
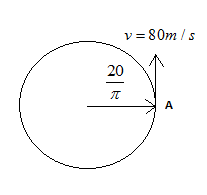
A particle moves along a circle of the radius \[\dfrac{{20}}{\pi }m\] with constant tangential acceleration. If the velocity of the particle is 80 m/s at the end of the second revolution after motion has begun, the tangential acceleration is
A. \[640\pi {\text{ m/se}}{{\text{c}}^2}\]
B. \[160\pi {\text{ m/se}}{{\text{c}}^2}\]
C. \[40\pi {\text{ m/se}}{{\text{c}}^2}\]
D. \[40{\text{ m/se}}{{\text{c}}^2}\]
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: The tangential acceleration is used to measure the change in the tangential velocity of a point with a specific radius with the change in time. The concept of linear and tangential acceleration is the same, but in the case of tangential acceleration, the direction of motion of the object is in a circular path; hence we can say tangential acceleration is the rate of change of tangential velocity on the circular path given as: \[{a_t} = \dfrac{{\vartriangle v}}{{\vartriangle t}}\]
In this question given the object starts from rest and moves with a constant tangential acceleration in a circular path. Tangential acceleration is to be calculated after the second revolution of motion.
Complete step by step solution:
The radius of the circular path \[r = \dfrac{{20}}{\pi }\]
Velocity in the second revolution \[v = 80{\text{ m/sec}}\]
Initial angular velocity, \[{\omega _0} = 0\]
Final angular velocity, \[\omega = \dfrac{{80}}{{\left( {\dfrac{{20}}{\pi }} \right)}} = 4\pi \]
Where angular velocity is given as: \[\omega = \dfrac{v}{r}\]
We know angular displacement is: \[\theta = \left( {2\pi } \right)\]
Hence, for the two revolution\[\theta = 2\left( {2\pi } \right) = 4\pi \]
The equation of motion is given as: \[{\omega ^2} = \omega _0^2 + 2a\theta \]
By substituting the values, we can write:
\[
{\left( {4\pi } \right)^2} = {0^2} + 2a\left( {4\pi } \right) \\
16{\pi ^2} = 8a\pi \\
a = 2\pi \\
\]
Also, we know the relation between angular and tangential acceleration is given as
\[
{a_t} = ar \\
= \left( {2\pi } \right)\left( {\dfrac{{20}}{\pi }} \right) \\
= 40 \\
\]
Hence the tangential acceleration after the second revolution is \[40\] m/$s^2$
Option (D) is correct.
Note: It is to be noted down here that the tangential acceleration of the particle is always perpendicular to the circle and it has a force known as centripetal force always directed towards the center of the circle.
In this question given the object starts from rest and moves with a constant tangential acceleration in a circular path. Tangential acceleration is to be calculated after the second revolution of motion.
Complete step by step solution:
The radius of the circular path \[r = \dfrac{{20}}{\pi }\]
Velocity in the second revolution \[v = 80{\text{ m/sec}}\]

Initial angular velocity, \[{\omega _0} = 0\]
Final angular velocity, \[\omega = \dfrac{{80}}{{\left( {\dfrac{{20}}{\pi }} \right)}} = 4\pi \]
Where angular velocity is given as: \[\omega = \dfrac{v}{r}\]
We know angular displacement is: \[\theta = \left( {2\pi } \right)\]
Hence, for the two revolution\[\theta = 2\left( {2\pi } \right) = 4\pi \]
The equation of motion is given as: \[{\omega ^2} = \omega _0^2 + 2a\theta \]
By substituting the values, we can write:
\[
{\left( {4\pi } \right)^2} = {0^2} + 2a\left( {4\pi } \right) \\
16{\pi ^2} = 8a\pi \\
a = 2\pi \\
\]
Also, we know the relation between angular and tangential acceleration is given as
\[
{a_t} = ar \\
= \left( {2\pi } \right)\left( {\dfrac{{20}}{\pi }} \right) \\
= 40 \\
\]
Hence the tangential acceleration after the second revolution is \[40\] m/$s^2$
Option (D) is correct.
Note: It is to be noted down here that the tangential acceleration of the particle is always perpendicular to the circle and it has a force known as centripetal force always directed towards the center of the circle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




