
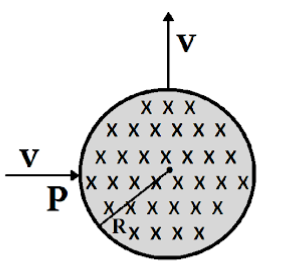
A particle of charge \[q\] and mass \[m\] enters normally (at point P) in a region of the magnetic field with speed \[v\]. It comes out normally from Q after time T as shown in fig. The magnetic field \[B\] is present only in the region of radius \[R\] and is uniform. Initial and final velocities are along the radial direction and they are perpendicular to each other. For this to happen, which of the following expression(s) is/are correct?
\[\begin{align}
& \text{A}\text{. }B=\dfrac{mv}{qR} \\
& \text{B}\text{. }T=\dfrac{\pi R}{2v} \\
& \text{C}\text{. }T=\dfrac{\pi m}{2qB} \\
& \text{D}\text{. none} \\
\end{align}\]

Answer
594k+ views
Hint: When a charged particle enters a uniform magnetic field, the magnetic force provides centripetal force and the particle executes circular motion inside the magnetic field. For the initial and final velocities to be perpendicular to each other, we will apply the equation for the magnetic force on the particle and determine the expressions for the magnetic field and time period of the motion of the particle.
Formula used:
Magnetic force, $\overrightarrow{F}=q\left( v\times B \right)$
Centrifugal force, ${{F}_{c}}=\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{r}$
The radius of motion of a particle in the magnetic field, $r=\dfrac{mv}{qB}$
Complete step by step solution:
We know that when a charged particle in motion is subjected to a magnetic field that is perpendicular to its direction of motion, it results in the circular motion of the particle.
Magnetic force on a particle moving of charge \[q\] and mass \[m\] moving with velocity $v$ when subjected to a perpendicular magnetic field $B$ the force experienced by the particle is:
$\overrightarrow{F}=q\left( v\times B \right)$
As the cross product of two vectors is always perpendicular to both the vectors, so the resulting force will always be perpendicular to the velocity of the particle.
Thus, it will lead the particle into a circular motion.
$\begin{align}
& \overrightarrow{F}=q\left( v\times B \right) \\
& F=qvB\sin \theta \\
\end{align}$
Where $\theta $ is the angle between $v$ and $B$
Now, for velocity of particle and magnetic field to be perpendicular,
$\sin \theta =1$
Or, $F=qvB$
Now, the magnetic force will provide the necessary centripetal force for the circulation motion.
Centripetal force acting on a particle of mass \[m\] moving with velocity $v$ in a circular path of radius $r$ is:
${{F}_{c}}=\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{r}$
Equating the two forces,
$\begin{align}
& qvB=\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{r} \\
& r=\dfrac{mv}{qB} \\
\end{align}$
Now, for the given particle, its velocity vector is always perpendicular to the magnetic field, so it will undergo circular motion.
Also, it enters from P and comes out at Q with velocity normal to initial, so making its path a quarter circle.
Radius of this quarter circle will be equal to $R$
So, using the above result, $r=\dfrac{mv}{qB}$ for this particle, we have:
$\begin{align}
& R=\dfrac{mv}{qB} \\
& B=\dfrac{mv}{qR} \\
\end{align}$
So, option A is correct.
Now, distance travelled by the particle is one-fourth of the circumference of a complete circle of radius $R$
So, distance travelled: $\dfrac{1}{4}\left( 2\pi R \right)=\dfrac{\pi R}{2}$
Speed of particle remains the same as $v$
So time taken is distance divided by speed.
$\begin{align}
& T=\dfrac{D}{s} \\
& T=\dfrac{\dfrac{\pi R}{2}}{v} \\
& T=\dfrac{\pi R}{2v} \\
\end{align}$
So option B is correct.
We have: $B=\dfrac{mv}{qR}$
So, $v=\dfrac{BqR}{m}$
Substituting $v=\dfrac{BqR}{m}$in $T=\dfrac{\pi R}{2v}$
We get,
$\begin{align}
& T=\dfrac{\pi R}{2\times \dfrac{BqR}{m}} \\
& T=\dfrac{\pi Rm}{2BqR} \\
& T=\dfrac{\pi m}{2Bq} \\
\end{align}$
So, option C is also correct.
Hence, correct options are A, B, and C.
Note: In a circular motion, the velocity of the particle is always perpendicular to the force acting on it. When a charged particle enters the magnetic field, we know that the magnetic force is given as the charge times the cross product of velocity and magnetic field. As a cross-product given the vector which is perpendicular to both the vectors in the cross product, therefore, the magnetic force is always perpendicular to the velocity of the particle and the particle starts executing circular motion.
Formula used:
Magnetic force, $\overrightarrow{F}=q\left( v\times B \right)$
Centrifugal force, ${{F}_{c}}=\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{r}$
The radius of motion of a particle in the magnetic field, $r=\dfrac{mv}{qB}$
Complete step by step solution:
We know that when a charged particle in motion is subjected to a magnetic field that is perpendicular to its direction of motion, it results in the circular motion of the particle.
Magnetic force on a particle moving of charge \[q\] and mass \[m\] moving with velocity $v$ when subjected to a perpendicular magnetic field $B$ the force experienced by the particle is:
$\overrightarrow{F}=q\left( v\times B \right)$
As the cross product of two vectors is always perpendicular to both the vectors, so the resulting force will always be perpendicular to the velocity of the particle.
Thus, it will lead the particle into a circular motion.
$\begin{align}
& \overrightarrow{F}=q\left( v\times B \right) \\
& F=qvB\sin \theta \\
\end{align}$
Where $\theta $ is the angle between $v$ and $B$
Now, for velocity of particle and magnetic field to be perpendicular,
$\sin \theta =1$
Or, $F=qvB$
Now, the magnetic force will provide the necessary centripetal force for the circulation motion.
Centripetal force acting on a particle of mass \[m\] moving with velocity $v$ in a circular path of radius $r$ is:
${{F}_{c}}=\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{r}$
Equating the two forces,
$\begin{align}
& qvB=\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{r} \\
& r=\dfrac{mv}{qB} \\
\end{align}$
Now, for the given particle, its velocity vector is always perpendicular to the magnetic field, so it will undergo circular motion.
Also, it enters from P and comes out at Q with velocity normal to initial, so making its path a quarter circle.
Radius of this quarter circle will be equal to $R$
So, using the above result, $r=\dfrac{mv}{qB}$ for this particle, we have:
$\begin{align}
& R=\dfrac{mv}{qB} \\
& B=\dfrac{mv}{qR} \\
\end{align}$
So, option A is correct.
Now, distance travelled by the particle is one-fourth of the circumference of a complete circle of radius $R$
So, distance travelled: $\dfrac{1}{4}\left( 2\pi R \right)=\dfrac{\pi R}{2}$
Speed of particle remains the same as $v$
So time taken is distance divided by speed.
$\begin{align}
& T=\dfrac{D}{s} \\
& T=\dfrac{\dfrac{\pi R}{2}}{v} \\
& T=\dfrac{\pi R}{2v} \\
\end{align}$
So option B is correct.
We have: $B=\dfrac{mv}{qR}$
So, $v=\dfrac{BqR}{m}$
Substituting $v=\dfrac{BqR}{m}$in $T=\dfrac{\pi R}{2v}$
We get,
$\begin{align}
& T=\dfrac{\pi R}{2\times \dfrac{BqR}{m}} \\
& T=\dfrac{\pi Rm}{2BqR} \\
& T=\dfrac{\pi m}{2Bq} \\
\end{align}$
So, option C is also correct.
Hence, correct options are A, B, and C.
Note: In a circular motion, the velocity of the particle is always perpendicular to the force acting on it. When a charged particle enters the magnetic field, we know that the magnetic force is given as the charge times the cross product of velocity and magnetic field. As a cross-product given the vector which is perpendicular to both the vectors in the cross product, therefore, the magnetic force is always perpendicular to the velocity of the particle and the particle starts executing circular motion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




