
A lens produces a magnification of -0.5.Is this a converging or diverging lens? If the focal length of the lens is 6cm, draw a ray diagram showing the image formation in this case.
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: We are given the magnification and the focal length of the lens. Find the image distance with the use of formula of magnification M=\[\dfrac{{image{\text{ }}distance\;}}{{object{\text{ }}distance}} = \dfrac{v}{u}\], and the lens formula :
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u}$
Complete step by step answer:
Now from the question, given
Magnification of the lens M=-0.5
Focal length of the lens $f$ =6cm
We know that if a lens is a converging lens the image produced is real and inverted and has positive image distance whereas in a diverging lens the image produced is virtual and the image distance is negative as image is formed on the same side of the lens as the object.
Now keeping that in mind we calculate the image distance using the magnification and the Lens formula
Using formula of magnification, we have
M=$\dfrac{v}{u}$
Now put the value of magnification M into the formula
- 0.5=$\dfrac{v}{u}$
\[v\] = - 0.5$u$
To find the values of $v$ and $u$ we will use the lens formula
Now, from the Lens formula
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u}$
Put the value of $f$ and \[v\] into the formula, we get:
$\dfrac{1}{6} = \dfrac{1}{{ - 0.5u}} - \dfrac{1}{u}$
$\dfrac{1}{6} = \dfrac{{ - 1.5}}{{0.5u}}$
$u$ = - 18 cm
Now putting the value of u in formula for magnification
- 0.5 = $\dfrac{v}{{ - 18}}$
\[v\] = 9 cm
Thus the lens will be a converging lens.
The ray diagram of the given converging lens is given below:
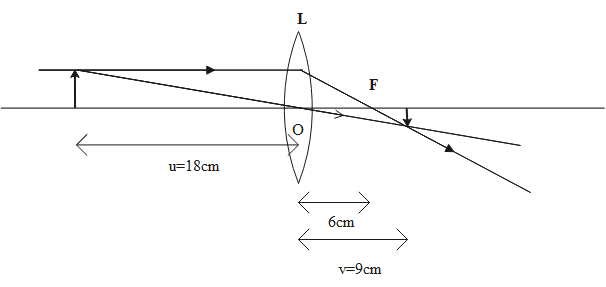
Note:
Magnification of a lens is defined as the ratio of the height of an image to the height of an object. It can be given in the terms of the image distance and object distance, which is the ratio of image distance to that of object distance.
M=$\dfrac{{{h_i}}}{{{h_0}}} = \dfrac{v}{u}$
Where, M= magnification
${h_i}$ = height of image
${h_0}$ = height of an object
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u}$
Complete step by step answer:
Now from the question, given
Magnification of the lens M=-0.5
Focal length of the lens $f$ =6cm
We know that if a lens is a converging lens the image produced is real and inverted and has positive image distance whereas in a diverging lens the image produced is virtual and the image distance is negative as image is formed on the same side of the lens as the object.
Now keeping that in mind we calculate the image distance using the magnification and the Lens formula
Using formula of magnification, we have
M=$\dfrac{v}{u}$
Now put the value of magnification M into the formula
- 0.5=$\dfrac{v}{u}$
\[v\] = - 0.5$u$
To find the values of $v$ and $u$ we will use the lens formula
Now, from the Lens formula
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u}$
Put the value of $f$ and \[v\] into the formula, we get:
$\dfrac{1}{6} = \dfrac{1}{{ - 0.5u}} - \dfrac{1}{u}$
$\dfrac{1}{6} = \dfrac{{ - 1.5}}{{0.5u}}$
$u$ = - 18 cm
Now putting the value of u in formula for magnification
- 0.5 = $\dfrac{v}{{ - 18}}$
\[v\] = 9 cm
Thus the lens will be a converging lens.
The ray diagram of the given converging lens is given below:

Note:
Magnification of a lens is defined as the ratio of the height of an image to the height of an object. It can be given in the terms of the image distance and object distance, which is the ratio of image distance to that of object distance.
M=$\dfrac{{{h_i}}}{{{h_0}}} = \dfrac{v}{u}$
Where, M= magnification
${h_i}$ = height of image
${h_0}$ = height of an object
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




