
A raindrop falling from a height $h$ above the ground, attains a near terminal velocity when it has fallen through a height $\dfrac{3}{4}h$. Which of the diagrams shown in the figure correctly shows the change in kinetic and potential energy of the drop during its fall up to the ground?
A.
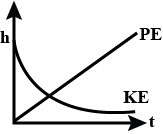
B.

C.
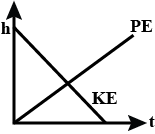
D.

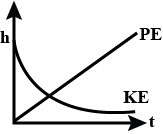

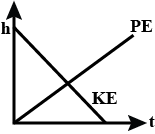

Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: When a body falls freely under the influence of the gravitational force, its potential and kinetic energy changes during its motion but the sum of the potential energy and kinetic energy at every point remains constant.
Complete step by step answer:When a raindrop falls freely, then at a height $h$ above the ground its potential energy is maximum and kinetic energy is zero. During the fall, the potential energy of the raindrop keeps decreasing and kinetic energy goes on increasing up to a height $\dfrac{h}{4}$ above the ground. At this stage, rain drop has acquired terminal velocity. Thereafter its velocity remains constant. Therefore, at this stage, kinetic energy becomes constant. Potential energy becomes zero when a raindrop falls to the ground.
Hence, option (B) is correct.
Note:When a body falls freely through the atmosphere, two external forces will act on it. One of them is the gravitational force, expressed as the weight of the object. The other force is the air resistance, or drag of the object. An object dropped from rest such as a raindrop will increase its speed until it reaches terminal velocity. When terminal velocity of the object is achieved, then the speed of a moving object is no longer increased or decreased, that is the object’s acceleration becomes zero. At terminal velocity the air resistance equals in magnitude to the weight of the falling object. As the two forces are oppositely directed, the total force on the object is zero and the speed of the object becomes constant.
Complete step by step answer:When a raindrop falls freely, then at a height $h$ above the ground its potential energy is maximum and kinetic energy is zero. During the fall, the potential energy of the raindrop keeps decreasing and kinetic energy goes on increasing up to a height $\dfrac{h}{4}$ above the ground. At this stage, rain drop has acquired terminal velocity. Thereafter its velocity remains constant. Therefore, at this stage, kinetic energy becomes constant. Potential energy becomes zero when a raindrop falls to the ground.
Hence, option (B) is correct.
Note:When a body falls freely through the atmosphere, two external forces will act on it. One of them is the gravitational force, expressed as the weight of the object. The other force is the air resistance, or drag of the object. An object dropped from rest such as a raindrop will increase its speed until it reaches terminal velocity. When terminal velocity of the object is achieved, then the speed of a moving object is no longer increased or decreased, that is the object’s acceleration becomes zero. At terminal velocity the air resistance equals in magnitude to the weight of the falling object. As the two forces are oppositely directed, the total force on the object is zero and the speed of the object becomes constant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




