
A right triangle, whose sides are 15 cm and 20 cm is made to revolve about its hypotenuse. Find the volume and surface area of the double cone so formed $\left( Use\ \pi =3.14 \right).$
Answer
540.6k+ views
Hint: We will be using the concepts of surface area and volume to simplify the problem. We will be using the concept of rotation of a 2-D figure about an axis to produce a 3-D figure. We will first use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the hypotenuse of the triangle then we will use the hypotenuse to find the length of the perpendicular on hypotenuse and then use this data to find the volume and surface of the figure obtained.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, we have been given a right angled triangle whose sides as 15 cm and 20 cm are rotated about its hypotenuse.
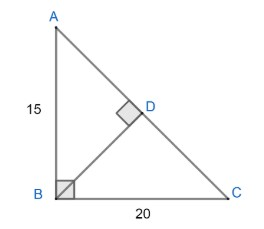
Now, we know that according to Pythagoras theorem,
$\begin{align}
& A{{C}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}} \\
& A{{C}^{2}}={{\left( 15 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 20 \right)}^{2}} \\
& A{{C}^{2}}=225+400 \\
& A{{C}^{2}}=625 \\
& AC=25cm \\
\end{align}$
Also, the area of $\Delta ABC\ is\ \dfrac{1}{2}\times base\times height$. Here BC and AC are the bases of triangle ,BD and AB are height of triangle So equating both the area of triangle, we can get the value of BD as,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{2}\times 20\times 15=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 25\times BD \\
& 20\times 15=25\times BD \\
& 4\times 3=BD \\
& BD=12cm \\
\end{align}$
Now, after revolving it about hypotenuse the figure obtained will be,
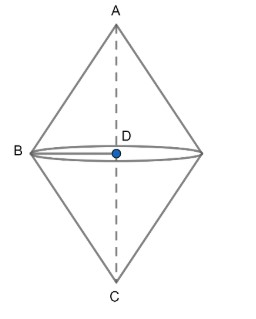
So, BD will become the radius of both the cone and AB and BC will be slant height.
Now, the volume of double cone = volume of upper cone + volume of lower cone
We know that volume of cone is $\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{r}^{2}}h$ , where r is radius of cone and h is height of cone. Therefore, we have,
The total volume$=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi B{{D}^{2}}\times AD+\dfrac{1}{3}\pi B{{D}^{2}}\times DC$
$\begin{align}
& =\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( B{{D}^{2}}\times AD+B{{D}^{2}}\times DC \right) \\
& =\dfrac{1}{3}\pi B{{D}^{2}}\left( AD+DC \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we can see from the figure that AD + DC = AC. Therefore,
$=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi B{{D}^{2}}\left( AC \right)$
Now, we substitute BD = 12 cm and AC = 25 cm.
$\begin{align}
& =\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{\left( 12 \right)}^{2}}\left( 25 \right) \\
& =\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \times 144\times 25 \\
& =\pi \times 48\times 25\ c{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Now, using $\pi =3.14$ we have,
Volume of double cone $=3.14\times 1200\ c{{m}^{3}}$
$=3768\ c{{m}^{3}}$
Now, we have to find the surface area of the double cone and we know that,
Surface area of cone = surface area of upper cone + surface area of lower cone.
Now, we know that the curved surface area of the cone is $\pi rl$ , where r is radius and l is slant height.
Surface area of cone $=\pi \times BD\times AB+\pi \times BD\times BC$
$=\pi BD\left( AB+BC \right)$
Now, we substitute the values of BD = 12 cm, AB = 15 cm and BC = 20
$\begin{align}
& =\pi \times 12\left( 15+20 \right) \\
& =\pi \times 12\times 35 \\
\end{align}$
Now taking $\pi =3.14$ we have;
Surface area of double cone $=3.14\times 420$
$=1318.8\ c{{m}^{2}}$
Note: To solve these types of questions it is important to clearly draw a diagram depicting the situation and So, that the question becomes clear also it is important to note in the solution that BD is perpendicular to hypotenuse AC but radius for the double cone.Students should remember the formula of finding volume and surface of the cone.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, we have been given a right angled triangle whose sides as 15 cm and 20 cm are rotated about its hypotenuse.

Now, we know that according to Pythagoras theorem,
$\begin{align}
& A{{C}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}} \\
& A{{C}^{2}}={{\left( 15 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 20 \right)}^{2}} \\
& A{{C}^{2}}=225+400 \\
& A{{C}^{2}}=625 \\
& AC=25cm \\
\end{align}$
Also, the area of $\Delta ABC\ is\ \dfrac{1}{2}\times base\times height$. Here BC and AC are the bases of triangle ,BD and AB are height of triangle So equating both the area of triangle, we can get the value of BD as,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{2}\times 20\times 15=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 25\times BD \\
& 20\times 15=25\times BD \\
& 4\times 3=BD \\
& BD=12cm \\
\end{align}$
Now, after revolving it about hypotenuse the figure obtained will be,

So, BD will become the radius of both the cone and AB and BC will be slant height.
Now, the volume of double cone = volume of upper cone + volume of lower cone
We know that volume of cone is $\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{r}^{2}}h$ , where r is radius of cone and h is height of cone. Therefore, we have,
The total volume$=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi B{{D}^{2}}\times AD+\dfrac{1}{3}\pi B{{D}^{2}}\times DC$
$\begin{align}
& =\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( B{{D}^{2}}\times AD+B{{D}^{2}}\times DC \right) \\
& =\dfrac{1}{3}\pi B{{D}^{2}}\left( AD+DC \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we can see from the figure that AD + DC = AC. Therefore,
$=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi B{{D}^{2}}\left( AC \right)$
Now, we substitute BD = 12 cm and AC = 25 cm.
$\begin{align}
& =\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{\left( 12 \right)}^{2}}\left( 25 \right) \\
& =\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \times 144\times 25 \\
& =\pi \times 48\times 25\ c{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Now, using $\pi =3.14$ we have,
Volume of double cone $=3.14\times 1200\ c{{m}^{3}}$
$=3768\ c{{m}^{3}}$
Now, we have to find the surface area of the double cone and we know that,
Surface area of cone = surface area of upper cone + surface area of lower cone.
Now, we know that the curved surface area of the cone is $\pi rl$ , where r is radius and l is slant height.
Surface area of cone $=\pi \times BD\times AB+\pi \times BD\times BC$
$=\pi BD\left( AB+BC \right)$
Now, we substitute the values of BD = 12 cm, AB = 15 cm and BC = 20
$\begin{align}
& =\pi \times 12\left( 15+20 \right) \\
& =\pi \times 12\times 35 \\
\end{align}$
Now taking $\pi =3.14$ we have;
Surface area of double cone $=3.14\times 420$
$=1318.8\ c{{m}^{2}}$
Note: To solve these types of questions it is important to clearly draw a diagram depicting the situation and So, that the question becomes clear also it is important to note in the solution that BD is perpendicular to hypotenuse AC but radius for the double cone.Students should remember the formula of finding volume and surface of the cone.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




