
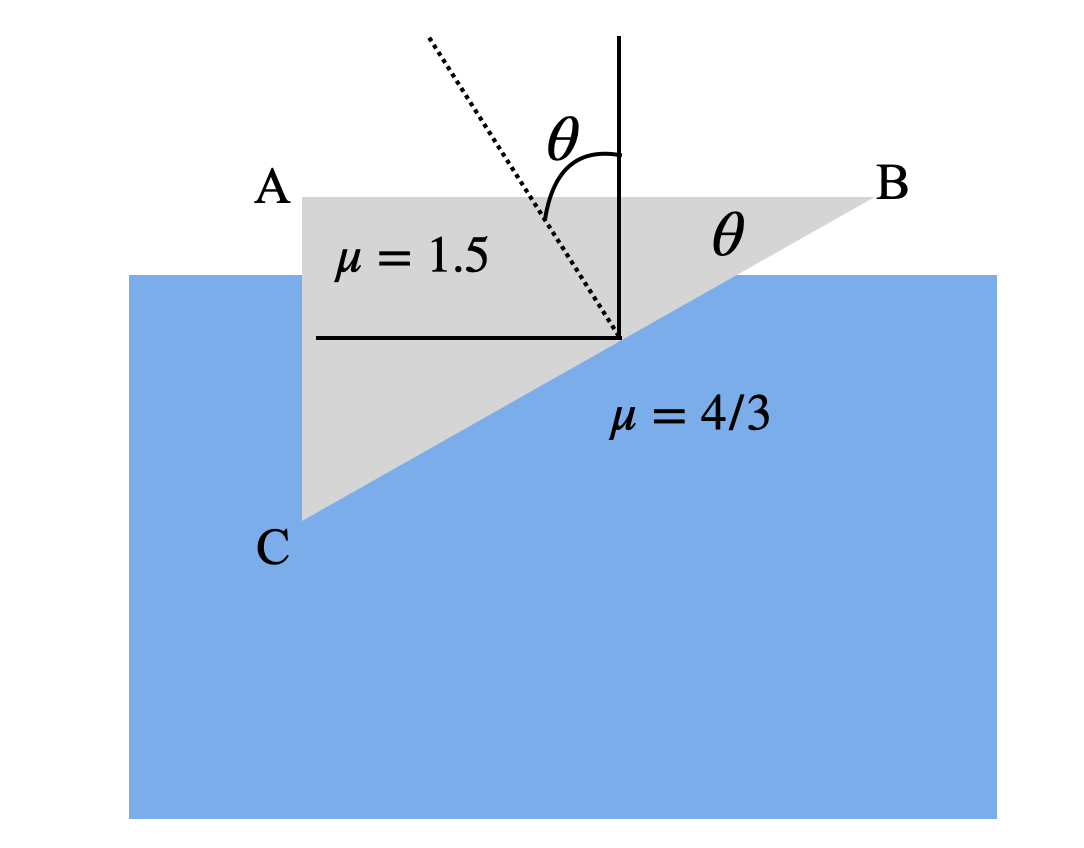
A glass prism of refractive index 1.5 is immersed in water (refractive index 4/3). A light beam is normally projected on the face AB which will reflect on the face BC if
A. $\operatorname{Sin}\theta \ge \dfrac{8}{9}$
B. $\dfrac{2}{3}<\operatorname{Sin}\theta \ge \dfrac{8}{9}$
C. $\operatorname{Sin}\theta \le \dfrac{2}{3}$
D. $\operatorname{Sin}\theta \le \dfrac{8}{9}$

Answer
595.8k+ views
Hint: The relative refractive index of water will be different when we are considering the light is travelling from glass to water. Use the concept of total internal reflecting to determine the angle of incidence. When a light is perpendicular to a surface, it does not go through refraction.
Formula Used:
When a light beam is travelling from medium 1 to medium 2, the relative refractive index is given by,
${{\mu }_{r}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{2}}}{{{\mu }_{1}}}$
Where,
${{\mu }_{1}}$ is the refractive index of medium 1,
${{\mu }_{2}}$ is the refractive index of medium 2.
The condition of total internal reflection is,
The incident angle must be more than,
$\theta \ge {{\theta }_{c}}$
Where,
${{\theta }_{c}}$ is the critical angle of the medium.
Critical angle of the medium is given by,
${{\theta }_{c}}={{\sin }^{-1}}\mu $
Complete step by step answer:
First, let us look at the diagram.
With simple geometry we can find that the incident angle on surface BC is θ.
Now the light beam is travelling from glass to water. Hence, the relative refractive index of the water is,
${{\mu }_{r}}=\dfrac{(\dfrac{4}{3})}{1.5}=\dfrac{8}{9}$
As the light is travelling from the medium with higher refractive index to lower refractive index, total internal reflection is possible.
The critical angle is given by,
${{\theta }_{c}}={{\sin }^{-1}}({{\mu }_{r}})$
$={{\sin }^{-1}}(\dfrac{8}{9})$
When the angle of incidence is more than the critical angle of the surface, total internal reflection is possible.
Hence, we can write that,
${{\theta }_{c}}>{{\sin }^{-1}}(\dfrac{8}{9})$
$\Rightarrow \sin {{\theta }_{c}}>\dfrac{8}{9}$
So, the correct answer is, (A).
Note:
You need to be extremely careful while finding the relative refractive index of the surface. You need to consider the mediums accordingly to determine the correct value. Total internal reflection is a well-known phenomenon. If you dive underwater, then you can only see a circular region through which you can see outside water. Otherwise, you will only see the reflection.
Formula Used:
When a light beam is travelling from medium 1 to medium 2, the relative refractive index is given by,
${{\mu }_{r}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{2}}}{{{\mu }_{1}}}$
Where,
${{\mu }_{1}}$ is the refractive index of medium 1,
${{\mu }_{2}}$ is the refractive index of medium 2.
The condition of total internal reflection is,
The incident angle must be more than,
$\theta \ge {{\theta }_{c}}$
Where,
${{\theta }_{c}}$ is the critical angle of the medium.
Critical angle of the medium is given by,
${{\theta }_{c}}={{\sin }^{-1}}\mu $
Complete step by step answer:
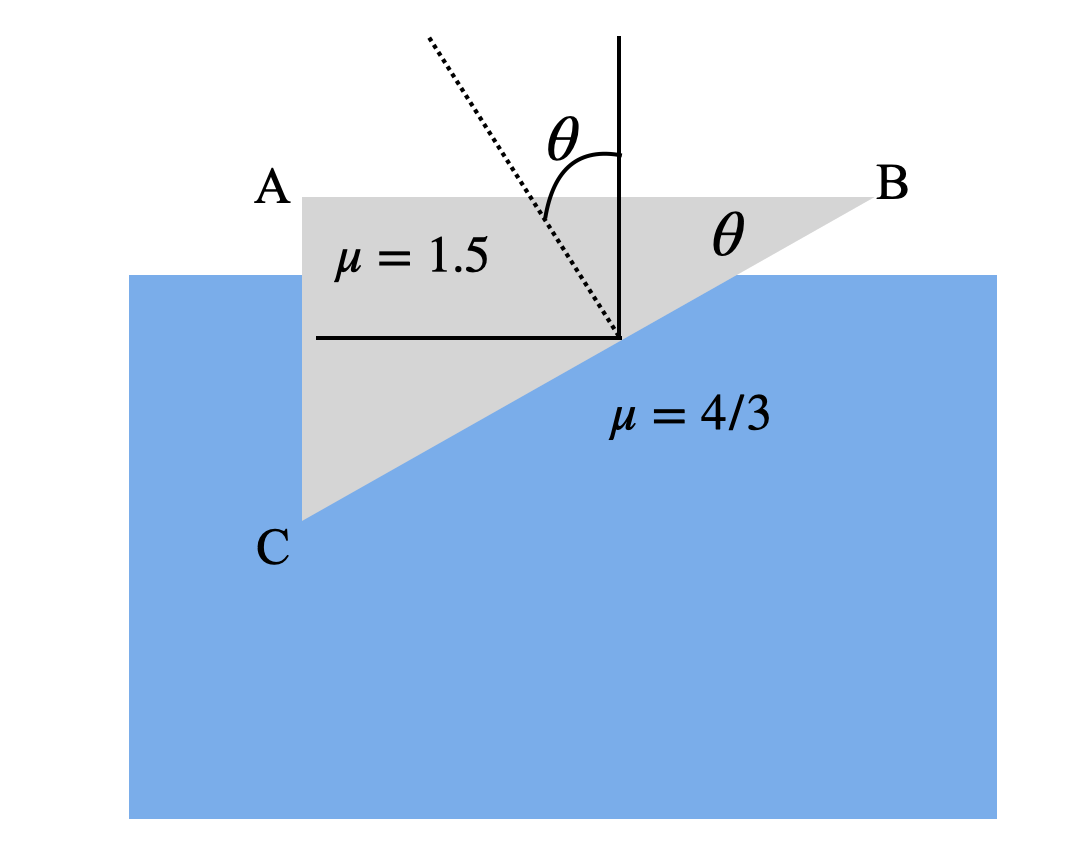
First, let us look at the diagram.

With simple geometry we can find that the incident angle on surface BC is θ.
Now the light beam is travelling from glass to water. Hence, the relative refractive index of the water is,
${{\mu }_{r}}=\dfrac{(\dfrac{4}{3})}{1.5}=\dfrac{8}{9}$
As the light is travelling from the medium with higher refractive index to lower refractive index, total internal reflection is possible.
The critical angle is given by,
${{\theta }_{c}}={{\sin }^{-1}}({{\mu }_{r}})$
$={{\sin }^{-1}}(\dfrac{8}{9})$
When the angle of incidence is more than the critical angle of the surface, total internal reflection is possible.
Hence, we can write that,
${{\theta }_{c}}>{{\sin }^{-1}}(\dfrac{8}{9})$
$\Rightarrow \sin {{\theta }_{c}}>\dfrac{8}{9}$
So, the correct answer is, (A).
Note:
You need to be extremely careful while finding the relative refractive index of the surface. You need to consider the mediums accordingly to determine the correct value. Total internal reflection is a well-known phenomenon. If you dive underwater, then you can only see a circular region through which you can see outside water. Otherwise, you will only see the reflection.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




