
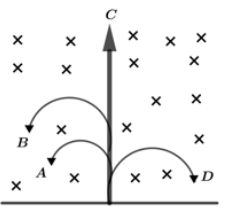
A neutron, a proton, an electron and alpha particle enter a region of the constant magnetic field with equal velocities. The magnetic field is along the inward normal to the plane of the paper, the tracks of the particle are labelled in figure, the electron follows track __ and alpha particle follows track____
A. A, C
B. C, A
C. D, B
D. B, D

Answer
522.9k+ views
Hint:We will use the concept of magnetic force formula which determines the trajectory of a charged particle moving inside the magnetic field. And also neutron particles have no charge whereas protons and electrons have positive and negative charge whereas alpha particles have positive charge.
Complete step by step answer:
Firstly we need to understand the magnetic force formula which is given as,
$\overrightarrow F = q(\overrightarrow v \times \overrightarrow {B)} $
where $F$ is the force, $v$ is velocity and $B$ is magnetic field.
We have given that $\overrightarrow v $ and $\overrightarrow B $ are perpendicular to each other since magnetic field is in downward direction so term $(\overrightarrow v \times \overrightarrow {B)} $ will be simply as $vB\sin {90^ \circ }$ which results
$F = qvB$. And Force will be in direction right to the initial point if charge is negative and left to the initial point if charge is positive. Using Fleming Right hand rule.
Now, Let us check for electron, since electron has a negative charge so force will act in right to the initial point so best path is described by D. $F = - qvB$. For alpha particles, since alpha particle and proton both have positive charge so their path must be in left but as we know greater the charge greater the deflection and we know that alpha particle has greater charge than proton so path must be followed by B. $F = + 2qvB$.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note:Fleming right hand rule states “point index finger in the direction of magnetic field and thumb in the direction of velocity of particle then middle finger gives us the direction of force”. Here, the neutron has no charge so force on the neutron will be zero so its path is shown by C (no deflection).
Complete step by step answer:
Firstly we need to understand the magnetic force formula which is given as,
$\overrightarrow F = q(\overrightarrow v \times \overrightarrow {B)} $
where $F$ is the force, $v$ is velocity and $B$ is magnetic field.
We have given that $\overrightarrow v $ and $\overrightarrow B $ are perpendicular to each other since magnetic field is in downward direction so term $(\overrightarrow v \times \overrightarrow {B)} $ will be simply as $vB\sin {90^ \circ }$ which results
$F = qvB$. And Force will be in direction right to the initial point if charge is negative and left to the initial point if charge is positive. Using Fleming Right hand rule.
Now, Let us check for electron, since electron has a negative charge so force will act in right to the initial point so best path is described by D. $F = - qvB$. For alpha particles, since alpha particle and proton both have positive charge so their path must be in left but as we know greater the charge greater the deflection and we know that alpha particle has greater charge than proton so path must be followed by B. $F = + 2qvB$.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note:Fleming right hand rule states “point index finger in the direction of magnetic field and thumb in the direction of velocity of particle then middle finger gives us the direction of force”. Here, the neutron has no charge so force on the neutron will be zero so its path is shown by C (no deflection).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




