
A carrom board has the queen at the centre. The queen, hit by the striker moves to the front edge, rebounds and goes in the hole behind the striking line. Find the magnitude of displacement of the queen:
(i) from the centre to the front edge
(ii) from the front edge to the hole and
(iii) from the centre of the hole.
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: In this question, we will use the relation of incidence angle and reflection angle; this will help us to find the required displacement. Further, we will discuss the basics of light and law of reflection. We will also see the difference between reflection and refraction for our better understanding.
Formula used:
$\tan i = \tan r$
Complete answer:
As we know by law of reflection, angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection.
$\tan i = \tan r$
By substituting the values in above equation we get:
$\eqalign{& \dfrac{{2 - x}}{x} = \dfrac{4}{2} \cr
& \Rightarrow 4 - 2x = x \cr
& \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{2}{3} \cr} $
We have the following diagram of the carrom board:
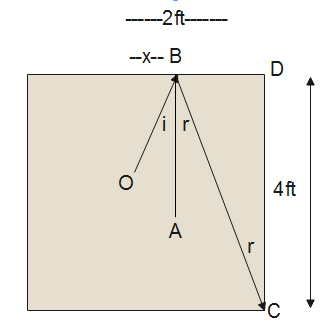
Now, we get the value of BD as:
$BD = 2 - \dfrac{2}{3} = \dfrac{4}{3}$
i).Thus displacement of queen from front edge to hole BC, which is given by:
$B\vec C = \dfrac{{2\hat i}}{3} + 2\hat j$
Now, we calculate the magnitude of displacement, which is given by:
$O\vec B = \sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}} \right)}^2} + {2^2}} = \dfrac{2}{3}\sqrt {10} ft$
ii).Thus, displacement of queen from center to front edge is given by:
$B\vec C = \dfrac{{4\hat i}}{3} - 4\hat j$
Now, we calculate the magnitude of displacement, which is given by:
$B\vec C = \sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{4}{3}} \right)}^2} + {4^2}} = \dfrac{4}{3}\sqrt {10} ft$
iii).Thus, the displacement of queen from the center to hole is given as:
$O\vec C = 2\hat i - 2\hat j$
Now, we calculate the magnitude of displacement, which is given by:
$O\vec C = \sqrt {{{\left( 2 \right)}^2} + {2^2}} = 2\sqrt 2 ft$
Therefore, we get the required result in all the three cases.
Additional information:
As we know that light is known to behave in a very predictable manner, it has dual property. Light can be a wave of particles.
When a beam or ray of light is observed approaching and reflecting off of a flat mirror i.e., smooth surface, then the behavior of the light as it reflects would follow a predictable law which is known as the law of reflection. The law of reflection is defined as the reflection from a smooth surface, the angle of the reflected ray is equal to the angle of the incident ray
Also, we know that light rays change their direction when they reflect off a surface, they move from one transparent medium into another, or can travel through a medium whose composition is continuously changing.
Note:
We should remember the difference between reflection and refraction. Reflection is observed, when a beam or ray of light falling on a smooth surface changes its direction, whereas refraction is defined as the bending of light towards normal when travelling from one medium to another.
Formula used:
$\tan i = \tan r$
Complete answer:
As we know by law of reflection, angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection.
$\tan i = \tan r$
By substituting the values in above equation we get:
$\eqalign{& \dfrac{{2 - x}}{x} = \dfrac{4}{2} \cr
& \Rightarrow 4 - 2x = x \cr
& \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{2}{3} \cr} $
We have the following diagram of the carrom board:

Now, we get the value of BD as:
$BD = 2 - \dfrac{2}{3} = \dfrac{4}{3}$
i).Thus displacement of queen from front edge to hole BC, which is given by:
$B\vec C = \dfrac{{2\hat i}}{3} + 2\hat j$
Now, we calculate the magnitude of displacement, which is given by:
$O\vec B = \sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}} \right)}^2} + {2^2}} = \dfrac{2}{3}\sqrt {10} ft$
ii).Thus, displacement of queen from center to front edge is given by:
$B\vec C = \dfrac{{4\hat i}}{3} - 4\hat j$
Now, we calculate the magnitude of displacement, which is given by:
$B\vec C = \sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{4}{3}} \right)}^2} + {4^2}} = \dfrac{4}{3}\sqrt {10} ft$
iii).Thus, the displacement of queen from the center to hole is given as:
$O\vec C = 2\hat i - 2\hat j$
Now, we calculate the magnitude of displacement, which is given by:
$O\vec C = \sqrt {{{\left( 2 \right)}^2} + {2^2}} = 2\sqrt 2 ft$
Therefore, we get the required result in all the three cases.
Additional information:
As we know that light is known to behave in a very predictable manner, it has dual property. Light can be a wave of particles.
When a beam or ray of light is observed approaching and reflecting off of a flat mirror i.e., smooth surface, then the behavior of the light as it reflects would follow a predictable law which is known as the law of reflection. The law of reflection is defined as the reflection from a smooth surface, the angle of the reflected ray is equal to the angle of the incident ray
Also, we know that light rays change their direction when they reflect off a surface, they move from one transparent medium into another, or can travel through a medium whose composition is continuously changing.
Note:
We should remember the difference between reflection and refraction. Reflection is observed, when a beam or ray of light falling on a smooth surface changes its direction, whereas refraction is defined as the bending of light towards normal when travelling from one medium to another.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




