
A straight line joining the object point and image point is always perpendicular to the mirror:
(A) If mirror is plane only
(B) If mirror is concave only
(C) If mirror is convex only
(D) Irrespective of the type of mirror
Answer
572.4k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we need to investigate the image formation by each kind of mirror. For checking that a line is perpendicular to a circular mirror, we have to use the property of the normal to a circle, which always passes through its centre.
Complete step by step solution:
For plane mirror:
We know that for a plane mirror, the distance of the image from the mirror is always equal to the distance of the object from the mirror. Also, it always produces a virtual image of the object. The image production by the plane mirror is as shown below.
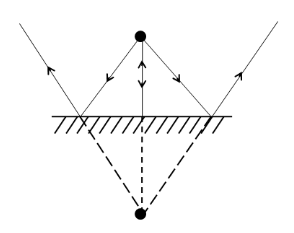
As we can clearly see, the line joining the object and the image is perpendicular to the mirror.
For circular mirrors:
For the circular mirrors, namely the concave mirror and the convex mirror, we know that any ray originating from the object, if it passes through the centre of curvature of the mirror, then retraces its path. Since each reflected ray contributes in the image formation, so the image formed by a circular mirror will lie on this retracing reflected ray. As it passes through the centre of curvature, so it is normal to the mirror. Therefore, for both the concave and the convex mirrors the line joining the object with the image is perpendicular to the mirror.
From the above two cases, we conclude that a straight line joining the object point and image point is always perpendicular to the mirror, irrespective of the type of the mirror.
Hence, the correct answer is option D.
Note:
We may get confused in the case of circular mirrors, when the object and the image both lie at the centre of curvature of the mirror. We might think that the line joining the image with the object is not perpendicular to the mirror. But this is not true. If we complete the curvature of the mirror to form the corresponding sphere, and then extend the line joining object and image to intersect this sphere, then we would find the line to be perpendicular to the mirror.
Complete step by step solution:
For plane mirror:
We know that for a plane mirror, the distance of the image from the mirror is always equal to the distance of the object from the mirror. Also, it always produces a virtual image of the object. The image production by the plane mirror is as shown below.

As we can clearly see, the line joining the object and the image is perpendicular to the mirror.
For circular mirrors:
For the circular mirrors, namely the concave mirror and the convex mirror, we know that any ray originating from the object, if it passes through the centre of curvature of the mirror, then retraces its path. Since each reflected ray contributes in the image formation, so the image formed by a circular mirror will lie on this retracing reflected ray. As it passes through the centre of curvature, so it is normal to the mirror. Therefore, for both the concave and the convex mirrors the line joining the object with the image is perpendicular to the mirror.
From the above two cases, we conclude that a straight line joining the object point and image point is always perpendicular to the mirror, irrespective of the type of the mirror.
Hence, the correct answer is option D.
Note:
We may get confused in the case of circular mirrors, when the object and the image both lie at the centre of curvature of the mirror. We might think that the line joining the image with the object is not perpendicular to the mirror. But this is not true. If we complete the curvature of the mirror to form the corresponding sphere, and then extend the line joining object and image to intersect this sphere, then we would find the line to be perpendicular to the mirror.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




