
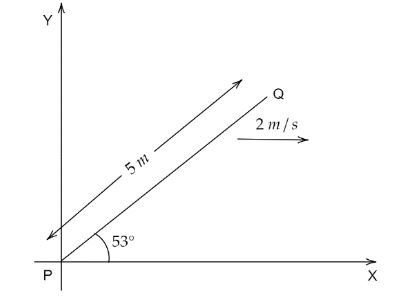
A conducting rod PQ of length $5{\text{ }}m$ oriented as shown in figure is moving with velocity $\left( {2{\text{ }}\dfrac{m}{s}} \right)\widehat i$ without rotation in a uniform magnetic field $\left( {3\widehat j + 4\widehat k} \right){\text{ }}Tesla$. The emf induced in the rod is
A. $32{\text{ }}Volts$
B. ${\text{40 }}Volts$
C. ${\text{50 }}Volts$
D. none

Answer
493.8k+ views
Hint: In the given question, we are given with the magnitude of the length of the rod. We have to convert it to vector form in order to solve the equation. Then by using the formula of induced emf in vector form we will find the answer.
Complete step by step answer:
It is given in the question that the length $l$ of the conducting rod PQ is $5{\text{ }}m$. The velocity $\overrightarrow v $ is given in the X-direction, $\left( {2{\text{ }}\dfrac{m}{s}} \right)\widehat i$. The uniform magnetic field $\overrightarrow B $ associated with the rod PQ is $\left( {3\widehat j + 4\widehat k} \right){\text{ }}Tesla$.
Now, the vector form of the length of the rod is,
$\overrightarrow l = l\cos {53^ \circ }\overrightarrow i + l\sin {53^ \circ }\overrightarrow j $
Substituting the value of length $l = 5{\text{ }}m$
$\overrightarrow l = 5\cos {53^ \circ }\overrightarrow i + 5\sin {53^ \circ }\overrightarrow j $
$\therefore \overrightarrow l = 3\overrightarrow i + 4\overrightarrow j $
The formula for the induced emf in vector form is $\left| {\left( {\overrightarrow v \times \overrightarrow B } \right).\overrightarrow l } \right|$
Firstly, let us solve, $\left( {\overrightarrow v \times \overrightarrow B } \right)$,
Substituting the value of uniform magnetic field $\overrightarrow B $ and velocity $\overrightarrow v $ and getting the cross-product of them as,
$\left( {\overrightarrow v \times \overrightarrow B } \right) = \left[ {2\widehat i \times \left( {3\widehat j + 4\widehat k} \right)} \right] = 6\overrightarrow k - 8\overrightarrow j $
Hence, we got the value of $\left( {\overrightarrow v \times \overrightarrow B } \right) = 6\overrightarrow k - 8\overrightarrow j $
Now, by the dot product of $\left( {\overrightarrow v \times \overrightarrow B } \right)$ and $\overrightarrow l $ will give the emf of the rod,
Thus, $\left( {\overrightarrow v \times \overrightarrow B } \right).\overrightarrow l = \left( {6\overrightarrow k - 8\overrightarrow j } \right).3\overrightarrow i + 4\overrightarrow j = - 32$
Therefore, the emf of the rod is, $\left| {\left( {\overrightarrow v \times \overrightarrow B } \right).\overrightarrow l } \right| = \left| { - 32} \right| = 32$
So, the emf of the rod is $32{\text{ }}Volts$.
Therefore, the correct option is A.
Note:It must be noted that emf is defined as the electric potential developed due to changing magnetic fields. The vector cross-product is involved with the direction vectors which must be calculated carefully. In the case of a dot product of vectors, the direction of the vector's multiplication results in value $1$ and unlike direction corresponds to $0$.
Complete step by step answer:
It is given in the question that the length $l$ of the conducting rod PQ is $5{\text{ }}m$. The velocity $\overrightarrow v $ is given in the X-direction, $\left( {2{\text{ }}\dfrac{m}{s}} \right)\widehat i$. The uniform magnetic field $\overrightarrow B $ associated with the rod PQ is $\left( {3\widehat j + 4\widehat k} \right){\text{ }}Tesla$.
Now, the vector form of the length of the rod is,
$\overrightarrow l = l\cos {53^ \circ }\overrightarrow i + l\sin {53^ \circ }\overrightarrow j $
Substituting the value of length $l = 5{\text{ }}m$
$\overrightarrow l = 5\cos {53^ \circ }\overrightarrow i + 5\sin {53^ \circ }\overrightarrow j $
$\therefore \overrightarrow l = 3\overrightarrow i + 4\overrightarrow j $
The formula for the induced emf in vector form is $\left| {\left( {\overrightarrow v \times \overrightarrow B } \right).\overrightarrow l } \right|$
Firstly, let us solve, $\left( {\overrightarrow v \times \overrightarrow B } \right)$,
Substituting the value of uniform magnetic field $\overrightarrow B $ and velocity $\overrightarrow v $ and getting the cross-product of them as,
$\left( {\overrightarrow v \times \overrightarrow B } \right) = \left[ {2\widehat i \times \left( {3\widehat j + 4\widehat k} \right)} \right] = 6\overrightarrow k - 8\overrightarrow j $
Hence, we got the value of $\left( {\overrightarrow v \times \overrightarrow B } \right) = 6\overrightarrow k - 8\overrightarrow j $
Now, by the dot product of $\left( {\overrightarrow v \times \overrightarrow B } \right)$ and $\overrightarrow l $ will give the emf of the rod,
Thus, $\left( {\overrightarrow v \times \overrightarrow B } \right).\overrightarrow l = \left( {6\overrightarrow k - 8\overrightarrow j } \right).3\overrightarrow i + 4\overrightarrow j = - 32$
Therefore, the emf of the rod is, $\left| {\left( {\overrightarrow v \times \overrightarrow B } \right).\overrightarrow l } \right| = \left| { - 32} \right| = 32$
So, the emf of the rod is $32{\text{ }}Volts$.
Therefore, the correct option is A.
Note:It must be noted that emf is defined as the electric potential developed due to changing magnetic fields. The vector cross-product is involved with the direction vectors which must be calculated carefully. In the case of a dot product of vectors, the direction of the vector's multiplication results in value $1$ and unlike direction corresponds to $0$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




