
A convex lens of focal length 15cm is placed in front of a plane mirror at a distance of 25cm from the mirror. Where on the optical axis from the centre of the lens should a small object be placed such that the final image coincides with the object?
(A) $15cm$ and on the opposite side of the mirror
(B) $15cm$ and between the mirror and lens
(C) $7.5cm$ on the opposite side of the mirror
(D) $7.5cm$ and between the mirror and lens
Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint: The light rays from the object placed at a certain distance from the lens, first undergo refraction, then reflection and finally refraction again to form the final image which coincides with the object. Using properties of lens and mirror and properties of light rays, the final image can be traced.
Complete step by step solution:
A convex lens is thicker in the middle and thinner at the edges; Image formation takes place by refraction of light. It can form real as well as virtual images for different positions of the object.
A plane mirror has a straight surface; image formation takes place by reflection. It can form only virtual images at the same distance as the object behind the mirror.
Let the object be placed at a distance $x\,cm$ from the lens
The image is formed such that the final image coincides with the object. The image forms on the other side of the lens, same side as the mirror.
Let us assume that the object is placed at $15cm$, i.e. the focus.
The rays from the object after refraction become parallel to the optical axis; therefore, when they fall on the mirror they trace their path back. Light rays parallel to the optical axis pass through the focus therefore, after a second refraction, the image is formed on the focus.
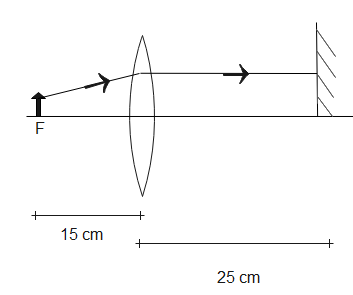
Since the final image coincides with the object when it is kept at the focus, the correct option is (A).
Note:
The object is assumed to be a point object. The final image formed will be real and inverted. For the second refraction, the focal length of the convex lens will be negative, by convention. When light gets reflected from the mirror, as the angle of incidence is zero, angle of reflection becomes zero and the light ray traces back its path.
Complete step by step solution:
A convex lens is thicker in the middle and thinner at the edges; Image formation takes place by refraction of light. It can form real as well as virtual images for different positions of the object.
A plane mirror has a straight surface; image formation takes place by reflection. It can form only virtual images at the same distance as the object behind the mirror.
Let the object be placed at a distance $x\,cm$ from the lens
The image is formed such that the final image coincides with the object. The image forms on the other side of the lens, same side as the mirror.
Let us assume that the object is placed at $15cm$, i.e. the focus.
The rays from the object after refraction become parallel to the optical axis; therefore, when they fall on the mirror they trace their path back. Light rays parallel to the optical axis pass through the focus therefore, after a second refraction, the image is formed on the focus.

Since the final image coincides with the object when it is kept at the focus, the correct option is (A).
Note:
The object is assumed to be a point object. The final image formed will be real and inverted. For the second refraction, the focal length of the convex lens will be negative, by convention. When light gets reflected from the mirror, as the angle of incidence is zero, angle of reflection becomes zero and the light ray traces back its path.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




