
A small coil of radius r is placed at the center of a large coil of radius R, where R>>r. The two coils are coplanar. The mutual inductance between the coils is proportional to
A. \[\dfrac{r}{R}\]
B. \[\dfrac{{{r^2}}}{R}\]
C. \[\dfrac{{{r^2}}}{{{R^2}}}\]
D. \[\dfrac{r}{{{R^2}}}\]
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: When a current-carrying conductor is linked with another coil, then a voltage is induced in the second coil, and this phenomenon is called mutual inductance. Mutual inductance is the basic operating principle of transformers, motors, and generators having the magnetic field.
In this question, we need to determine the mutual inductance between the coils for which we will use the formulae of magnetic field and of the coil which is given as \[B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{2R}}\].
Complete step by step answer: Given the radius of a small coil\[ = r\]
The radius of the large coil \[ = R\]
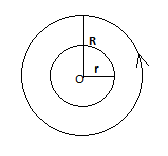
When current flows through the larger coil, it will produce a magnetic field, so the magnetic field at the center due to the larger coil of radius R will be
\[B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{2R}} - - (i)\], where I am the current through the coil
Now when current flows through the coil, it produces magnetic flux, which tends to flow to the smaller coil; hence the magnetic flux linkage between the two coils will be
\[\phi = B \times A\], where\[A\]is the area of the smaller loop
This can be written as
\[\phi = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{2R}} \times \pi {r^2} - - (ii)\]
Now when this magnetic flux from the larger coil links with a smaller coil, this will induce a voltage in the smaller coil due to the larger coil, and this is known as mutual inductance, given as
\[M = \dfrac{\phi }{i}\]
From equation (ii)
\[\dfrac{\phi }{I} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{2R}} \times \pi {r^2} - - (iii)\]
Where \[M = \dfrac{\phi }{i}\]
Hence the mutual inductance will be
\[M = \dfrac{\phi }{I} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}\pi {r^2}}}{{2R}} - - (iv)\]
Now from equation (iv), we can say
\[M = \dfrac{{{r^2}}}{R}\]
Option (B) is correct.
Note: Students must note that the mutual voltage in the secondary coil can be positive or the negative based on the direction of the orientation of both the coils
In this question, we need to determine the mutual inductance between the coils for which we will use the formulae of magnetic field and of the coil which is given as \[B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{2R}}\].
Complete step by step answer: Given the radius of a small coil\[ = r\]
The radius of the large coil \[ = R\]

When current flows through the larger coil, it will produce a magnetic field, so the magnetic field at the center due to the larger coil of radius R will be
\[B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{2R}} - - (i)\], where I am the current through the coil
Now when current flows through the coil, it produces magnetic flux, which tends to flow to the smaller coil; hence the magnetic flux linkage between the two coils will be
\[\phi = B \times A\], where\[A\]is the area of the smaller loop
This can be written as
\[\phi = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{2R}} \times \pi {r^2} - - (ii)\]
Now when this magnetic flux from the larger coil links with a smaller coil, this will induce a voltage in the smaller coil due to the larger coil, and this is known as mutual inductance, given as
\[M = \dfrac{\phi }{i}\]
From equation (ii)
\[\dfrac{\phi }{I} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{2R}} \times \pi {r^2} - - (iii)\]
Where \[M = \dfrac{\phi }{i}\]
Hence the mutual inductance will be
\[M = \dfrac{\phi }{I} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}\pi {r^2}}}{{2R}} - - (iv)\]
Now from equation (iv), we can say
\[M = \dfrac{{{r^2}}}{R}\]
Option (B) is correct.
Note: Students must note that the mutual voltage in the secondary coil can be positive or the negative based on the direction of the orientation of both the coils
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




