
(a) Account for the following:
(i) Acidic character increases from HF to HI.
(ii) There is a large difference between melting and boiling points of oxygen and sulphur.
(iii) Nitrogen does not form pentahalide.
(b) Draw the structures of the following
(i) \[{\text{Cl}}{{\text{F}}_3}\]
(ii) \[{\text{Xe}}{{\text{F}}_4}\]
Answer
522.5k+ views
Hint: (a)
(i) Acid strength increases with decrease in bond dissociation energy.
(ii) Atomic size, electronegativity and atomicity affects melting and boiling points.
(iii) Lack of d orbitals in the valence shell.
(b)\[{\text{Cl}}{{\text{F}}_3}\] and \[{\text{Xe}}{{\text{F}}_4}\] have T shaped and square planar geometry respectively.
Complete answer:
(i) The acidic strength of the hydrohalic acids increase from HF because the stability of the acids decrease from HF to HI on account of decrease in bond dissociation enthalpy of H−X bond from HF to HI.
> With increase in the size of the halogen atom, bond dissociation energy decreases from HF to HI. The ease with which protons can be donated increases from HF to HI. Hence, acidic character increases from HF to HI.
(ii) Oxygen atoms are smaller in size than sulphur atoms. Oxygen is more electronegative than sulphur. Also oxygen is a diatomic ($O_2$) molecule whereas sulphur ($S_8$) has eight atoms in the molecule. Due to these factors, there is a large difference between melting and boiling points of oxygen and sulphur.
In the modern periodic table, nitrogen atoms are present in the second period. Hence, nitrogen does not have ‘d’ orbitals. Due to this, in the valence shell of nitrogen, only one s three and p orbitals can be used. This restricts the maximum covalency of nitrogen to four. So nitrogen cannot form pentahalides.
(b)
The structures are as shown below:
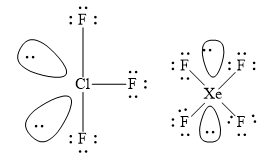
(i) \[{\text{Cl}}{{\text{F}}_3}\] has three bond pairs of electrons and two lone pairs of electrons. The electron pair geometry is trigonal bipyramidal and molecular geometry is T shaped.
(ii) \[{\text{Xe}}{{\text{F}}_4}\] has four bond pairs of electrons and two lone pairs of electrons. The electron pair geometry is octahedral and molecular geometry is square planar.
Note: :The shape of the molecule is determined by the nature of hybridisation. Hybridisation depends on steric numbers. Steric number is the total number of bond pairs and lone pairs of electrons.
(i) Acid strength increases with decrease in bond dissociation energy.
(ii) Atomic size, electronegativity and atomicity affects melting and boiling points.
(iii) Lack of d orbitals in the valence shell.
(b)\[{\text{Cl}}{{\text{F}}_3}\] and \[{\text{Xe}}{{\text{F}}_4}\] have T shaped and square planar geometry respectively.
Complete answer:
(i) The acidic strength of the hydrohalic acids increase from HF because the stability of the acids decrease from HF to HI on account of decrease in bond dissociation enthalpy of H−X bond from HF to HI.
> With increase in the size of the halogen atom, bond dissociation energy decreases from HF to HI. The ease with which protons can be donated increases from HF to HI. Hence, acidic character increases from HF to HI.
(ii) Oxygen atoms are smaller in size than sulphur atoms. Oxygen is more electronegative than sulphur. Also oxygen is a diatomic ($O_2$) molecule whereas sulphur ($S_8$) has eight atoms in the molecule. Due to these factors, there is a large difference between melting and boiling points of oxygen and sulphur.
In the modern periodic table, nitrogen atoms are present in the second period. Hence, nitrogen does not have ‘d’ orbitals. Due to this, in the valence shell of nitrogen, only one s three and p orbitals can be used. This restricts the maximum covalency of nitrogen to four. So nitrogen cannot form pentahalides.
(b)
The structures are as shown below:

(i) \[{\text{Cl}}{{\text{F}}_3}\] has three bond pairs of electrons and two lone pairs of electrons. The electron pair geometry is trigonal bipyramidal and molecular geometry is T shaped.
(ii) \[{\text{Xe}}{{\text{F}}_4}\] has four bond pairs of electrons and two lone pairs of electrons. The electron pair geometry is octahedral and molecular geometry is square planar.
Note: :The shape of the molecule is determined by the nature of hybridisation. Hybridisation depends on steric numbers. Steric number is the total number of bond pairs and lone pairs of electrons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




