
A beam of light composed of red and green rays is incident obliquely at a point on the face of a rectangular glass slab. When coming out on the opposite parallel face, the red and green rays emerge from:-
(A)Two points and propagating in two different non-parallel directions.
(B)Two points and propagate in two different parallel directions.
(C)One point and propagating in two different directions.
(D)One point and propagate in the same directions.
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint:To solve this question we must have knowledge about dispersion of white light through a prism, a glass slab and splitting of light from air to glass and glass to air.
We should know about different types of angles used in two interfaces.
Complete step by step answer:
Dispersion is the phenomena of splitting up of light into its constituent colours.
In prism: The dispersion of the beam within the glass prism occurs. This is further dispersed in the beam within the glass and we observe the spectrum emerging from the other end of the prism. So if a white light is passed through a triangular prism we will get \[7\]colours on the other side.
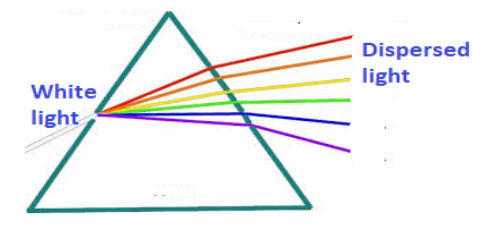
But in rectangular slab, the dispersion happens in the first air-glass interface but in the second interface, since the entering and exiting plane is parallel, the constituent colours diverge and at certain distance it appears to be parallel to each other and sees as a white light.So if we pass red and green rays through the rectangular slab, at first interface dispersion occur and deviate from each other and in second interface it moves in a parallel way after certain distance. So the answer is Option B. Two points and propagating in two different parallel directions.
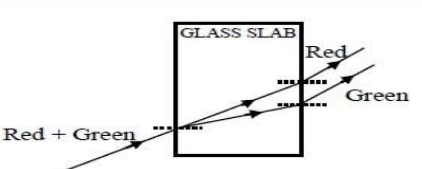
Note:The line drawn normal to the second interface is parallel for each light that is; angle of emergence will be equal for both red and green rays. Even though both the red and green rays have different wavelengths they are going parallel with each other.
We should know about different types of angles used in two interfaces.
Complete step by step answer:
Dispersion is the phenomena of splitting up of light into its constituent colours.
In prism: The dispersion of the beam within the glass prism occurs. This is further dispersed in the beam within the glass and we observe the spectrum emerging from the other end of the prism. So if a white light is passed through a triangular prism we will get \[7\]colours on the other side.

But in rectangular slab, the dispersion happens in the first air-glass interface but in the second interface, since the entering and exiting plane is parallel, the constituent colours diverge and at certain distance it appears to be parallel to each other and sees as a white light.So if we pass red and green rays through the rectangular slab, at first interface dispersion occur and deviate from each other and in second interface it moves in a parallel way after certain distance. So the answer is Option B. Two points and propagating in two different parallel directions.

Note:The line drawn normal to the second interface is parallel for each light that is; angle of emergence will be equal for both red and green rays. Even though both the red and green rays have different wavelengths they are going parallel with each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




