
What is a DC motor? Explain its construction and working with the help of labelled diagrams.
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint The DC motor is an electrical device which converts the electrical energy into the mechanical energy. The DC motor is fully based on the principle of the magnetic effect of the current. IT consists of the several parts which help to convert the electrical energy into the mechanical energy.
Complete step by step solution
The DC motor can be defined as the machine which converts the electrical energy to the mechanical energy which is based on the magnetic effect. It completely works based on the law of Fleming’s right hand rule. The DC motor consists of the four parts. They are field magnets, armature, split rings and brushes. In common dynamo, it uses the horse shoe magnet but generally the strong electromagnet is used as a field magnet.
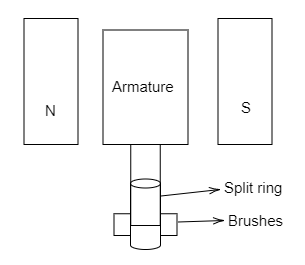
Construction
The armature is the insulated copper wire which wound on the soft iron core which is rotated between the pole pieces using an external magnetic field. The brushes are used to flow the induced current in the armature coil to the internal circuit. The brushes are made up of the carbon material because it slides against the split rings.
Working
When the armature coil is rotated between the field magnet in clockwise direction, the split rings are connected to the brushes. At this point, the current is induced in the circuit and the direction of the current in the circuit can be given by Fleming’s right hand rule. For every half rotation of the armature the direction of the current in the armature keeps changing its direction.
Note For a DC motor, the efficiency can be calculated by dividing the mechanical output power by the electrical input power. For a DC generator, the efficiency can be calculated by dividing the electrical output power by the mechanical input power.
Complete step by step solution
The DC motor can be defined as the machine which converts the electrical energy to the mechanical energy which is based on the magnetic effect. It completely works based on the law of Fleming’s right hand rule. The DC motor consists of the four parts. They are field magnets, armature, split rings and brushes. In common dynamo, it uses the horse shoe magnet but generally the strong electromagnet is used as a field magnet.

Construction
The armature is the insulated copper wire which wound on the soft iron core which is rotated between the pole pieces using an external magnetic field. The brushes are used to flow the induced current in the armature coil to the internal circuit. The brushes are made up of the carbon material because it slides against the split rings.
Working
When the armature coil is rotated between the field magnet in clockwise direction, the split rings are connected to the brushes. At this point, the current is induced in the circuit and the direction of the current in the circuit can be given by Fleming’s right hand rule. For every half rotation of the armature the direction of the current in the armature keeps changing its direction.
Note For a DC motor, the efficiency can be calculated by dividing the mechanical output power by the electrical input power. For a DC generator, the efficiency can be calculated by dividing the electrical output power by the mechanical input power.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




