
A lamp is 50ft above the ground. A ball is dropped from the same height from a point 30 ft away from the light pole. If a ball falls a distance of $s=16{{t}^{2}}$ ft in t seconds, then how fast is the shadow of the ball moving along the ground $\dfrac{1}{2}$ sec later?
A. -2000ft/sec
B. -1500ft/sec
C. -3000ft/sec
D. -1000ft/sec
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: We here have to find the speed of the shadow of the ball after 0.5sec. for that, we will first draw a figure of this situation from the given data. It will come as two similar right angled triangles with the same base. Then we will take the angle of the triangle to be $\alpha $ and the lateral distance between the ball and its shadow to be x and then calculate the value of tan$\alpha $from both these triangles. Then, we will take the height of the ball from the ground to be y and hence, it will be 50-s. Then we will keep the value of s in this equation and find $\dfrac{dy}{dt}$. After that, we will equate both the values of tan$\alpha $obtained and then we will again find $\dfrac{dy}{dt}$ which will come in the form of x and $\dfrac{dx}{dt}$. Then we will equate both the $\dfrac{dy}{dx}$ and hence, we will get the value of $\dfrac{dx}{dt}$. Then we will form an equation in x and t by equating both the equations in which y came in terms of x and in terms of t. then we will put $t=\dfrac{1}{2}$ and obtain the value of x at that point. Then we will keep this value of x and $t=\dfrac{1}{2}$ in $\dfrac{dx}{dt}$ and hence, we will obtain our required answer.
Complete step by step answer:
Now, we have been given that the lamp is 50ft above the ground and the ball is thrown from the same height from a height 30 ft away from the light pole. And we have to calculate the speed of its shadow.
If we draw a figure from the given data, it will look something as follows:
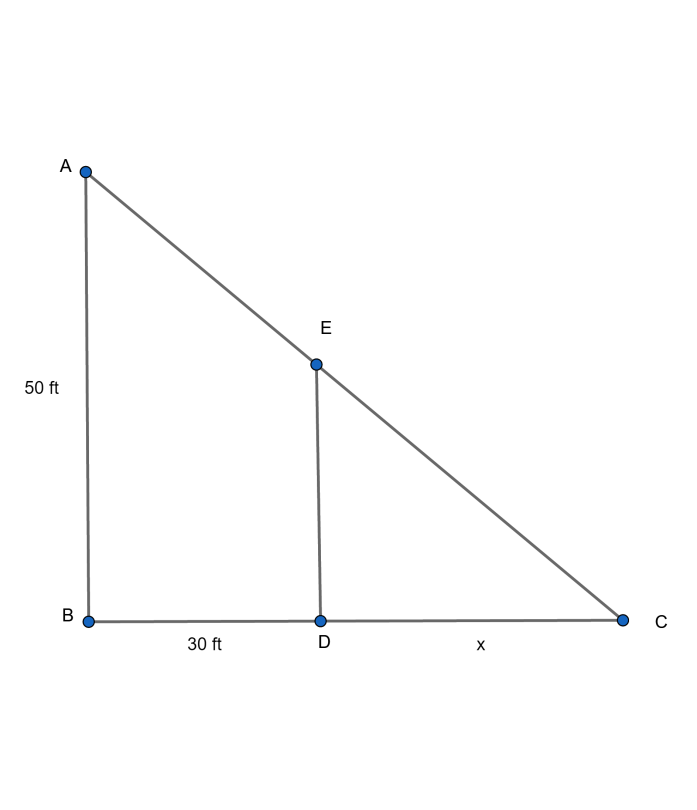
Here, we have taken the lateral distance between the ball and its shadow to be x. Let the angle formed of the triangle be $\alpha $.
Now, since we have to calculate the speed of the shadow, it means that we have to calculate the value of $\dfrac{dx}{dt}$ when $t=\dfrac{1}{2}\sec $.
Now, from the figure, if we take the $\Delta ABC$ , we can see that:
\[\tan \alpha =\dfrac{AB}{BC}\]
Now, if we take the $\Delta EDC$, we can see that:
$\tan \alpha =\dfrac{ED}{DC}$
$\Rightarrow \tan \alpha =\dfrac{50}{30+x}$ …..(i)
Now, let ED=y
Hence, we get:
$\tan \alpha =\dfrac{ED}{DC}$
$\Rightarrow \tan \alpha =\dfrac{y}{x}$ …..(ii)
Now, we have been given that the distance the ball falls down in t sec is given by $s=16{{t}^{2}}$.
Hence, the value of ED will be the difference of 50 and s.
Hence, we can say that:
$\begin{align}
& y=50-s \\
& \Rightarrow y=50-16{{t}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Now, if we differentiate this equation both sides with respect to t, we will get:
$\begin{align}
& y=50-16{{t}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=0-16.2.t \\
\end{align}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=-32t$ …..(iii)
Now, if we see the equations (i) and (ii), we can see that:
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{y}{x}=\dfrac{50}{30+x} \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{50}{30+x}x \\
\end{align}$
Now, if we differentiate this equation both sides with respect to t we will get:
$\begin{align}
& y=\dfrac{50x}{30+x} \\
& \text{Using quotient rule, we get:} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=\dfrac{\left( 30+x \right).50.\dfrac{dx}{dt}-50x\left( 0+1.\dfrac{dx}{dt} \right)}{{{\left( 30+x \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=\dfrac{1500+50x-50x}{{{\left( 30+x \right)}^{2}}}.\dfrac{dx}{dt} \\
\end{align}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=\dfrac{1500}{{{\left( 30+x \right)}^{2}}}.\dfrac{dx}{dt}$ …..(iv)
Now, if see the equations (iii) and (iv), we can see that:
$\begin{align}
& -32t=\dfrac{1500}{{{\left( 30+x \right)}^{2}}}.\dfrac{dx}{dt} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dx}{dt}=-32t\dfrac{{{\left( 30+x \right)}^{2}}}{1500} \\
\end{align}$
Now, as mentioned above, we need to find $\dfrac{dx}{dt}$ when t=$\dfrac{1}{2}$ sec.
For, that, we also need to find the value of x at that moment.
We can obtain it as follows:
We established above that:
$\begin{align}
& y=50-16{{t}^{2}} \\
& y=\dfrac{50}{30+x}x \\
\end{align}$
Hence, we get:
\[\begin{align}
& 50-16{{t}^{2}}=\dfrac{50}{30+x}x \\
& \text{Putting t=}\dfrac{1}{2}, \\
& \Rightarrow 50-16{{\left( \dfrac{1}{2} \right)}^{2}}=\dfrac{50x}{30+x} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 50-4=\dfrac{50x}{30+x} \\
& \Rightarrow 46=\dfrac{50x}{30+x} \\
& \Rightarrow 1380+46x=50x \\
& \Rightarrow 4x=1380 \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{1380}{4}=345 \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, putting t=$\dfrac{1}{2}$ and x=345 in $\dfrac{dx}{dt}$ we get:
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{dx}{dt}=-32t\dfrac{{{\left( 30+x \right)}^{2}}}{1500} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dx}{dt}=-32\left( \dfrac{1}{2} \right)\dfrac{{{\left( 30+345 \right)}^{2}}}{1500} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dx}{dt}=-16.\dfrac{{{\left( 375 \right)}^{2}}}{1500} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dx}{dt}=-16.\dfrac{140625}{1500} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dx}{dt}=-\dfrac{2250000}{1500} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dx}{dt}=-1500 \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, the required answer is -1500ft/sec.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: We here calculated $\dfrac{dy}{dx}$ two times and equated them to obtain $\dfrac{dx}{dt}$. But we could have also obtained the equation \[50-16{{t}^{2}}=\dfrac{50}{30+x}x\] first and then directly calculated $\dfrac{dx}{dt}$. But as this equation is complicated, we didn’t do this as this will increase the scope of committing a mistake and hence it will result in a wrong answer. Thus, we went for the intermediate approach of calculating $\dfrac{dy}{dx}$.
Complete step by step answer:
Now, we have been given that the lamp is 50ft above the ground and the ball is thrown from the same height from a height 30 ft away from the light pole. And we have to calculate the speed of its shadow.
If we draw a figure from the given data, it will look something as follows:

Here, we have taken the lateral distance between the ball and its shadow to be x. Let the angle formed of the triangle be $\alpha $.
Now, since we have to calculate the speed of the shadow, it means that we have to calculate the value of $\dfrac{dx}{dt}$ when $t=\dfrac{1}{2}\sec $.
Now, from the figure, if we take the $\Delta ABC$ , we can see that:
\[\tan \alpha =\dfrac{AB}{BC}\]
Now, if we take the $\Delta EDC$, we can see that:
$\tan \alpha =\dfrac{ED}{DC}$
$\Rightarrow \tan \alpha =\dfrac{50}{30+x}$ …..(i)
Now, let ED=y
Hence, we get:
$\tan \alpha =\dfrac{ED}{DC}$
$\Rightarrow \tan \alpha =\dfrac{y}{x}$ …..(ii)
Now, we have been given that the distance the ball falls down in t sec is given by $s=16{{t}^{2}}$.
Hence, the value of ED will be the difference of 50 and s.
Hence, we can say that:
$\begin{align}
& y=50-s \\
& \Rightarrow y=50-16{{t}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Now, if we differentiate this equation both sides with respect to t, we will get:
$\begin{align}
& y=50-16{{t}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=0-16.2.t \\
\end{align}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=-32t$ …..(iii)
Now, if we see the equations (i) and (ii), we can see that:
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{y}{x}=\dfrac{50}{30+x} \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{50}{30+x}x \\
\end{align}$
Now, if we differentiate this equation both sides with respect to t we will get:
$\begin{align}
& y=\dfrac{50x}{30+x} \\
& \text{Using quotient rule, we get:} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=\dfrac{\left( 30+x \right).50.\dfrac{dx}{dt}-50x\left( 0+1.\dfrac{dx}{dt} \right)}{{{\left( 30+x \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=\dfrac{1500+50x-50x}{{{\left( 30+x \right)}^{2}}}.\dfrac{dx}{dt} \\
\end{align}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=\dfrac{1500}{{{\left( 30+x \right)}^{2}}}.\dfrac{dx}{dt}$ …..(iv)
Now, if see the equations (iii) and (iv), we can see that:
$\begin{align}
& -32t=\dfrac{1500}{{{\left( 30+x \right)}^{2}}}.\dfrac{dx}{dt} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dx}{dt}=-32t\dfrac{{{\left( 30+x \right)}^{2}}}{1500} \\
\end{align}$
Now, as mentioned above, we need to find $\dfrac{dx}{dt}$ when t=$\dfrac{1}{2}$ sec.
For, that, we also need to find the value of x at that moment.
We can obtain it as follows:
We established above that:
$\begin{align}
& y=50-16{{t}^{2}} \\
& y=\dfrac{50}{30+x}x \\
\end{align}$
Hence, we get:
\[\begin{align}
& 50-16{{t}^{2}}=\dfrac{50}{30+x}x \\
& \text{Putting t=}\dfrac{1}{2}, \\
& \Rightarrow 50-16{{\left( \dfrac{1}{2} \right)}^{2}}=\dfrac{50x}{30+x} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 50-4=\dfrac{50x}{30+x} \\
& \Rightarrow 46=\dfrac{50x}{30+x} \\
& \Rightarrow 1380+46x=50x \\
& \Rightarrow 4x=1380 \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{1380}{4}=345 \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, putting t=$\dfrac{1}{2}$ and x=345 in $\dfrac{dx}{dt}$ we get:
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{dx}{dt}=-32t\dfrac{{{\left( 30+x \right)}^{2}}}{1500} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dx}{dt}=-32\left( \dfrac{1}{2} \right)\dfrac{{{\left( 30+345 \right)}^{2}}}{1500} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dx}{dt}=-16.\dfrac{{{\left( 375 \right)}^{2}}}{1500} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dx}{dt}=-16.\dfrac{140625}{1500} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dx}{dt}=-\dfrac{2250000}{1500} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dx}{dt}=-1500 \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, the required answer is -1500ft/sec.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: We here calculated $\dfrac{dy}{dx}$ two times and equated them to obtain $\dfrac{dx}{dt}$. But we could have also obtained the equation \[50-16{{t}^{2}}=\dfrac{50}{30+x}x\] first and then directly calculated $\dfrac{dx}{dt}$. But as this equation is complicated, we didn’t do this as this will increase the scope of committing a mistake and hence it will result in a wrong answer. Thus, we went for the intermediate approach of calculating $\dfrac{dy}{dx}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




