and O22 is in order A O2 langle class 11 chemistry CBSE

Draw a labelled diagram of the human heart and label class 11 biology CBSE

What is 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p class 11 chemistry CBSE




