
A ray incident at a point at an angle of incidence of \[{60^{\text{o}}}\] enters a glass sphere of \[R.l.n = \sqrt 3 \] and is reflected and refracted at the further surface of the sphere. The angle between the reflected and refracted rays at this surface is
A. \[{50^{\text{o}}}\]
B. \[{60^{\text{o}}}\]
C. \[{90^{\text{o}}}\]
D. \[{40^{\text{o}}}\]
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint:We will use Snell's law to find the to find the first refracted angle as we have the angle of incidence and the refractive index of the medium. We will thereby use the angle sum property of a triangle to find the angle between the reflected and refracted rays at this surface
Formula used:
Using Snell’s law
\[\dfrac{{\sin {\theta _2}}}{{\sin {\theta _1}}} = \dfrac{{{n_1}}}{{{n_2}}}\] …… (1)
Where,
\[{n_1}\] is incident index
\[{n_2}\] is refractive index
\[{\theta _1}\] is incident angle
\[{\theta _2}\] is a refracted angle.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given question, we are supplied with the following data:
The refracted angle is \[{60^{\text{o}}}\]. The incident index is \[R.l.n = \sqrt 3 \]. And let the incident angle as \[{r_1}\]
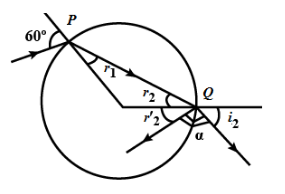
By using Snell’s law,
The refraction at \[P\] we get,
$\dfrac{{\sin {{60}^{\text{o}}}}}{{\sin {r_1}}} = \sqrt 3 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}}}{{\sin {r_1}}} = \sqrt 3 \\
\Rightarrow \sin {r_1} = \dfrac{1}{2} \\
\Rightarrow {r_1} = {30^{\text{o}}} \\$
As we know that,
${r_1} = {r_2} \\
\therefore {r_2} = {30^{\text{o}}} \\$
Using Snell’s law,
The refraction at \[Q\]we get,
$\dfrac{{\sin {{30}^{\text{o}}}}}{{\sin {i_2}}} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{2}}}{{\sin {i_2}}} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
\Rightarrow \sin {i_2} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} \\
\Rightarrow {i_2} = {60^{\text{o}}} \\$
Since the reflection occurs at point \[Q\],
\[{r'_2} = {r_2} = 60\]
Let,
The angle between the refracted ray and reflected ray by \[\alpha \], we get,
$\alpha = {180^{\text{o}}} - \left( {{{r'}_2} + {r_2}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \alpha = {180^{\text{o}}} - \left( {{{30}^{\text{o}}} + {{60}^{\text{o}}}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \alpha = {90^{\text{o}}} \\$
Hence, the required answer is \[{90^{\text{o}}}\].
The correct option is C.
Additional information:
Snell’s law: The law of Snell (also known as the law of Snell-Descartes and the law of refraction) is a formula used to explain the relationship between incidence and refraction angles when referring to light or other waves moving through a boundary between two separate isotropic media, such as water, glass or air.
In optics, the law is used to compute the angles of incidence or refraction in ray tracing, and in experimental optics to find a material's refractive index. In meta-materials, which allow light to be bent “backward” at a negative angle of refraction with a negative refractive index, the rule is also satisfied.
Note:Remember that for optical devices, such as fiber optics, Snell’s Law is particularly relevant. Snell’s Law states that the ratio of the incidence and transmission angles of the sinus is equal to the ratio of the refractive index of the interface materials. The refractive index is always constant for a particular medium.
Formula used:
Using Snell’s law
\[\dfrac{{\sin {\theta _2}}}{{\sin {\theta _1}}} = \dfrac{{{n_1}}}{{{n_2}}}\] …… (1)
Where,
\[{n_1}\] is incident index
\[{n_2}\] is refractive index
\[{\theta _1}\] is incident angle
\[{\theta _2}\] is a refracted angle.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given question, we are supplied with the following data:
The refracted angle is \[{60^{\text{o}}}\]. The incident index is \[R.l.n = \sqrt 3 \]. And let the incident angle as \[{r_1}\]

By using Snell’s law,
The refraction at \[P\] we get,
$\dfrac{{\sin {{60}^{\text{o}}}}}{{\sin {r_1}}} = \sqrt 3 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}}}{{\sin {r_1}}} = \sqrt 3 \\
\Rightarrow \sin {r_1} = \dfrac{1}{2} \\
\Rightarrow {r_1} = {30^{\text{o}}} \\$
As we know that,
${r_1} = {r_2} \\
\therefore {r_2} = {30^{\text{o}}} \\$
Using Snell’s law,
The refraction at \[Q\]we get,
$\dfrac{{\sin {{30}^{\text{o}}}}}{{\sin {i_2}}} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{2}}}{{\sin {i_2}}} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
\Rightarrow \sin {i_2} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} \\
\Rightarrow {i_2} = {60^{\text{o}}} \\$
Since the reflection occurs at point \[Q\],
\[{r'_2} = {r_2} = 60\]
Let,
The angle between the refracted ray and reflected ray by \[\alpha \], we get,
$\alpha = {180^{\text{o}}} - \left( {{{r'}_2} + {r_2}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \alpha = {180^{\text{o}}} - \left( {{{30}^{\text{o}}} + {{60}^{\text{o}}}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \alpha = {90^{\text{o}}} \\$
Hence, the required answer is \[{90^{\text{o}}}\].
The correct option is C.
Additional information:
Snell’s law: The law of Snell (also known as the law of Snell-Descartes and the law of refraction) is a formula used to explain the relationship between incidence and refraction angles when referring to light or other waves moving through a boundary between two separate isotropic media, such as water, glass or air.
In optics, the law is used to compute the angles of incidence or refraction in ray tracing, and in experimental optics to find a material's refractive index. In meta-materials, which allow light to be bent “backward” at a negative angle of refraction with a negative refractive index, the rule is also satisfied.
Note:Remember that for optical devices, such as fiber optics, Snell’s Law is particularly relevant. Snell’s Law states that the ratio of the incidence and transmission angles of the sinus is equal to the ratio of the refractive index of the interface materials. The refractive index is always constant for a particular medium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




