
A person wants a real image of his own 3 times enlarged. Where should he stand in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm?
A) 10 cm
B) 30 cm
C) 90 cm
D) 20 cm
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: From the given radius of curvature find the focal length of the concave mirror. From the enlargement i.e. the magnification gets a relation between object and image distance. Use the mirror formula to get the answer.
Formulae used:
Focal length:
$f = \dfrac{R}{2}$ ………………..(1)
Where,
$f$ is the focal length of the concave mirror,
$R$ is the radius of curvature of the concave mirror.
Magnification formula:
$m = - \dfrac{v}{u}$ ……………..(2)
Where,
$v$ is the image distance from the mirror,
$u$ is the object distance from the mirror.
Mirror formula:
$\dfrac{1}{u} + \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{f}$ …………....(3)
Complete step by step answer:
Given:
Radius of curvature of the concave mirror, $R = - 30cm$.
Here, the sign will be negative because the center of the curvature for the concave mirror lies on the same side of the object. So, the distance measured from the mirror is in the opposite direction of the incident ray.
Magnification of the image, $m = - 3$.
Here, the negative sign indicates that the image will be inverted.
To find Object distance, $u$.
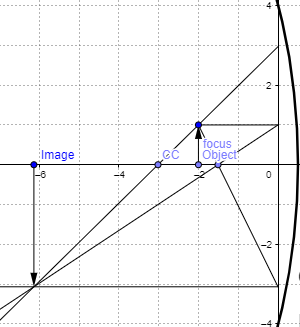
Step 1
Substitute the value of R in eq(1) to find the focal length:
$f = - \dfrac{{30}}{2}cm = - 15cm$ ………... (4)
Step 2:
Substitute value of m in eq(2) to get a relation between u and v:
$
- 3 = - \dfrac{v}{u} \\
\Rightarrow v = 3u \\
$ ………….. (5)
Step 3:
Now, substitute value of f and the relation from eq(5) into eq(3):
$
\dfrac{1}{u} + \dfrac{1}{{3u}} = \dfrac{1}{{ - 15}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{u}\left( {1 + \dfrac{1}{3}} \right) = - \dfrac{1}{{15}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{{3u}} = - \dfrac{1}{{15}} \\
\Rightarrow u = - \dfrac{{15 \times 4}}{3} = - 20cm \\
$
The person should stand at a distance 20 cm in front of the concave mirror. Therefore option (D) is correct.
Additional information:
Always place the object on the left of the mirror and place the mirror at the origin. Since the incident beam direction is from left to right so any distance measured in the right side of the mirror will be positive and any distance measured in the left will be negative. Notice, now the sign convention is just the same as that of the Cartesian coordinate system.
Note:
This type of problem focuses on two pieces of information.
First, the image should be real. For a concave lens, any image created for any $u < f$ is virtual. So, for having a real image, it must be $u > f$.
Second, the image is enlarged. For having an enlarged image the object position must be $u < 2f$.
Combining these two conditions you will get, $2f > u > f$.
Now, if you closely observe the given options you’ll notice only option (d) satisfies it. So, you will get the answer without solving anything!!!
While answering this type of question many students confuse the sign convention. If you follow the technique (shown in the picture) mentioned above then the focal length of the concave mirror is always negative. Just keep a careful eye to the signs you use for writing the distances.
Formulae used:
Focal length:
$f = \dfrac{R}{2}$ ………………..(1)
Where,
$f$ is the focal length of the concave mirror,
$R$ is the radius of curvature of the concave mirror.
Magnification formula:
$m = - \dfrac{v}{u}$ ……………..(2)
Where,
$v$ is the image distance from the mirror,
$u$ is the object distance from the mirror.
Mirror formula:
$\dfrac{1}{u} + \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{f}$ …………....(3)
Complete step by step answer:
Given:
Radius of curvature of the concave mirror, $R = - 30cm$.
Here, the sign will be negative because the center of the curvature for the concave mirror lies on the same side of the object. So, the distance measured from the mirror is in the opposite direction of the incident ray.
Magnification of the image, $m = - 3$.
Here, the negative sign indicates that the image will be inverted.
To find Object distance, $u$.

Step 1
Substitute the value of R in eq(1) to find the focal length:
$f = - \dfrac{{30}}{2}cm = - 15cm$ ………... (4)
Step 2:
Substitute value of m in eq(2) to get a relation between u and v:
$
- 3 = - \dfrac{v}{u} \\
\Rightarrow v = 3u \\
$ ………….. (5)
Step 3:
Now, substitute value of f and the relation from eq(5) into eq(3):
$
\dfrac{1}{u} + \dfrac{1}{{3u}} = \dfrac{1}{{ - 15}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{u}\left( {1 + \dfrac{1}{3}} \right) = - \dfrac{1}{{15}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{{3u}} = - \dfrac{1}{{15}} \\
\Rightarrow u = - \dfrac{{15 \times 4}}{3} = - 20cm \\
$
The person should stand at a distance 20 cm in front of the concave mirror. Therefore option (D) is correct.
Additional information:
Always place the object on the left of the mirror and place the mirror at the origin. Since the incident beam direction is from left to right so any distance measured in the right side of the mirror will be positive and any distance measured in the left will be negative. Notice, now the sign convention is just the same as that of the Cartesian coordinate system.
Note:
This type of problem focuses on two pieces of information.
First, the image should be real. For a concave lens, any image created for any $u < f$ is virtual. So, for having a real image, it must be $u > f$.
Second, the image is enlarged. For having an enlarged image the object position must be $u < 2f$.
Combining these two conditions you will get, $2f > u > f$.
Now, if you closely observe the given options you’ll notice only option (d) satisfies it. So, you will get the answer without solving anything!!!
While answering this type of question many students confuse the sign convention. If you follow the technique (shown in the picture) mentioned above then the focal length of the concave mirror is always negative. Just keep a careful eye to the signs you use for writing the distances.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




