
A. Draw a neat labeled diagram of human heart
B. Name the three kinds of blood vessels of the human circulatory system. Write the function of each.
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: The human circulatory system involves three main components- the heart, blood, and blood vessels. The heart is the organ that pumps blood to various parts of the body. Blood flows throughout the body, providing nourishment to various tissues and cells. Humans have a closed circulatory system.
Complete answer:
A. Labeled diagram of the heart along with the various blood vessels and valves
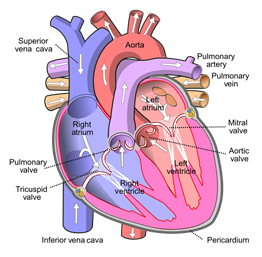
B. The arteries, veins, and capillaries are the three types of blood vessels found in humans.
Arteries are blood vessels with thick walls, three layered walls. It’s because of this feature the arteries can stretch, ensure proper flow of blood, and maintain blood pressure. Arteries usually carry oxygenated blood from the heart to other organs. Pulmonary arteries, however, carry deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs. Arteries branch out to form arterioles.
Capillaries are blood vessels with narrow, thin walls. Capillaries join the arterioles to the venules (veins branch out to form venules). Because these blood vessels have thin, single-layered walls they help in the process of diffusion of nutrients, oxygen, and even wastes.
Veins compared to arteries have larger lumen and thin walls, therefore; the blood pressure is the lowest in the case of veins. Valves present in veins prevent the backward flow of blood. Veins usually carry deoxygenated blood from other organs to the heart. However, the pulmonary veins transport
Note: The pericardium is the membrane that protects the heart. The blood enters the right atrium via the vena cava and the coronary sinus passes through the tricuspid valve to enter the right ventricle. This blood passes the pulmonary valve and enters the pulmonary artery which carries the blood to the lungs to be oxygenated. Pulmonary veins transport this oxygenated blood to the left atrium which enters the left ventricle via a bicuspid valve. The aorta then carries this oxygenated blood pumped out by the left ventricle via the aortic valve to the other organs
Complete answer:
A. Labeled diagram of the heart along with the various blood vessels and valves

B. The arteries, veins, and capillaries are the three types of blood vessels found in humans.
Arteries are blood vessels with thick walls, three layered walls. It’s because of this feature the arteries can stretch, ensure proper flow of blood, and maintain blood pressure. Arteries usually carry oxygenated blood from the heart to other organs. Pulmonary arteries, however, carry deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs. Arteries branch out to form arterioles.
Capillaries are blood vessels with narrow, thin walls. Capillaries join the arterioles to the venules (veins branch out to form venules). Because these blood vessels have thin, single-layered walls they help in the process of diffusion of nutrients, oxygen, and even wastes.
Veins compared to arteries have larger lumen and thin walls, therefore; the blood pressure is the lowest in the case of veins. Valves present in veins prevent the backward flow of blood. Veins usually carry deoxygenated blood from other organs to the heart. However, the pulmonary veins transport
Note: The pericardium is the membrane that protects the heart. The blood enters the right atrium via the vena cava and the coronary sinus passes through the tricuspid valve to enter the right ventricle. This blood passes the pulmonary valve and enters the pulmonary artery which carries the blood to the lungs to be oxygenated. Pulmonary veins transport this oxygenated blood to the left atrium which enters the left ventricle via a bicuspid valve. The aorta then carries this oxygenated blood pumped out by the left ventricle via the aortic valve to the other organs
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




