
A potentiometer wire of length L and resistance $10\Omega $ is connected in a series with a battery of e.m.f. $2.5V$ and resistance $R$ in its primary circuit. The null point corresponding to the cell of e.m.f. $1V$ is obtained at a distance of $\dfrac{L}{2}$. If the resistance in the primary circuit is doubled then the position of the new null point will be:
A. $0.4L$
B. $0.5L$
C. $0.6L$
D. $0.8L$
Answer
489.6k+ views
Hint: The potentiometer works on the null point method, it is the point in the wire where the galvanometer shows no deflection. The devices based on the null point method have high accuracy. The potentiometer is used to find the unknown resistances as well as unknown potential.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us first write the information given in the question.
Length of potentiometer wire $ = L$ , resistance $R = 10\Omega $, emf of battery and resistance in the primary circuit \[ = R\] , $V = 2.5V$, null point = $\dfrac{L}{2}$,
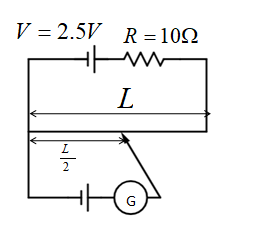
We have to find the new null point when resistance is doubled.
To calculate the current, we have ohm’s law.
$I = \dfrac{V}{R}$
So, let us calculate the current in the primary circuit.
$I = \dfrac{{2.5}}{{10 + R}}$ …………….(1)
It is given that the potential difference across the length $\dfrac{L}{2}$ is $1V$. So, we can write the following relation.
$\dfrac{{2.5}}{{10 + R}} \times 5 = 1V$
Let us simplify the expression.
$R = 12.5 - 10 = 2.5\Omega $
So, from here we get the value of resistance as $2.5$ .
Now, if we double this resistance, it becomes $5\Omega $ , and current through the circuit can be found as below using equation (1).
$I = \dfrac{{2.5}}{{10 + 5}} = \dfrac{{2.5}}{{15}} = \dfrac{1}{6}A$
Let the new null point is $x$ then it is calculated as below.
$\dfrac{{Potential}}{L} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{6} \times 10}}{L} = \dfrac{1}{x}$
So, a new null point is given by,
$x = \dfrac{6}{{10}}L = 0.6L$
Hence, the new null point when we double the resistance is $0.6L$.
Note:
When the length of the wire is changed or resistance is changed then the null point also changes.
When resistance is increased, the null point also increases. Similarly, when the length is increased null point increases.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us first write the information given in the question.
Length of potentiometer wire $ = L$ , resistance $R = 10\Omega $, emf of battery and resistance in the primary circuit \[ = R\] , $V = 2.5V$, null point = $\dfrac{L}{2}$,

We have to find the new null point when resistance is doubled.
To calculate the current, we have ohm’s law.
$I = \dfrac{V}{R}$
So, let us calculate the current in the primary circuit.
$I = \dfrac{{2.5}}{{10 + R}}$ …………….(1)
It is given that the potential difference across the length $\dfrac{L}{2}$ is $1V$. So, we can write the following relation.
$\dfrac{{2.5}}{{10 + R}} \times 5 = 1V$
Let us simplify the expression.
$R = 12.5 - 10 = 2.5\Omega $
So, from here we get the value of resistance as $2.5$ .
Now, if we double this resistance, it becomes $5\Omega $ , and current through the circuit can be found as below using equation (1).
$I = \dfrac{{2.5}}{{10 + 5}} = \dfrac{{2.5}}{{15}} = \dfrac{1}{6}A$
Let the new null point is $x$ then it is calculated as below.
$\dfrac{{Potential}}{L} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{6} \times 10}}{L} = \dfrac{1}{x}$
So, a new null point is given by,
$x = \dfrac{6}{{10}}L = 0.6L$
Hence, the new null point when we double the resistance is $0.6L$.
Note:
When the length of the wire is changed or resistance is changed then the null point also changes.
When resistance is increased, the null point also increases. Similarly, when the length is increased null point increases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




