
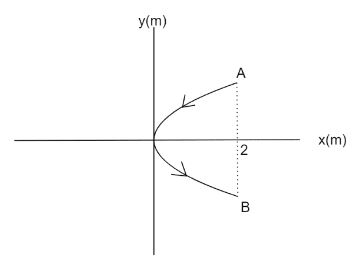
A conducting wire bent in the form of a parabola \[{y^2} = 2x\] carries a current \[i = 2{\text{ A}}\] as shown in figure. This wire is placed in a uniform magnetic field \[\overrightarrow B = 4\overrightarrow k \] Tesla. The magnetic force on the wire in region \[0 < x < 2m\] is (in Newtons)
A. \[ - 16\widehat i\]
B. \[32\widehat i\]
C. \[ - 32\widehat i\]
D. \[16\widehat i\]

Answer
490.2k+ views
Hint:When a current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, then the conductor experiences a force in a direction perpendicular to both the directions of the magnetic field and the direction of current flowing in the conductor. If the magnetic field is uniform, the magnetic force for an arbitrary shape wire can be written as \[F = i\left( {l \times B} \right)\] where \[l\] is the effective length of the arbitrary wire.
Formula used:
Magnetic force on a current carrying conductor,
\[F = \int {dF = } i\left( {\int d l \times B} \right)\]
If the magnetic field is uniform,
Magnetic force can be written as,
\[F = i\left( {l \times B} \right)\]
where \[l\] is the effective length of the arbitrary wire, \[B\] is the uniform magnetic field and \[i\] is the current in the conductor.
Complete step by step answer:
We are given, a conducting wire bent in the form of a parabola \[{y^2} = 2x\] carries a current \[i = 2{\text{ A}}\]. The Magnetic field present is \[\overrightarrow B = 4\overrightarrow k \] Tesla. We need to find the magnetic force on the wire. Magnetic force on a current carrying conductor is given by,
\[F = \int {dF = } i\left( {\int d l \times B} \right)\]
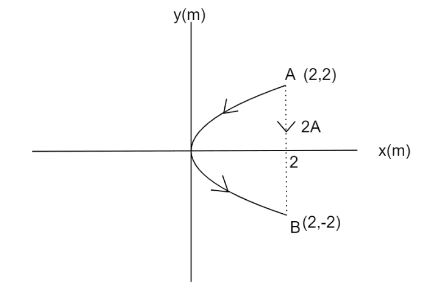
Coordinates of point \[A\] is \[\left( {2,2} \right)\] and coordinates of point \[B\] is \[\left( {2, - 2} \right)\]. Therefore, the effective length of the conducting wire will be length of \[AB\] i.e.,\[4{\text{ m}}\]. Since, the current is flowing from point \[A\] to point \[B\] therefore, current in the imaginary conductor will also flow from point \[A\] to point \[B\] in \[ - \widehat j\] direction. If the magnetic field is uniform, magnetic force becomes,
\[F = i\left( {l \times B} \right)\]
where \[l\] is the effective length of the arbitrary wire.
Substituting the values in the equation,
\[F = 2 \times \left( {\left( { - 4\widehat j} \right) \times \left( {4\widehat k} \right)} \right)\]
After performing the cross product, we get,
\[F = 2 \times - 16\widehat i\]
\[\therefore F = - 32\widehat i\]
Thus, the magnetic force acting on the current-carrying inductor is equal to \[ - 32\widehat i\].
Thus, option C is the correct answer.
Note:Magnetic force on the conductor will be maximum when it is placed perpendicular to the magnetic field and force on the conductor will be zero when it is placed parallel to the magnetic field. Force on a closed current-carrying loop in a uniform magnetic field is also zero.
Formula used:
Magnetic force on a current carrying conductor,
\[F = \int {dF = } i\left( {\int d l \times B} \right)\]
If the magnetic field is uniform,
Magnetic force can be written as,
\[F = i\left( {l \times B} \right)\]
where \[l\] is the effective length of the arbitrary wire, \[B\] is the uniform magnetic field and \[i\] is the current in the conductor.
Complete step by step answer:
We are given, a conducting wire bent in the form of a parabola \[{y^2} = 2x\] carries a current \[i = 2{\text{ A}}\]. The Magnetic field present is \[\overrightarrow B = 4\overrightarrow k \] Tesla. We need to find the magnetic force on the wire. Magnetic force on a current carrying conductor is given by,
\[F = \int {dF = } i\left( {\int d l \times B} \right)\]

Coordinates of point \[A\] is \[\left( {2,2} \right)\] and coordinates of point \[B\] is \[\left( {2, - 2} \right)\]. Therefore, the effective length of the conducting wire will be length of \[AB\] i.e.,\[4{\text{ m}}\]. Since, the current is flowing from point \[A\] to point \[B\] therefore, current in the imaginary conductor will also flow from point \[A\] to point \[B\] in \[ - \widehat j\] direction. If the magnetic field is uniform, magnetic force becomes,
\[F = i\left( {l \times B} \right)\]
where \[l\] is the effective length of the arbitrary wire.
Substituting the values in the equation,
\[F = 2 \times \left( {\left( { - 4\widehat j} \right) \times \left( {4\widehat k} \right)} \right)\]
After performing the cross product, we get,
\[F = 2 \times - 16\widehat i\]
\[\therefore F = - 32\widehat i\]
Thus, the magnetic force acting on the current-carrying inductor is equal to \[ - 32\widehat i\].
Thus, option C is the correct answer.
Note:Magnetic force on the conductor will be maximum when it is placed perpendicular to the magnetic field and force on the conductor will be zero when it is placed parallel to the magnetic field. Force on a closed current-carrying loop in a uniform magnetic field is also zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




