
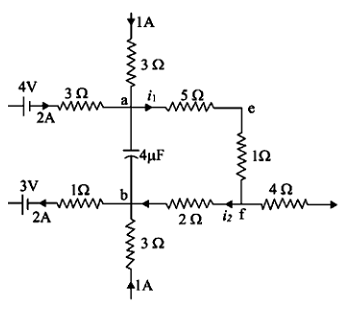
A part of circuit in steady state along with the currents flowing in the branches, the value of resistances etc., is shown in figure. Calculate the energy stored in the capacitor.
$A. 8\times 10^{-1}J$
$B.8\times {{10}^{-2}}J$
$C.8\times {{10}^{-3}}J$
$D.8\times {{10}^{-4}}J$

Answer
598.8k+ views
Hint: In order to know the energy of a capacitor, we need to know the voltage across a capacitor. To find the voltage across the capacitor in the given circuit we will use Kirchhoff’s voltage and current laws at different parts of the circuit. Therefore, the energy stored in the capacitor can be found easily.
Formula used:
$E=\dfrac{1}{2} CV^2$
Complete step by step solution:
Kirchhoff’s current law states that the total algebraic sum of currents in any point in the circuit is basically zero. Actually, we have to put positive signs for currents coming inside the point and negative signs for currents going outwards from the point. Or we may assume the opposite as well, but the answer will be the same. Applying this law at the point a, in the given circuit, we
obtain,
$1A+2A-i_1=0$
This gives, $i_1=3A$.
Similarly, applying this law at the point b we get,
$i_2+1A=2A$
This gives, $i_2=1A$ .
Now, Kirchhoff’s voltage law is applicable for a loop in the circuit. It states that the algebraic
the sum of the voltage in any loop of a circuit is zero. Now applying this law in the loop (‘aefb’) of
the given circuit, we get,
$V=5{{i}_{1}}+1{{i}_{1}}+2{{i}_{2}}=20$Volt
Here, V is the voltage across the capacitor, which is found to be 20 volts by our calculation.
Now the energy stored in the capacitor is given by,
$E=\dfrac{1}{2}CV^2=\dfrac{1}{2}.4\times 10^{-6} .(20)^2=8\times 10^{-4} J$
After doing the calculation we find out that option D is the correct answer.
Additional information:
Kirchhoff’s current law is another form of the law of conservation of electric charge. On the other hand, Kirchhoff’s voltage law is another form of the law of conservation of energy.
Note: While putting different values in Kirchhoff’s law, keep in mind the signs of different terms. When the resistance is given in ohm and the current is given in Ampere, the voltage will be obtained in Volt. If current were given in milli-ampere, the voltage would be in milli-volt, and 1milli $={{10}^{-3}}$. So, the answer will change in terms of power of 10.
Formula used:
$E=\dfrac{1}{2} CV^2$
Complete step by step solution:
Kirchhoff’s current law states that the total algebraic sum of currents in any point in the circuit is basically zero. Actually, we have to put positive signs for currents coming inside the point and negative signs for currents going outwards from the point. Or we may assume the opposite as well, but the answer will be the same. Applying this law at the point a, in the given circuit, we
obtain,
$1A+2A-i_1=0$
This gives, $i_1=3A$.
Similarly, applying this law at the point b we get,
$i_2+1A=2A$
This gives, $i_2=1A$ .
Now, Kirchhoff’s voltage law is applicable for a loop in the circuit. It states that the algebraic
the sum of the voltage in any loop of a circuit is zero. Now applying this law in the loop (‘aefb’) of
the given circuit, we get,
$V=5{{i}_{1}}+1{{i}_{1}}+2{{i}_{2}}=20$Volt
Here, V is the voltage across the capacitor, which is found to be 20 volts by our calculation.
Now the energy stored in the capacitor is given by,
$E=\dfrac{1}{2}CV^2=\dfrac{1}{2}.4\times 10^{-6} .(20)^2=8\times 10^{-4} J$
After doing the calculation we find out that option D is the correct answer.
Additional information:
Kirchhoff’s current law is another form of the law of conservation of electric charge. On the other hand, Kirchhoff’s voltage law is another form of the law of conservation of energy.
Note: While putting different values in Kirchhoff’s law, keep in mind the signs of different terms. When the resistance is given in ohm and the current is given in Ampere, the voltage will be obtained in Volt. If current were given in milli-ampere, the voltage would be in milli-volt, and 1milli $={{10}^{-3}}$. So, the answer will change in terms of power of 10.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




