
A balloon of mass M with a light rope and monkey of mass m are at rest in mid-air. If the monkey climbs up the rope and reaches the top of the rope, the distance by which the balloon descends will be- (Total length of the rope is L)
A. \[\dfrac{{mL}}{{{{(m + M)}^2}}}\]
B. $\dfrac{{mL}}{{m + M}}$
C. $\dfrac{{(m + M)L}}{m}$
D. $\dfrac{{(m + M)}}{{mL}}$

Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint:To solve this question we must have knowledge of centre of mass. For now, we can understand it as a point on or outside the body where we can say the whole mass of the system is concentrated. We already know the centre of mass of a system remains in the same state until an external force is applied. So, calculate \[{Y_{cm}}\] and in this case \[{Y_{cm}}\] will not change, apply this condition and you will get the answer.
Formula to calculate centre of mass of a body is \[Ycm = \dfrac{{\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^n {MiYi} }}{{\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^n {Mi} }}\]
Here,
\[Mi = \]Mass of $i$ th part
\[Yi = \] position of $i$ th particle from reference point.
Complete step-by-step solution:
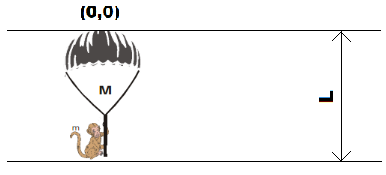
Consider the above figure with the length of rope of ‘L’ and origin at top.
Since there is no external force acting on the system, the position of \[{Y_{cm}}\] will remain the same.
So, using the above given formula \[Ycm = \dfrac{{\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^n {MiYi} }}{{\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^n {Mi} }}\]
${Y_{cm}} = \dfrac{{M \times 0 + m \times ( - L)}}{{M + m}}$
$ \Rightarrow {Y_{cm}} = \dfrac{{ - mL}}{{M + m}}$
Now, we know monkeys climbed by ‘L’ and now both masses are concentrated at the same place and a new centre of mass has been created. So, now in order to position the centre of mass at the previous place whole system will descend by $\dfrac{{mL}}{{M + m}}$
Note:- This was a case of single dimension but in two or three dimensions the same calculation is performed for each to obtain coordinates of centre of mass. Newton laws of motion are also generalised for point objects. So, its generalised expressions show results for a point object or centre of mass. Calculations in mechanics are simplified when things are calculated with respect to centre of mass.
Formula to calculate centre of mass of a body is \[Ycm = \dfrac{{\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^n {MiYi} }}{{\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^n {Mi} }}\]
Here,
\[Mi = \]Mass of $i$ th part
\[Yi = \] position of $i$ th particle from reference point.
Complete step-by-step solution:

Consider the above figure with the length of rope of ‘L’ and origin at top.
Since there is no external force acting on the system, the position of \[{Y_{cm}}\] will remain the same.
So, using the above given formula \[Ycm = \dfrac{{\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^n {MiYi} }}{{\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^n {Mi} }}\]
${Y_{cm}} = \dfrac{{M \times 0 + m \times ( - L)}}{{M + m}}$
$ \Rightarrow {Y_{cm}} = \dfrac{{ - mL}}{{M + m}}$
Now, we know monkeys climbed by ‘L’ and now both masses are concentrated at the same place and a new centre of mass has been created. So, now in order to position the centre of mass at the previous place whole system will descend by $\dfrac{{mL}}{{M + m}}$
Note:- This was a case of single dimension but in two or three dimensions the same calculation is performed for each to obtain coordinates of centre of mass. Newton laws of motion are also generalised for point objects. So, its generalised expressions show results for a point object or centre of mass. Calculations in mechanics are simplified when things are calculated with respect to centre of mass.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




