
A superconductor has ${{T}_{c}}(0)=100K$. When a magnetic field of 7.5 Tesla is, applied its ${{T}_{c}}$ decreases to 75 Kelvin. For this material one can definitely say that, when
A. $\mathbf{B}=5\,Tesla,\,\,{{T}_{c}}(B)=80K$
B. $\mathbf{B}=5\,Tesla,\,\,75K < {{T}_{c}}(B)<100K$
C. $\mathbf{B}=10\,Tesla,\,\,75K < {{T}_{c}}(B)<100K$
D. $\mathbf{B}=10\,Tesla,\,\,{{T}_{c}}(B)=70K$

Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: The temperature ${{T}_{c}}$, at which the electrical resistivity of a metal reaches to zero, is said to be the critical temperature for the superconductor.
We need to study this graph and determine the relation between critical temperature and magnetic field to solve this problem.
Complete answer:
Electrical resistance of certain materials, called superconductors, decreases from a non-zero value to zero as their temperature is lowered below a certain temperature, known as the critical temperature of the superconductor.
In other words, A superconductor is a substance that conducts electricity without resistance when its temperature is less than a certain temperature known as critical temperature.
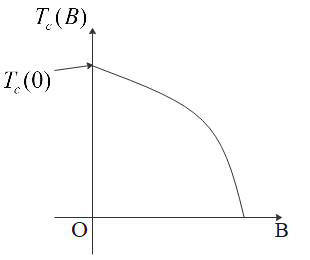
The critical temperature of superconductors decreases when a superconductor is placed in a magnetic field. It means critical temperature depends on the magnetic field in which it is placed. The dependence of ${{T}_{c}}(B)$ on $B$ is shown in the figure above.
We can observe from the graph that when $B$ increases, ${{T}_{c}}(B)$ decreases and becomes a superconductor. But its exact dependence on the magnetic field cannot be determined from the graph.
It is given that the superconductor has critical temperature $100K$ when no magnetic field is applied and it decreases to 75 K when magnetic field is increased to 7.5 Tesla. Since, we know that with increase in magnetic field, critical temperature decreases.
When $B=5Tesla$ which lies between magnetic field 0Tesla and 7.5 Tesla, critical temperature of superconductor will lie between ${{T}_{c}}(0)$ and ${{T}_{c}}(100)$. That is, the critical temperature of a superconductor will lie between 75 K and 100 K when the magnitude of the magnetic field is 5 Tesla.
For $\mathbf{B}=5\,Tesla,\,\,75K < {{T}_{c}}(B)<100K$
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
The critical temperature of superconductors decreases when a superconductor is placed in a magnetic field. It means critical temperature depends on the magnetic field in which it is placed.
The superconducting state cannot exist, even at absolute zero, in the presence of a magnetic field greater than a critical value.
We need to study this graph and determine the relation between critical temperature and magnetic field to solve this problem.
Complete answer:
Electrical resistance of certain materials, called superconductors, decreases from a non-zero value to zero as their temperature is lowered below a certain temperature, known as the critical temperature of the superconductor.
In other words, A superconductor is a substance that conducts electricity without resistance when its temperature is less than a certain temperature known as critical temperature.
The critical temperature of superconductors decreases when a superconductor is placed in a magnetic field. It means critical temperature depends on the magnetic field in which it is placed. The dependence of ${{T}_{c}}(B)$ on $B$ is shown in the figure above.
We can observe from the graph that when $B$ increases, ${{T}_{c}}(B)$ decreases and becomes a superconductor. But its exact dependence on the magnetic field cannot be determined from the graph.
It is given that the superconductor has critical temperature $100K$ when no magnetic field is applied and it decreases to 75 K when magnetic field is increased to 7.5 Tesla. Since, we know that with increase in magnetic field, critical temperature decreases.
When $B=5Tesla$ which lies between magnetic field 0Tesla and 7.5 Tesla, critical temperature of superconductor will lie between ${{T}_{c}}(0)$ and ${{T}_{c}}(100)$. That is, the critical temperature of a superconductor will lie between 75 K and 100 K when the magnitude of the magnetic field is 5 Tesla.
For $\mathbf{B}=5\,Tesla,\,\,75K < {{T}_{c}}(B)<100K$
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
The critical temperature of superconductors decreases when a superconductor is placed in a magnetic field. It means critical temperature depends on the magnetic field in which it is placed.
The superconducting state cannot exist, even at absolute zero, in the presence of a magnetic field greater than a critical value.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




