
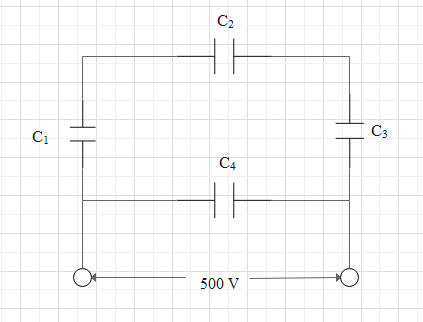
A network of four capacitors each of $15\mu F$ is connected to a $500\,V$ supply as shown in the figure. Determine
(a)Equivalent capacitance of the network
(b)Charge of each capacitor.

Answer
580.8k+ views
Hint: For series connection the total capacitance is as the reciprocal of the sum of reciprocals of individual capacitance. For parallel connection total capacitance is the sum of individual capacitance. Using this we can find the total effective capacitance of the given arrangement of capacitors.
Charge stored in a capacitor is the product of capacitance and the voltage. In the case of capacitors in series the charge in each capacitor will be the same.
Complete step by step answer:
Given that 4 capacitors of $15\mu F$ capacitance is connected to $500\,V$ supply.
Thus, Voltage $V = 500V$
Capacitance,
${C_1} = {C_2} = {C_3} = {C_4} = 15\mu F$
We know that in series connection one end of one capacitor is connected to one end of the other.
We can see from the figure that the capacitors ${C_1}$, ${C_2}$ and ${C_3}$ are connected in series.
While in parallel, both the ends will be connected to the same point.
So we can say that the branch containing ${C_1}$, ${C_2}$ and ${C_3}$ together is parallel to the capacitor ${C_4}$ .
First let us find the equivalent capacitance of ${C_1}$, ${C_2}$ and ${C_3}$ which are in series.
For series connection the total capacitance is as the reciprocal of the sum of reciprocals of individual capacitance.
$\dfrac{1}{{{C_S}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{C_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{C_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{C_3}}}$
$\dfrac{1}{{{C_S}}} = \dfrac{1}{{15}} + \dfrac{1}{{15}} + \dfrac{1}{{15}} = \dfrac{3}{{15}}$
$\therefore {C_S} = \dfrac{{15}}{3} = 5\mu F$
This ${C_S}$ is parallel to ${C_4}$ .
In parallel connection total capacitance is the sum of individual capacitance. Thus,
${C_P} = {C_S} + {C_4}$
On substituting the values we get
${C_P} = 5 + 15$
$\therefore {C_P} = 20\mu F$
Now let us find charge on each capacitor.
We know the relationship between capacitance, voltage and charge of a capacitor is given as
$Q = CV$
Thus, for capacitor ${C_4}$ the charge is given as,
${Q_4} = {C_4} \times V$
$ \Rightarrow {Q_4} = 15 \times {10^{ - 6}} \times 500$
$\therefore {Q_4} = 7 \cdot 5\,mC$
We know that the charge stored in each of the capacitors in series will be the same because current flowing through each capacitor in series is the same.
Since total capacitance is ${C_S}$, we get charge $Q$ through each of the capacitor ${C_1}$, ${C_2}$ and ${C_3}$ as
$Q = {C_S} \times V$
$ \Rightarrow Q = 5 \times {10^{ - 6}} \times 500$
$\therefore Q = 2 \cdot 5\,mC$
Thus charge flowing through ${C_4}$ is $7 \cdot 5\,mC$ and charge flowing through ${C_1}$, ${C_2}$ and ${C_3}$ is $2 \cdot 5\,mC$.
Note:Remember that in series connection the charge that is flowing through each capacitor ${C_1}$, ${C_2}$ and ${C_3}$ will be the same because the same current is flowing through each capacitor. Thus, the charge stored will also be the same. Whereas in the case of parallel connection the charge stored will be different but the potential difference will be the same since the end points are connected to the same point.
Charge stored in a capacitor is the product of capacitance and the voltage. In the case of capacitors in series the charge in each capacitor will be the same.
Complete step by step answer:
Given that 4 capacitors of $15\mu F$ capacitance is connected to $500\,V$ supply.
Thus, Voltage $V = 500V$
Capacitance,
${C_1} = {C_2} = {C_3} = {C_4} = 15\mu F$
We know that in series connection one end of one capacitor is connected to one end of the other.
We can see from the figure that the capacitors ${C_1}$, ${C_2}$ and ${C_3}$ are connected in series.
While in parallel, both the ends will be connected to the same point.
So we can say that the branch containing ${C_1}$, ${C_2}$ and ${C_3}$ together is parallel to the capacitor ${C_4}$ .
First let us find the equivalent capacitance of ${C_1}$, ${C_2}$ and ${C_3}$ which are in series.
For series connection the total capacitance is as the reciprocal of the sum of reciprocals of individual capacitance.
$\dfrac{1}{{{C_S}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{C_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{C_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{C_3}}}$
$\dfrac{1}{{{C_S}}} = \dfrac{1}{{15}} + \dfrac{1}{{15}} + \dfrac{1}{{15}} = \dfrac{3}{{15}}$
$\therefore {C_S} = \dfrac{{15}}{3} = 5\mu F$
This ${C_S}$ is parallel to ${C_4}$ .
In parallel connection total capacitance is the sum of individual capacitance. Thus,
${C_P} = {C_S} + {C_4}$
On substituting the values we get
${C_P} = 5 + 15$
$\therefore {C_P} = 20\mu F$
Now let us find charge on each capacitor.
We know the relationship between capacitance, voltage and charge of a capacitor is given as
$Q = CV$
Thus, for capacitor ${C_4}$ the charge is given as,
${Q_4} = {C_4} \times V$
$ \Rightarrow {Q_4} = 15 \times {10^{ - 6}} \times 500$
$\therefore {Q_4} = 7 \cdot 5\,mC$
We know that the charge stored in each of the capacitors in series will be the same because current flowing through each capacitor in series is the same.
Since total capacitance is ${C_S}$, we get charge $Q$ through each of the capacitor ${C_1}$, ${C_2}$ and ${C_3}$ as
$Q = {C_S} \times V$
$ \Rightarrow Q = 5 \times {10^{ - 6}} \times 500$
$\therefore Q = 2 \cdot 5\,mC$
Thus charge flowing through ${C_4}$ is $7 \cdot 5\,mC$ and charge flowing through ${C_1}$, ${C_2}$ and ${C_3}$ is $2 \cdot 5\,mC$.
Note:Remember that in series connection the charge that is flowing through each capacitor ${C_1}$, ${C_2}$ and ${C_3}$ will be the same because the same current is flowing through each capacitor. Thus, the charge stored will also be the same. Whereas in the case of parallel connection the charge stored will be different but the potential difference will be the same since the end points are connected to the same point.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




