
A transistor is used in common emitter mode as an amplifier. Then
(A) The base-emitter junction is forward biased
(B) The base emitter junction is reverse biased
(C) The input signal is connected in series with the voltage applied to the base-emitter junction.
(D) The input signal is connected in series with the voltage applied to the base collector junction.
Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: When a transistor is configured as common emitter, common base and common collector, the input is connected to the terminal which is taken as common. Emitter is always forward based with respect to base, to supply majority charge carriers to the base. Collector terminal is always reverse biased with respect to the base to remove the charge carriers from the base collector junction.
Complete step by step answer:
Common emitter amplifier circuit
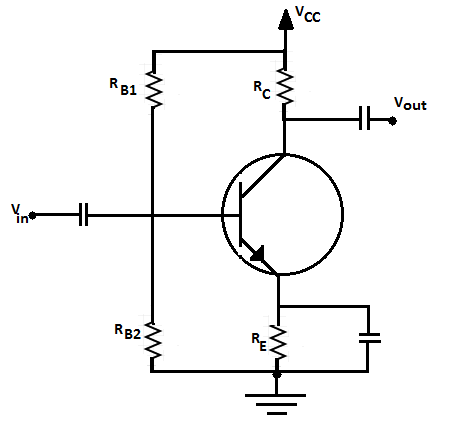
An amplifier is a device which is used for increasing the amplitude of input signals. And it produces an enlarged version of the input signal. In an amplifier there are two input terminals for connecting input and two output terminals for connecting load. In a common emitter amplifier configuration, base is one of the input terminals and collector is one of the output terminals. Emitter is common for both input and output. Hence, the input signal is connected in series with the voltage applied to the base-emitter junction.
For a proper functioning of a transistor, the emitter-base junction must be forward-biased and collector-base junction must be reverse-biased. Usually Emitter is forward biased with respect to base so as to supply the majority of the charge carriers to the base.
So, the correct answer is “Option A and C”.
Note:
Common emitter circuits are the most popular configuration in amplifier circuits. Because it's current, voltage and power gains are quite high and the ratio of output impedance and input impedance are quite moderate. As it provides high voltage gain and moderate current gain, CE circuits are well suited for voltage amplification, especially for low frequencies. Also, it is used as low noise amplifiers and radio frequency amplifiers.
Complete step by step answer:
Common emitter amplifier circuit

An amplifier is a device which is used for increasing the amplitude of input signals. And it produces an enlarged version of the input signal. In an amplifier there are two input terminals for connecting input and two output terminals for connecting load. In a common emitter amplifier configuration, base is one of the input terminals and collector is one of the output terminals. Emitter is common for both input and output. Hence, the input signal is connected in series with the voltage applied to the base-emitter junction.
For a proper functioning of a transistor, the emitter-base junction must be forward-biased and collector-base junction must be reverse-biased. Usually Emitter is forward biased with respect to base so as to supply the majority of the charge carriers to the base.
So, the correct answer is “Option A and C”.
Note:
Common emitter circuits are the most popular configuration in amplifier circuits. Because it's current, voltage and power gains are quite high and the ratio of output impedance and input impedance are quite moderate. As it provides high voltage gain and moderate current gain, CE circuits are well suited for voltage amplification, especially for low frequencies. Also, it is used as low noise amplifiers and radio frequency amplifiers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




