
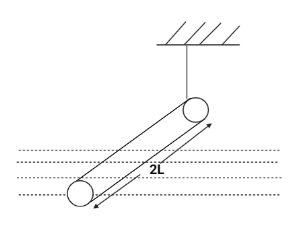
A Slender homogeneous of length $ 2L $ floats partly immersed in water, being supported by a straight fastened to one of its ends as shown. The specific gravity of the rod is $ 0.75 $ . The length of rod that extends out of water is:
A) $ L $
B) $ \dfrac{1}{2}L $
C) $ \dfrac{1}{4}L $
D) $ 3L $

Answer
533.7k+ views
Hint :Buoyancy is the upward force experienced by an object when it is immersed into the water. The object displaces the water owing to its weight. We also know that as the depth of the water increases the pressure on the object also increases. Hence, this variation in pressure leads to an upward force which is known as Buoyancy.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let us consider the length of the rod immersed in water as $ x $ .
There are two forces acting on the rod. The buoyant force that acts on the length of the rod which is immersed in water pushes the rod upwards. Whereas, the force created due to the centre of gravity pulls the rod downwards. Since the rod is in equilibrium, the net torque produced by the rod will be zero.
Hence,
$ 0 = \sum {{\tau _0}} $
$ 0 = wl\cos \theta - {F_B}\left( {2l - \dfrac{x}{2}} \right)\cos \theta $
Substituting the values we get,
$
0 = {\rho _{rod}}gA(2l)(l\cos \theta ) - {\rho _{water}}Ax\left( {2l - \dfrac{x}{2}} \right) \\
0 = \left( {\dfrac{1}{2}{\rho _{water}}gA\cos \theta } \right)\left( {{x^2} - 4lx + 4\dfrac{{{\rho _{rod}}}}{{{\rho _{water}}}}{l^2}} \right) \\
$
Where A is the cross sectional area
Now, we solve the quadratic equation,
$
{x^2} - 4lx + 3{l^2} = 0 \\
{x^2} - lx - 3lx + 3{l^2} = 0 \\
x(x - l) - 3l(x - l) = 0 \\
(x - l)(x - 3l) = 0 \\
$
Hence, $ x = 3L,L $
Since, the total length of wire is $ 2L $ , hence length of rod immersed in water cannot be $ 3L $
Hence $ x = L $
The length of the rod that extends out of the water is $ 2L - L = L $ .
The correct option is (A).
Note :
There are two forces coming into play when an object is immersed in water. Buoyancy as well as the gravitational force. Hence there is both pulling upward and pulling downward force. These phenomena result in the floating of an object on a water surface.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let us consider the length of the rod immersed in water as $ x $ .
There are two forces acting on the rod. The buoyant force that acts on the length of the rod which is immersed in water pushes the rod upwards. Whereas, the force created due to the centre of gravity pulls the rod downwards. Since the rod is in equilibrium, the net torque produced by the rod will be zero.
Hence,
$ 0 = \sum {{\tau _0}} $
$ 0 = wl\cos \theta - {F_B}\left( {2l - \dfrac{x}{2}} \right)\cos \theta $
Substituting the values we get,
$
0 = {\rho _{rod}}gA(2l)(l\cos \theta ) - {\rho _{water}}Ax\left( {2l - \dfrac{x}{2}} \right) \\
0 = \left( {\dfrac{1}{2}{\rho _{water}}gA\cos \theta } \right)\left( {{x^2} - 4lx + 4\dfrac{{{\rho _{rod}}}}{{{\rho _{water}}}}{l^2}} \right) \\
$
Where A is the cross sectional area
Now, we solve the quadratic equation,
$
{x^2} - 4lx + 3{l^2} = 0 \\
{x^2} - lx - 3lx + 3{l^2} = 0 \\
x(x - l) - 3l(x - l) = 0 \\
(x - l)(x - 3l) = 0 \\
$
Hence, $ x = 3L,L $
Since, the total length of wire is $ 2L $ , hence length of rod immersed in water cannot be $ 3L $
Hence $ x = L $
The length of the rod that extends out of the water is $ 2L - L = L $ .
The correct option is (A).
Note :
There are two forces coming into play when an object is immersed in water. Buoyancy as well as the gravitational force. Hence there is both pulling upward and pulling downward force. These phenomena result in the floating of an object on a water surface.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




