
A monkey of mass 40 kg climbs on a massless rope of breaking strength 600N. The rope will break if the monkey $\left( {g = 10{\text{ m/se}}{{\text{c}}^2}} \right)$
(A) Climbs up with a uniform speed of $5{\text{ m/sec}}$
(B) Climbs up with an acceleration of $6{\text{ m/se}}{{\text{c}}^2}$
(C) Climbs down with an acceleration of $4{\text{ m/se}}{{\text{c}}^2}$
(D) Climbs down with a uniform speed of $5{\text{ m/sec}}$
Answer
593.1k+ views
Hint: In this question, we need to evaluate the options such that when the monkey climbs the rope, when will the rope break. For this, we will follow the free body diagram of the monkey and the rope and apply the newton’s equation of motion.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the conditions given in the question, the free body diagram is sketched as below.
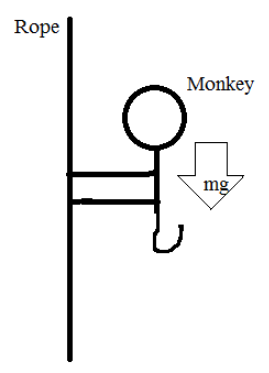
Here, due to the mass of the money, a gravitational force always acts downwards, which is equivalent to the product of the mass of the monkey and the acceleration due to gravity. Mathematically, ${F_d} = mg$.
The mass of the monkey has been given as 40 kg, so the gravitational force acting downwards is given as:
$
\Rightarrow{F_d} = 40g \\
\Rightarrow{F_d} = 40 \times 10 \\
\Rightarrow{F_d} = 400N \\
$
Now, we will proceed with the observation for each of the given options:
(A) When the monkey climbs up with the uniform velocity of $5{\text{ m/sec}}$ then, the acceleration of the monkey will be zero. Hence the net force acting will be 400N only, which is smaller than the tensile strength of the rope and so the rope will not break.
(B) When the monkey climbs up with an acceleration of $6{\text{ m/se}}{{\text{c}}^2}$ then, the net force acting on the rope is calculated as:
$
\Rightarrow{F_r} = ma + mg \\
\Rightarrow{F_r} = 40(6 + 10) \\
\Rightarrow{F_r} = 40 \times 16 \\
\Rightarrow{F_r} = 640N \\
$
But, the tensile strength of the rope is 600N, and so, the rope will break.
(C) When the monkey climbs down with an acceleration of $4{\text{ m/se}}{{\text{c}}^2}$ then, the net force acting on the rope is calculated as:
$
\Rightarrow{F_r} = mg - ma \\
\Rightarrow{F_r} = 40(10 - 4) \\
\Rightarrow{F_r} = 40 \times 6 \\
\Rightarrow{F_r} = 240N \\
$
But, the tensile strength of the rope is 600N, and so, the rope will not break.
(D) When the monkey climbs down with the uniform velocity of $5{\text{ m/sec}}$ then, the acceleration of the monkey will be zero. Hence the net force acting will be 400N only, which is smaller than the tensile strength of the rope, and so the rope will not break.Hence, the rope will break only under one condition, i.e., when the monkey climbs up with an acceleration of $6{\text{ m/se}}{{\text{c}}^2}$.
Hence,option B is correct.
Note: It is worth noting down here that we have taken the absolute value of the acceleration due to gravity as 10 instead of 9.8 as it is mentioned in the question. Moreover, when a body is moving with the constant velocity then, the acceleration of the body is zero only as the acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity with respect to time.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the conditions given in the question, the free body diagram is sketched as below.

Here, due to the mass of the money, a gravitational force always acts downwards, which is equivalent to the product of the mass of the monkey and the acceleration due to gravity. Mathematically, ${F_d} = mg$.
The mass of the monkey has been given as 40 kg, so the gravitational force acting downwards is given as:
$
\Rightarrow{F_d} = 40g \\
\Rightarrow{F_d} = 40 \times 10 \\
\Rightarrow{F_d} = 400N \\
$
Now, we will proceed with the observation for each of the given options:
(A) When the monkey climbs up with the uniform velocity of $5{\text{ m/sec}}$ then, the acceleration of the monkey will be zero. Hence the net force acting will be 400N only, which is smaller than the tensile strength of the rope and so the rope will not break.
(B) When the monkey climbs up with an acceleration of $6{\text{ m/se}}{{\text{c}}^2}$ then, the net force acting on the rope is calculated as:
$
\Rightarrow{F_r} = ma + mg \\
\Rightarrow{F_r} = 40(6 + 10) \\
\Rightarrow{F_r} = 40 \times 16 \\
\Rightarrow{F_r} = 640N \\
$
But, the tensile strength of the rope is 600N, and so, the rope will break.
(C) When the monkey climbs down with an acceleration of $4{\text{ m/se}}{{\text{c}}^2}$ then, the net force acting on the rope is calculated as:
$
\Rightarrow{F_r} = mg - ma \\
\Rightarrow{F_r} = 40(10 - 4) \\
\Rightarrow{F_r} = 40 \times 6 \\
\Rightarrow{F_r} = 240N \\
$
But, the tensile strength of the rope is 600N, and so, the rope will not break.
(D) When the monkey climbs down with the uniform velocity of $5{\text{ m/sec}}$ then, the acceleration of the monkey will be zero. Hence the net force acting will be 400N only, which is smaller than the tensile strength of the rope, and so the rope will not break.Hence, the rope will break only under one condition, i.e., when the monkey climbs up with an acceleration of $6{\text{ m/se}}{{\text{c}}^2}$.
Hence,option B is correct.
Note: It is worth noting down here that we have taken the absolute value of the acceleration due to gravity as 10 instead of 9.8 as it is mentioned in the question. Moreover, when a body is moving with the constant velocity then, the acceleration of the body is zero only as the acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity with respect to time.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




