
A beam of light of wavelength 600 nm from a distant source falls on a single slit 1.0 mm wide and the resulting diffraction pattern is observed on a screen 2m away. What is the distance between the first dark fringes on either side of the central bright fringe?
A). \[1.2cm\]
B). \[1.2mm\]
C). \[2.4cm\]
D). \[2.4mm\]
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: Single slit formula gives the relation between the slit width, wavelength of the light beam, angle of refraction for different values of \[n\]. For smaller values of \[n\], \[\theta \] can be considered as zero. When \[n=1\], the first dark fringe forms on either side of a central bright fringe. By substituting the values given, in the single slit formula, the distance can be found.
Formula used:
\[d\sin \theta =n\lambda \]
Complete step-by-step solution:
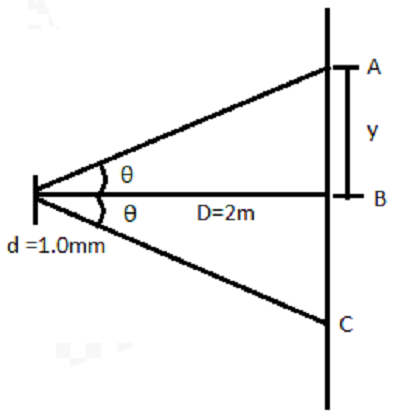
Let’s say, the first dark fringe formed at points A and C, and the central bright fringe at B. Here, the fringes formed on either side of the central fringe are symmetrical.
Hence, angle \[\theta \] is the same for both fringes.
We have single slit diffraction formula,
\[d\sin \theta =n\lambda \] --------- 1
Where,
\[\theta \] is the angle from the center of the wall to the dark fringe
\[n\] is a positive integer \[\left( n=1,2,3..... \right)\]
\[\lambda \] is the wavelength of light
\[d\] is the width of the slit
For small values of \[\theta \], \[\sin \theta \approx \theta \]
The, from figure
\[\theta =\dfrac{y}{D}\] ------- (2)
\[\text{D}\] is the distance from slit to screen.
The distance between points A and B = The distance between B and C \[\text{= y}\]
Then, The distance between points A and C
\[\text{= 2y}\]
Substitute 2 in equation 1.
\[d\dfrac{y}{D}=n\lambda \]
Then,
\[y=\dfrac{n\lambda D}{d}\]
For\[n=1\]
\[y=\dfrac{\lambda D}{d}\] --------- (3)
Given,
\[\lambda =600\times {{10}^{-9}}m\],
\[D=2m\], \[d=1\times {{10}^{-3}}m\]
Substitute the value of \[\lambda \],\[D\] and \[d\] in equation 3
\[y=\dfrac{600\times {{10}^{-9}}\times 2}{1\times {{10}^{-3}}}=1.2mm\]
Therefore, \[\text{Distance AC = 2y = 2}\times \text{1}\text{.2 = 2}\text{.4mm}\]
Hence, the answer is option D.
Note: For the fixed values of \[\lambda \] and \[n\], as the \[d\] gets smaller, \[\theta \] increases and vice versa. From the single slit formula, we can understand that the wave effects are most noticeable when the wave encountering object (here, slits a distance \[d\] apart) is small. Small values of \[d\] give large values of \[\theta \].
Formula used:
\[d\sin \theta =n\lambda \]
Complete step-by-step solution:

Let’s say, the first dark fringe formed at points A and C, and the central bright fringe at B. Here, the fringes formed on either side of the central fringe are symmetrical.
Hence, angle \[\theta \] is the same for both fringes.
We have single slit diffraction formula,
\[d\sin \theta =n\lambda \] --------- 1
Where,
\[\theta \] is the angle from the center of the wall to the dark fringe
\[n\] is a positive integer \[\left( n=1,2,3..... \right)\]
\[\lambda \] is the wavelength of light
\[d\] is the width of the slit
For small values of \[\theta \], \[\sin \theta \approx \theta \]
The, from figure
\[\theta =\dfrac{y}{D}\] ------- (2)
\[\text{D}\] is the distance from slit to screen.
The distance between points A and B = The distance between B and C \[\text{= y}\]
Then, The distance between points A and C
\[\text{= 2y}\]
Substitute 2 in equation 1.
\[d\dfrac{y}{D}=n\lambda \]
Then,
\[y=\dfrac{n\lambda D}{d}\]
For\[n=1\]
\[y=\dfrac{\lambda D}{d}\] --------- (3)
Given,
\[\lambda =600\times {{10}^{-9}}m\],
\[D=2m\], \[d=1\times {{10}^{-3}}m\]
Substitute the value of \[\lambda \],\[D\] and \[d\] in equation 3
\[y=\dfrac{600\times {{10}^{-9}}\times 2}{1\times {{10}^{-3}}}=1.2mm\]
Therefore, \[\text{Distance AC = 2y = 2}\times \text{1}\text{.2 = 2}\text{.4mm}\]
Hence, the answer is option D.
Note: For the fixed values of \[\lambda \] and \[n\], as the \[d\] gets smaller, \[\theta \] increases and vice versa. From the single slit formula, we can understand that the wave effects are most noticeable when the wave encountering object (here, slits a distance \[d\] apart) is small. Small values of \[d\] give large values of \[\theta \].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




