
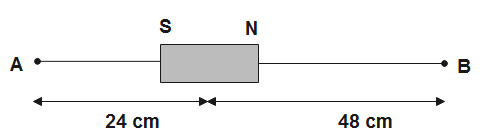
A bar magnet of length $3cm$ has points A and B along its axis at distances of $24cm$ and $48cm$ on the opposite sides. Ratio of magnetic fields at these points will be
(A). 8
(B). $\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{2}}$
(C). 3
(D). 4

Answer
542.1k+ views
Hint: Figure shows a magnet with some magnetic pole strength. Two points are given along its axis at some distance from the poles. The magnetic field depends on the magnetic pole strength, absolute permittivity and the cube of distance from the center of magnet. Substituting the corresponding values we can calculate the magnetic field for each. The ratio is calculated by dividing both the fields.
Formula used:
$B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{2M}{{{r}^{3}}}$
Complete step by step solution:
The magnetic field strength determines the force acting on a magnet of unit pole strength due to the given magnet.
The magnetic field on the axis of a bar magnet is given by-
$B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{2M}{{{r}^{3}}}$ - (1)
Here, $B$ is the magnetic field
${{\mu }_{0}}$ is the absolute permittivity
$M$ is the magnetic pole strength
$r$ is the distance from the centre of them magnet along the axis
Given distance of point O from the center of magnet is $24cm$ and the distance of point B is $48cm$
From eq (1), the magnetic field at point A will be-
${{B}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{2M}{{{(24)}^{3}}}$ - (2)
From eq 92), the magnetic field at point b will be-
${{B}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{2M}{{{(48)}^{3}}}$ - (3)
Dividing eq (2) and eq (3), we get the ratio of both magnetic fields. Therefore,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{B}_{1}}}{{{B}_{2}}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{2M}{{{(24)}^{3}}}}{\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{2M}{{{(48)}^{3}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{B}_{1}}}{{{B}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{(48)}^{3}}}{{{(24)}^{3}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{B}_{1}}}{{{B}_{2}}}=8 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the ratio of magnetic fields at point A and point B is 8. Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note: The magnetic pole strength of both north and south is the same as they are part of the same magnet. The dipole moment of a magnetic is the product of magnetic pole strength and the distance between the poles. The direction of dipole moment is from north to south.
Formula used:
$B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{2M}{{{r}^{3}}}$
Complete step by step solution:
The magnetic field strength determines the force acting on a magnet of unit pole strength due to the given magnet.
The magnetic field on the axis of a bar magnet is given by-
$B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{2M}{{{r}^{3}}}$ - (1)
Here, $B$ is the magnetic field
${{\mu }_{0}}$ is the absolute permittivity
$M$ is the magnetic pole strength
$r$ is the distance from the centre of them magnet along the axis
Given distance of point O from the center of magnet is $24cm$ and the distance of point B is $48cm$
From eq (1), the magnetic field at point A will be-
${{B}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{2M}{{{(24)}^{3}}}$ - (2)
From eq 92), the magnetic field at point b will be-
${{B}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{2M}{{{(48)}^{3}}}$ - (3)
Dividing eq (2) and eq (3), we get the ratio of both magnetic fields. Therefore,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{B}_{1}}}{{{B}_{2}}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{2M}{{{(24)}^{3}}}}{\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{4\pi }\dfrac{2M}{{{(48)}^{3}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{B}_{1}}}{{{B}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{(48)}^{3}}}{{{(24)}^{3}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{B}_{1}}}{{{B}_{2}}}=8 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the ratio of magnetic fields at point A and point B is 8. Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note: The magnetic pole strength of both north and south is the same as they are part of the same magnet. The dipole moment of a magnetic is the product of magnetic pole strength and the distance between the poles. The direction of dipole moment is from north to south.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




