
A charge Q is placed at each of the two opposite corners of a square. A charge q is placed at each of the other two comers. If the net electric force on Q is zero, then Q/q equals:
A) $ - 2\sqrt 2 $
B) $ - 1$
C) $1$
D) $ - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
Answer
530.6k+ views
Hint: Take the vector sum of the force acting on charge Q. If all the charges were of the same sign, the net force would never be zero for the configuration so we must have opposite charges in the system which suggests a negative value of the ratio.
The force between two charges Q and q: $F = \dfrac{{kQq}}{{{r^2}}}$ where $r$ is the distance between these two charges.
Complete step by step solution:
The net force on charge Q can be zero if the sum of the forces acting on it due to the other three charges must be 0.
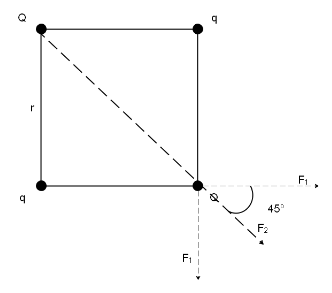
From the figure, the force acting on the charge Q on the bottom-right side in the horizontal direction acts due to ${F_1}$ exerted by charge q that acts only horizontally and the ${F_2}$ exerted by charge Q that acts diagonally.
The horizontal component of ${F_2}$ can then be calculated as ${F_2}\cos 45^\circ = \dfrac{{{F_2}}}{{\sqrt 2 }}$.
To have zero force acting on the charge Q in the horizontal direction, we must have
$\Rightarrow {F_1} + \dfrac{{{F_2}}}{{\sqrt 2 }} = 0$
Placing the value of ${F_1} = \dfrac{{kQq}}{{{r^2}}}$ and ${F_2} = \dfrac{{k{q^2}}}{{{{\left( {\sqrt 2 r} \right)}^2}}}$, we get
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{kQq}}{{{r^2}}} + \dfrac{{k{q^2}}}{{\sqrt 2 {{\left( {\sqrt 2 r} \right)}^2}}} = 0$
Dividing both sides $\dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}}$, we get
$\Rightarrow q + \dfrac{Q}{{2\sqrt 2 }} = 0$
On simplifying, we get
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{Q}{q} = - 2\sqrt 2 $ which corresponds to option (A) .
Note:
Since the total force acting on Q is zero, the force in all directions must be zero. So we can only calculate the ratio of the two charges by balancing forces in one direction and don’t need to calculate the force in the vertical and the horizontal direction. Since the net force has to be zero, the ratio of charges should be negative to balance all the forces in this configuration and we can rule out option (C) since it is positive.
The force between two charges Q and q: $F = \dfrac{{kQq}}{{{r^2}}}$ where $r$ is the distance between these two charges.
Complete step by step solution:
The net force on charge Q can be zero if the sum of the forces acting on it due to the other three charges must be 0.

From the figure, the force acting on the charge Q on the bottom-right side in the horizontal direction acts due to ${F_1}$ exerted by charge q that acts only horizontally and the ${F_2}$ exerted by charge Q that acts diagonally.
The horizontal component of ${F_2}$ can then be calculated as ${F_2}\cos 45^\circ = \dfrac{{{F_2}}}{{\sqrt 2 }}$.
To have zero force acting on the charge Q in the horizontal direction, we must have
$\Rightarrow {F_1} + \dfrac{{{F_2}}}{{\sqrt 2 }} = 0$
Placing the value of ${F_1} = \dfrac{{kQq}}{{{r^2}}}$ and ${F_2} = \dfrac{{k{q^2}}}{{{{\left( {\sqrt 2 r} \right)}^2}}}$, we get
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{kQq}}{{{r^2}}} + \dfrac{{k{q^2}}}{{\sqrt 2 {{\left( {\sqrt 2 r} \right)}^2}}} = 0$
Dividing both sides $\dfrac{{kq}}{{{r^2}}}$, we get
$\Rightarrow q + \dfrac{Q}{{2\sqrt 2 }} = 0$
On simplifying, we get
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{Q}{q} = - 2\sqrt 2 $ which corresponds to option (A) .
Note:
Since the total force acting on Q is zero, the force in all directions must be zero. So we can only calculate the ratio of the two charges by balancing forces in one direction and don’t need to calculate the force in the vertical and the horizontal direction. Since the net force has to be zero, the ratio of charges should be negative to balance all the forces in this configuration and we can rule out option (C) since it is positive.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




