
A cross was made between pure breeding pea plants, one with round and green seeds and the other with wrinkled and yellow seeds.
a) Write the phenotype of F1 progeny. Give reason for your answer.
b) Write the different types of F2 progeny obtained along with their ratio when F1 progeny was selfed.
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: As pea plants are fast growing and quick to rise, pea plants are a popular choice for Mendel. They still have some obvious features that differ.
Complete Answer:
Pea plants are self-pollinating normally. Pollen grains of anthers on one plant are moved to stigmas from flowers within the same plant during self-pollination. The offspring of two separate parent plants were of concern to Mendel, so he had to avoid self-pollination. In some of the plants in his studies, he extracted the anthers from the flowers. Then he hand-pollinated them with pollen from his preference of other parent plants. Crop shape and colour, flower colour, seed shape and colour, location of pods and flowers on stems, and stem diameter are some of these features.
a) Between wrinkled, yellow seeds and round, green seeds, the cross were created. Two characteristics were taken into consideration in the given cross, so it is a dihybrid cross.
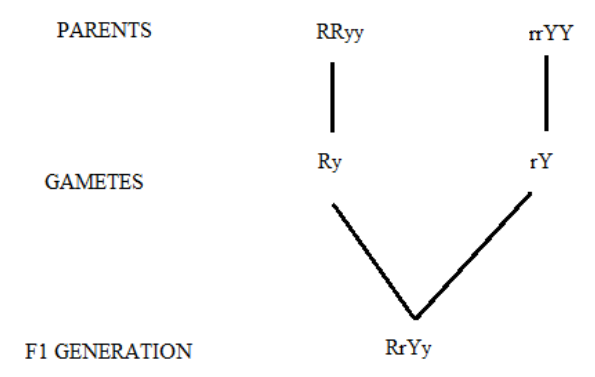
The yellow colour and rounded shape are dominant over the wrinkled form and green colour.
Round and yellow seeds are the phenotypes of all plants.
In the F1 generation, the above cross depicts round and yellow seeds. It happens when the heterozygous disease demonstrates dominant characteristics, while recessive characteristics are silenced.
b)
Round yellow- 9
Round green- 3
Wrinkled yellow- 3
Wrinkled green- 1
Phenotypic ratio- 9:3:3:1
Note: The blending theory of inheritance was popular during Mendel’s period. This is the idea that offspring have a mixture, or mixture, of the features of their parents. Mendel found plants that were not a combination of parents in his own garden.
Complete Answer:
Pea plants are self-pollinating normally. Pollen grains of anthers on one plant are moved to stigmas from flowers within the same plant during self-pollination. The offspring of two separate parent plants were of concern to Mendel, so he had to avoid self-pollination. In some of the plants in his studies, he extracted the anthers from the flowers. Then he hand-pollinated them with pollen from his preference of other parent plants. Crop shape and colour, flower colour, seed shape and colour, location of pods and flowers on stems, and stem diameter are some of these features.
a) Between wrinkled, yellow seeds and round, green seeds, the cross were created. Two characteristics were taken into consideration in the given cross, so it is a dihybrid cross.

The yellow colour and rounded shape are dominant over the wrinkled form and green colour.
Round and yellow seeds are the phenotypes of all plants.
In the F1 generation, the above cross depicts round and yellow seeds. It happens when the heterozygous disease demonstrates dominant characteristics, while recessive characteristics are silenced.
b)
| RY | Ry | rY | ry | |
| RY | RRYY | RRYy | RrYY | RrYy |
| Ry | RRYy | RRyy | RrYy | Rryy |
| rY | RrYY | RrYy | rrYY | rrYy |
| ry | RrYy | Rryy | rrYy | rryy |
Round yellow- 9
Round green- 3
Wrinkled yellow- 3
Wrinkled green- 1
Phenotypic ratio- 9:3:3:1
Note: The blending theory of inheritance was popular during Mendel’s period. This is the idea that offspring have a mixture, or mixture, of the features of their parents. Mendel found plants that were not a combination of parents in his own garden.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




