
A constant force F is applied in a horizontal direction as shown. The contact force between M and m is N and between m and M’ is N’ then:
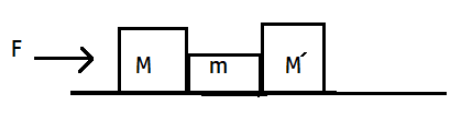
(A) N=N’
(B) N>N’
(C)N’>N
(D) cannot be determined from the given data

Answer
589.2k+ views
Hint: Here we have three bodies of given masses and placed close to each other in contact. The floor is smooth and there is no scope of any frictional force present. A constant force F acts on the first body and we need to find the force between the masses. Newton’s third law of motion can be used here.
Complete step by step answer:
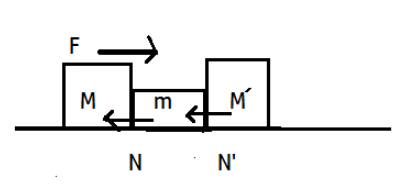
Since F acts on the M and this is constant, if we see the whole system then the total mass of the system is (M+m+M’)
Applying Newton’s second law we get, F=(M+m+M’)a
\[a=\dfrac{F}{M+m+M'}\]
Between M and m contact force is N, applying Newton’s third law
\[N=\dfrac{(m+M')F}{M+m+M'}\]-----(1)
Between m and M’ contact force is N’, applying Newton’s third law \[N'=\dfrac{M'F}{M+m+M'}\]----(2)
Comparing the above two it is visible that numerator of (1) is greater than the numerator of (2) while the denominators are same, so, N>N’
Hence, the correct option is (B).
Note:Newton’s second law states that force applied on a body is equal to the product of the mass of the body and acceleration produced in the body. If the external force is zero, then the acceleration of the body is zero. Newton’s third law states that forces always occur in pairs.
Complete step by step answer:

Since F acts on the M and this is constant, if we see the whole system then the total mass of the system is (M+m+M’)
Applying Newton’s second law we get, F=(M+m+M’)a
\[a=\dfrac{F}{M+m+M'}\]
Between M and m contact force is N, applying Newton’s third law
\[N=\dfrac{(m+M')F}{M+m+M'}\]-----(1)
Between m and M’ contact force is N’, applying Newton’s third law \[N'=\dfrac{M'F}{M+m+M'}\]----(2)
Comparing the above two it is visible that numerator of (1) is greater than the numerator of (2) while the denominators are same, so, N>N’
Hence, the correct option is (B).
Note:Newton’s second law states that force applied on a body is equal to the product of the mass of the body and acceleration produced in the body. If the external force is zero, then the acceleration of the body is zero. Newton’s third law states that forces always occur in pairs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




