
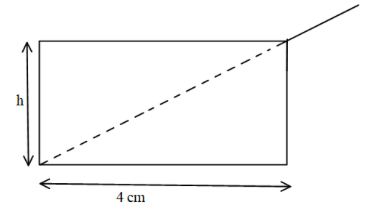
A shallow glass dish 4.00 cm wide at the bottom, as shown in figure. When an observer’s eye is positioned as shown, the observer sees the edge of the bottom of the empty dish. When this dish is filled with water, the observer sees the centre of the bottom of the dish. Find the height of the dish. $\left( {{\mu _w} = \dfrac{4}{3}} \right)$.
A) 1.4 cm.
B) 2.4 cm.
C) 3.4 cm.
D) 3.1 cm.

Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint:The refraction process is the process in which the beam of light changes its direction from the original path when the beam of light passes from one medium to another medium. Red Fraction is a very normal phenomenon that occurs in day to day life.
Formula used:The formula of the Snell’s law is given by,
$ \Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}}$
Where $\mu $ is the refractive index the incident angle is $i$ and the refraction angle is$r$.
Complete step by step solution:
It is given in the problem that a shallow glass dish 4.00 cm wide at the bottom when an observer’s eye is positioned as shown, the observer sees the edge of the bottom of the empty dish when this dish is filled with water, the observer sees the centre of the bottom of the dish then we need to find the height of the dish if refractive index is equal to$\left( {{\mu _w} = \dfrac{4}{3}} \right)$.
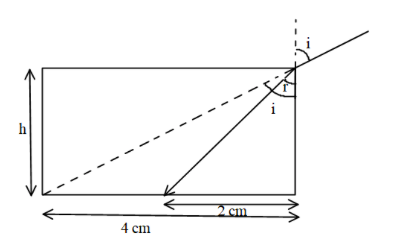
The length of AB is equal to,
$ \Rightarrow AB = \sqrt {{4^2} + {h^2}} $
The length of AC is equal to,
$ \Rightarrow AC = \sqrt {{2^2} + {h^2}} $
The sine of incident angle and refractive angle is equal to,
$ \Rightarrow \sin i = \dfrac{4}{{\sqrt {{4^2} + {h^2}} }}$………eq. (1)
$ \Rightarrow \sin r = \dfrac{2}{{\sqrt {{2^2} + {h^2}} }}$………eq. (2)
The formula of the Snell’s law is given by,
$ \Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}}$
Where $\mu $ is the refractive index the incident angle is $i$ and the refraction angle is$r$.
Replacing the value of the $\sin i$ and $\sin r$ in the formula of the Snell’s law.
$ \Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{3} = \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{4}{{\sqrt {{4^2} + {h^2}} }}} \right)}}{{\left( {\dfrac{2}{{\sqrt {{2^2} + {h^2}} }}} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{3} = \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{2}{{\sqrt {{4^2} + {h^2}} }}} \right)}}{{\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {{2^2} + {h^2}} }}} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{3} = \dfrac{{2 \cdot \sqrt {{2^2} + {h^2}} }}{{\sqrt {{4^2} + {h^2}} }}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{2}{3} = \dfrac{{\sqrt {{2^2} + {h^2}} }}{{\sqrt {{4^2} + {h^2}} }}$
Squaring on both sides,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}} \right)^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt {{2^2} + {h^2}} }}{{\sqrt {{4^2} + {h^2}} }}} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{9} = \dfrac{{{2^2} + {h^2}}}{{{4^2} + {h^2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{9} = \dfrac{{4 + {h^2}}}{{16 + {h^2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow 4\left( {16 + {h^2}} \right) = 9\left( {4 + {h^2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 64 + 4{h^2} = 36 + 9{h^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 5{h^2} = 28$
$ \Rightarrow {h^2} = \dfrac{{28}}{5}$
$ \Rightarrow h = \sqrt {\dfrac{{28}}{5}} $
$ \Rightarrow h = \sqrt {\dfrac{{28}}{5}} $
$ \Rightarrow h = 2 \cdot 4cm$
The height of the dish is equal to $h = 2 \cdot 4cm$.
The correct answer for this problem is option B.
Note:It is advisable for students to understand and remember the formula of the Snell’s law as it is very helpful in solving problems like these. The beam of light bends towards the normal whenever it travels from the rare to denser medium.
Formula used:The formula of the Snell’s law is given by,
$ \Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}}$
Where $\mu $ is the refractive index the incident angle is $i$ and the refraction angle is$r$.
Complete step by step solution:
It is given in the problem that a shallow glass dish 4.00 cm wide at the bottom when an observer’s eye is positioned as shown, the observer sees the edge of the bottom of the empty dish when this dish is filled with water, the observer sees the centre of the bottom of the dish then we need to find the height of the dish if refractive index is equal to$\left( {{\mu _w} = \dfrac{4}{3}} \right)$.

The length of AB is equal to,
$ \Rightarrow AB = \sqrt {{4^2} + {h^2}} $
The length of AC is equal to,
$ \Rightarrow AC = \sqrt {{2^2} + {h^2}} $
The sine of incident angle and refractive angle is equal to,
$ \Rightarrow \sin i = \dfrac{4}{{\sqrt {{4^2} + {h^2}} }}$………eq. (1)
$ \Rightarrow \sin r = \dfrac{2}{{\sqrt {{2^2} + {h^2}} }}$………eq. (2)
The formula of the Snell’s law is given by,
$ \Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}}$
Where $\mu $ is the refractive index the incident angle is $i$ and the refraction angle is$r$.
Replacing the value of the $\sin i$ and $\sin r$ in the formula of the Snell’s law.
$ \Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{3} = \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{4}{{\sqrt {{4^2} + {h^2}} }}} \right)}}{{\left( {\dfrac{2}{{\sqrt {{2^2} + {h^2}} }}} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{3} = \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{2}{{\sqrt {{4^2} + {h^2}} }}} \right)}}{{\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {{2^2} + {h^2}} }}} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{3} = \dfrac{{2 \cdot \sqrt {{2^2} + {h^2}} }}{{\sqrt {{4^2} + {h^2}} }}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{2}{3} = \dfrac{{\sqrt {{2^2} + {h^2}} }}{{\sqrt {{4^2} + {h^2}} }}$
Squaring on both sides,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}} \right)^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt {{2^2} + {h^2}} }}{{\sqrt {{4^2} + {h^2}} }}} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{9} = \dfrac{{{2^2} + {h^2}}}{{{4^2} + {h^2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{9} = \dfrac{{4 + {h^2}}}{{16 + {h^2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow 4\left( {16 + {h^2}} \right) = 9\left( {4 + {h^2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 64 + 4{h^2} = 36 + 9{h^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 5{h^2} = 28$
$ \Rightarrow {h^2} = \dfrac{{28}}{5}$
$ \Rightarrow h = \sqrt {\dfrac{{28}}{5}} $
$ \Rightarrow h = \sqrt {\dfrac{{28}}{5}} $
$ \Rightarrow h = 2 \cdot 4cm$
The height of the dish is equal to $h = 2 \cdot 4cm$.
The correct answer for this problem is option B.
Note:It is advisable for students to understand and remember the formula of the Snell’s law as it is very helpful in solving problems like these. The beam of light bends towards the normal whenever it travels from the rare to denser medium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




