
A straight wire of mass 200 g and length 1.5 m carries a current of 2 A. It is suspended in mid-air by a uniform horizontal magnetic field B. The magnitude of $B$ (in tesla) is:
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: As we all can see that the force acting on a current-carrying wire under a uniform magnetic field is equal to the weight of the wire because the wire is in equilibrium and has no acceleration so it is not moving.
Complete step by step answer:
Refer to the figure given below:
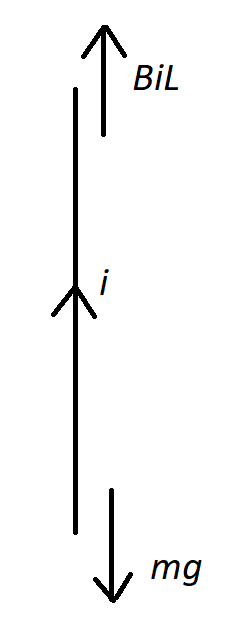
In this figure, ‘i’ is the current flowing in the conductor and the rest are the two forces acting on it.
The force on a current-carrying wire under uniform magnetic field is given by:
$F = BiL\sin \theta $
Where $F$ is the force, $B$ is the magnetic field, $L$ is the length of the wire, and $\theta $ is the angle between the current direction and magnetic field direction.
Here, we can see that the direction of current is perpendicular to the magnetic field $B$ horizontally, hence the angle $\theta = 90^\circ $.
Hence the above equation becomes,
$F = BiL$
As we know that, in the position of suspension, the magnetic force becomes equal to the weight of the wire. Therefore, the new equilibrium condition becomes
$BiL = mg$………………...… (i)
Here $m$ is the mass of the wire, and $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity.
We will now substitute $m = 200\;{\rm{g}}$, $L = 1.5\;{\rm{m}}$, $i = 2\;{\rm{A}}$ and $g = 9.8\;{\rm{m/}}{{\rm{s}}^{\rm{2}}}$ in equation (i) to find the value of $B$.
\[ \Rightarrow B \times 2\;{\rm{A}} \times {\rm{1}}{\rm{.5}}\;{\rm{m = 200}}\;{\rm{g}} \times {\rm{9}}{\rm{.8}}\;{\rm{m/}}{{\rm{s}}^{\rm{2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow B \times 2\;{\rm{A}} \times {\rm{1}}{\rm{.5}}\;{\rm{m = }}200\; \times {10^{ - 3}}\;{\rm{kg}} \times {\rm{9}}{\rm{.8}}\;{\rm{m/}}{{\rm{s}}^{\rm{2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow B = 0.65\;{\rm{T}}\]
Therefore, the magnitude of the magnetic field $B$ in tesla is \[0.65\;{\rm{T}}\].
Note:
- We must be aware that the force on a current-carrying conductor can also be found out using the formula $F = BQ\,v$. Here $F$ is the force, $B$ is the magnetic field, $Q$ is the charge in motion and $v$ is the velocity of the charge and this is also known as Lenz law.
- We all have studied that Fleming’s left-hand rule is used to describe the force on a current-carrying conductor placed at right angles to a magnetic field. The current-carrying conductor should be of ferromagnetic material.
Complete step by step answer:
Refer to the figure given below:

In this figure, ‘i’ is the current flowing in the conductor and the rest are the two forces acting on it.
The force on a current-carrying wire under uniform magnetic field is given by:
$F = BiL\sin \theta $
Where $F$ is the force, $B$ is the magnetic field, $L$ is the length of the wire, and $\theta $ is the angle between the current direction and magnetic field direction.
Here, we can see that the direction of current is perpendicular to the magnetic field $B$ horizontally, hence the angle $\theta = 90^\circ $.
Hence the above equation becomes,
$F = BiL$
As we know that, in the position of suspension, the magnetic force becomes equal to the weight of the wire. Therefore, the new equilibrium condition becomes
$BiL = mg$………………...… (i)
Here $m$ is the mass of the wire, and $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity.
We will now substitute $m = 200\;{\rm{g}}$, $L = 1.5\;{\rm{m}}$, $i = 2\;{\rm{A}}$ and $g = 9.8\;{\rm{m/}}{{\rm{s}}^{\rm{2}}}$ in equation (i) to find the value of $B$.
\[ \Rightarrow B \times 2\;{\rm{A}} \times {\rm{1}}{\rm{.5}}\;{\rm{m = 200}}\;{\rm{g}} \times {\rm{9}}{\rm{.8}}\;{\rm{m/}}{{\rm{s}}^{\rm{2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow B \times 2\;{\rm{A}} \times {\rm{1}}{\rm{.5}}\;{\rm{m = }}200\; \times {10^{ - 3}}\;{\rm{kg}} \times {\rm{9}}{\rm{.8}}\;{\rm{m/}}{{\rm{s}}^{\rm{2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow B = 0.65\;{\rm{T}}\]
Therefore, the magnitude of the magnetic field $B$ in tesla is \[0.65\;{\rm{T}}\].
Note:
- We must be aware that the force on a current-carrying conductor can also be found out using the formula $F = BQ\,v$. Here $F$ is the force, $B$ is the magnetic field, $Q$ is the charge in motion and $v$ is the velocity of the charge and this is also known as Lenz law.
- We all have studied that Fleming’s left-hand rule is used to describe the force on a current-carrying conductor placed at right angles to a magnetic field. The current-carrying conductor should be of ferromagnetic material.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




