
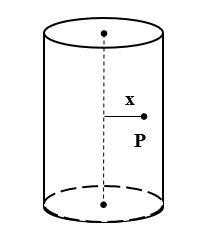
A long cylindrical volume contains a uniformly distributed charge of density $\rho$. Find the electric field at point P inside the cylindrical volume at a distance x from its axis.

Answer
583.5k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, initially, find the charge on the cylinder. Charge can be calculated by taking the product of volume charge density and volume of the cylinder. Then, use the integral form of Gauss law for volume charge density. Substitute the values and calculate the electric field at point P inside the cylindrical volume.
Formula used:
$Q= \rho V$
$\oint E. ds= \dfrac {Q}{{\epsilon}_{0}}$
Complete step by step answer:
Given: Volume charge density =$\rho$
Let the height of the cylinder be h
Charge on the cylinder is given by,
$Q= \rho V$
Where, V is the volume of the cylinder
Substituting values in above equation we get,
$Q= \rho \times 4\pi {x}^{2}h$
According to gauss law,
$\oint E. ds= \dfrac {Q}{{\epsilon}_{0}}$
$\therefore E= \dfrac {Q}{dx \times{\epsilon}_{0}}$
Substituting the values in above equation we get,
$\Rightarrow E= \dfrac { \rho \times 4\pi {x}^{2}h }{2\pi xh \times{\epsilon}_{0}}$
$\therefore E= \dfrac {\rho x}{2 {\epsilon}_{0}}$
Hence, the electric field at point P inside the cylinder is $\dfrac {\rho x}{2 {\epsilon}_{0}}$.
Note:
To answer these types of questions, students should remember the basic laws like Gauss law. There are two forms of Gauss law: integral form and differential form. Integral form of Gauss law is given by,
$\oint E. ds= \dfrac {Q}{{\epsilon}_{0}}$
Differential form is given by,
$\nabla . E= \dfrac {\rho}{{\epsilon}_{0}}$
Gauss law is a restatement of Coulomb's law. If we apply the Gauss law to a point charge, then we'll get back the Coulomb's law.
Formula used:
$Q= \rho V$
$\oint E. ds= \dfrac {Q}{{\epsilon}_{0}}$
Complete step by step answer:
Given: Volume charge density =$\rho$
Let the height of the cylinder be h
Charge on the cylinder is given by,
$Q= \rho V$
Where, V is the volume of the cylinder
Substituting values in above equation we get,
$Q= \rho \times 4\pi {x}^{2}h$
According to gauss law,
$\oint E. ds= \dfrac {Q}{{\epsilon}_{0}}$
$\therefore E= \dfrac {Q}{dx \times{\epsilon}_{0}}$
Substituting the values in above equation we get,
$\Rightarrow E= \dfrac { \rho \times 4\pi {x}^{2}h }{2\pi xh \times{\epsilon}_{0}}$
$\therefore E= \dfrac {\rho x}{2 {\epsilon}_{0}}$
Hence, the electric field at point P inside the cylinder is $\dfrac {\rho x}{2 {\epsilon}_{0}}$.
Note:
To answer these types of questions, students should remember the basic laws like Gauss law. There are two forms of Gauss law: integral form and differential form. Integral form of Gauss law is given by,
$\oint E. ds= \dfrac {Q}{{\epsilon}_{0}}$
Differential form is given by,
$\nabla . E= \dfrac {\rho}{{\epsilon}_{0}}$
Gauss law is a restatement of Coulomb's law. If we apply the Gauss law to a point charge, then we'll get back the Coulomb's law.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




