
A mixture of n-heptane and n- hexane can be separated through the process of:
A.Centrifugation
B.Paper chromatography
C.Simple distillation
D.All of the above
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint:A separation procedure is a process that transforms two or more different component mixtures into a combination or solution of chemical substances. At least one of the separation results is enriched in one or more constituents of the source combination. In certain cases, the mixture can be entirely separated into pure constituents by separation.
Complete step by step answer:
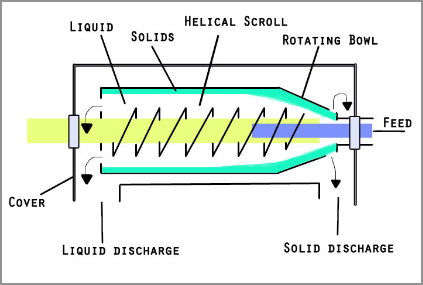
So, let's understand what is centrifugation? This is a separation process that relies on the action of centrifugal force( force acting on any object moving in a circular path when viewed from a rotating frame of reference) to separate heterogeneous mixtures ( mixtures which do not have uniform composition throughout, for example mixture of soil and sand or mixture of oil and water and so on). In simple words, centrifugation is a process where a mixture is separated through spinning. I hope that’s clear. Right? Here’s a diagram for you to understand clearly.
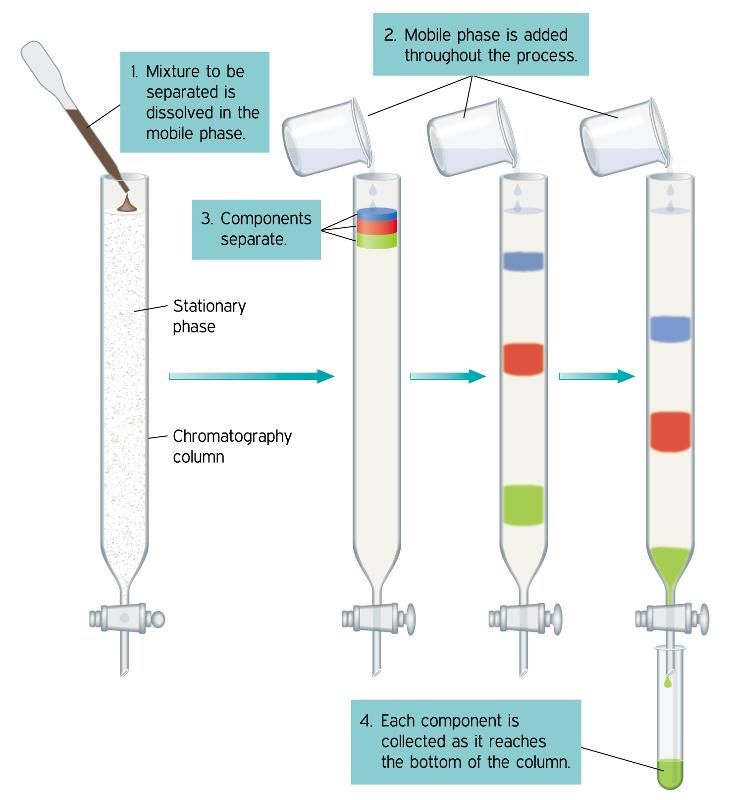
Okay, so now let’s move on and understand the other terms. What’s paper chromatography? This is an analytical method used to separate coloured chemicals or substances. This is useful for separating complex mixtures of compounds having similar polarity, for example, amino acids. Here’s a diagram for you to understand the process clearly.
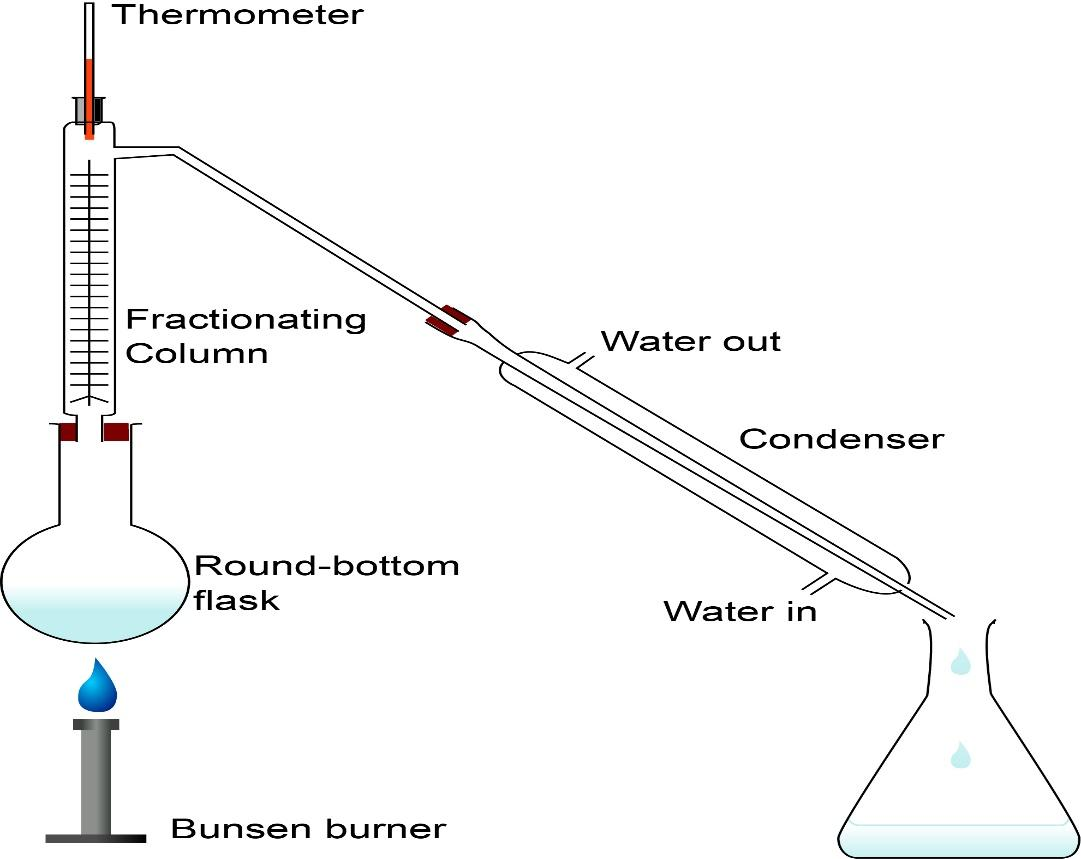
Now, let’s understand the process of simple distillation. This is the most common technique for purifying organic liquids. In simple distillation, the mixture is boiled and the one with low boiling point, boils faster and the vapours progress through the apparatus until they reach the condenser where they are cooled and reliquefy. This is how the mixture is separated and collected. Check out the diagram to understand better.
Now, let’s study the physical properties of $\,n - \,$ hexane and $\,n - \,$ heptane. Hexane or $\,n - \,$ hexane is essentially pure straight chain $\,{C_6}{H_{14}}\,$.It is an inert non -reactive and non- polar solvent. Its boiling point is $\,{68.73^o}C\,$. This is a colourless liquid. Heptane or $\,n - \,$ heptane is the straight chain alkane with the chemical formula $\,{H_3}C{(C{H_2})_5}C{H_3}\,$ or $\,{C_7}{H_{16}}\,$ .It is volatile and non- polar solvent also colourless. Boiling point is $\,{98.42^o}C\,$. One of the major differences in property is their boiling points, which makes the process of simple distillation the most efficient method of separation.
The vapours of $\,n - \,$ hexane has a lower boiling point so it passes through and gets condensed in the condenser whereas $\,n - \,$ heptane having higher boiling point condenses and flows back into the flask.
Thus, option C simple distillation is the correct answer.
Note:A mixture of $\,n - \,$ hexane and $\,n - \,$ heptane can be considered an ideal solution and closely follow Raoult’s law, which states “ that the partial pressure of each component of an ideal mixture of liquids is equal to the vapour pressure of the pure component multiplied by its mole fraction in the mixture”. Another piece of information: Intermolecular forces between $\,n - \,$ hexane and $\,n - \,$ heptane are nearly the same.
Complete step by step answer:
So, let's understand what is centrifugation? This is a separation process that relies on the action of centrifugal force( force acting on any object moving in a circular path when viewed from a rotating frame of reference) to separate heterogeneous mixtures ( mixtures which do not have uniform composition throughout, for example mixture of soil and sand or mixture of oil and water and so on). In simple words, centrifugation is a process where a mixture is separated through spinning. I hope that’s clear. Right? Here’s a diagram for you to understand clearly.

Okay, so now let’s move on and understand the other terms. What’s paper chromatography? This is an analytical method used to separate coloured chemicals or substances. This is useful for separating complex mixtures of compounds having similar polarity, for example, amino acids. Here’s a diagram for you to understand the process clearly.

Now, let’s understand the process of simple distillation. This is the most common technique for purifying organic liquids. In simple distillation, the mixture is boiled and the one with low boiling point, boils faster and the vapours progress through the apparatus until they reach the condenser where they are cooled and reliquefy. This is how the mixture is separated and collected. Check out the diagram to understand better.

Now, let’s study the physical properties of $\,n - \,$ hexane and $\,n - \,$ heptane. Hexane or $\,n - \,$ hexane is essentially pure straight chain $\,{C_6}{H_{14}}\,$.It is an inert non -reactive and non- polar solvent. Its boiling point is $\,{68.73^o}C\,$. This is a colourless liquid. Heptane or $\,n - \,$ heptane is the straight chain alkane with the chemical formula $\,{H_3}C{(C{H_2})_5}C{H_3}\,$ or $\,{C_7}{H_{16}}\,$ .It is volatile and non- polar solvent also colourless. Boiling point is $\,{98.42^o}C\,$. One of the major differences in property is their boiling points, which makes the process of simple distillation the most efficient method of separation.
The vapours of $\,n - \,$ hexane has a lower boiling point so it passes through and gets condensed in the condenser whereas $\,n - \,$ heptane having higher boiling point condenses and flows back into the flask.
Thus, option C simple distillation is the correct answer.
Note:A mixture of $\,n - \,$ hexane and $\,n - \,$ heptane can be considered an ideal solution and closely follow Raoult’s law, which states “ that the partial pressure of each component of an ideal mixture of liquids is equal to the vapour pressure of the pure component multiplied by its mole fraction in the mixture”. Another piece of information: Intermolecular forces between $\,n - \,$ hexane and $\,n - \,$ heptane are nearly the same.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




