
A beam of light consisting of red, green, and blue colors is incident on a right-angled prism. The reflective indices of the material of the prism for the above red, green, and blue wavelengths are 1.39, 1.44, and 1.47, respectively. The prism will
A. Separate part of the red color from the green and blue color.
B. Separate part of the blue color from the red and green color.
C. Separate all the three colors from one another.
D. Not separate even partially any color from the other two-color.

Answer
588k+ views
Hint: Total internal reflection is a phenomenon in which the ray of light is reflected back into the same medium and this phenomenon occurs only if the angle of incidence is greater than that of the critical angle.
Complete step by step solution:
Step 1:
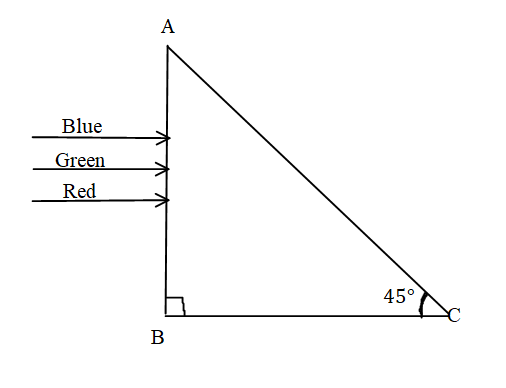
As the rays will fall perpendicular to the surface AB of the prism it will pass through and fall on the surface AC and then get reflected back or get refracted through it.
So, the angle of incidence from the normal of the surface is given by,

The normal angle from surface AC is perpendicular and the angle at which the ray of light is $45^\circ $ from the surface so the angle of incidence of all the rays is $i = 45^\circ $.
Step 2:
Applying Snell’s law for the condition of total internal reflection.
So, Snell’s law is
$\sin i = \dfrac{1}{\mu }$
Step 3:
The angle of incidence is $i = 45^\circ $,
$
\sin i = \dfrac{1}{\mu } \\
\sin 45^\circ = \dfrac{1}{\mu } \\
\mu = \sqrt 2 \\
$
Step 4:
The refractive index is equal to $\mu = \sqrt 2 $ the value of $\sqrt 2 $ is 1.414. So the refractive index of the rays should be more than $\mu = 1.414$ for the total internal reflection to take place.
Step 5:
Let us compare the refractive index of all rays of light given.
Red color beam has a refractive index as ${\mu _r} = 1.39$ since ${\mu _r} < \mu $ therefore red color beam will not show total internal reflection. Blue color beam has a refractive index of ${\mu _b} = 1.44$ since ${\mu _b} > \mu $ therefore blue color beam will show total internal reflection. Green color beam has a refractive index of ${\mu _g} = 1.47$ since ${\mu _g} > \mu $ so the green color beam will show total internal reflection.
So the correct answer is option A, a separate part of the red color from the green and blue color.
Note:
Students should note that whenever the ray of light will fall normal to another surface then the angle of incidence will be $90^\circ $ and also the angle of refraction becomes $90^\circ $ as the light doesn’t get deflected when it falls perpendicular to the surface.
Complete step by step solution:
Step 1:
As the rays will fall perpendicular to the surface AB of the prism it will pass through and fall on the surface AC and then get reflected back or get refracted through it.
So, the angle of incidence from the normal of the surface is given by,

The normal angle from surface AC is perpendicular and the angle at which the ray of light is $45^\circ $ from the surface so the angle of incidence of all the rays is $i = 45^\circ $.
Step 2:
Applying Snell’s law for the condition of total internal reflection.
So, Snell’s law is
$\sin i = \dfrac{1}{\mu }$
Step 3:
The angle of incidence is $i = 45^\circ $,
$
\sin i = \dfrac{1}{\mu } \\
\sin 45^\circ = \dfrac{1}{\mu } \\
\mu = \sqrt 2 \\
$
Step 4:
The refractive index is equal to $\mu = \sqrt 2 $ the value of $\sqrt 2 $ is 1.414. So the refractive index of the rays should be more than $\mu = 1.414$ for the total internal reflection to take place.
Step 5:
Let us compare the refractive index of all rays of light given.
Red color beam has a refractive index as ${\mu _r} = 1.39$ since ${\mu _r} < \mu $ therefore red color beam will not show total internal reflection. Blue color beam has a refractive index of ${\mu _b} = 1.44$ since ${\mu _b} > \mu $ therefore blue color beam will show total internal reflection. Green color beam has a refractive index of ${\mu _g} = 1.47$ since ${\mu _g} > \mu $ so the green color beam will show total internal reflection.
So the correct answer is option A, a separate part of the red color from the green and blue color.
Note:
Students should note that whenever the ray of light will fall normal to another surface then the angle of incidence will be $90^\circ $ and also the angle of refraction becomes $90^\circ $ as the light doesn’t get deflected when it falls perpendicular to the surface.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




