
8 The lubricant mucin of saliva is made up of
a) Unsaturated fats
b) Polysaccharides
c) Glycoproteins
d) Phospholipids
Answer
519k+ views
Hint: Saliva is the watery and somewhat frothy substance produced in the mouths of some animals, including humans. It is produced in salivary glands and is $98\%$ water along with electrolytes, mucus, antibacterial compounds and various enzymes. Mucin is the heavily glycosylated protein (glycoconjugates) produced by the epithelial tissues in most animals.
Complete Answer:
Glycoproteins are the principal organic constituents of mucus in saliva. Mucus is the slimy, viscoelastic material which envelopes all the mucosal surfaces of the body. Within the mouth, mucins coat the hard and soft tissues and assists in the lubrication and hydration oral structures. Mucins are high-molecular-weight glycoproteins which share some common features. It includes a peptide core (apomucin) enriched in serine, threonine and proline residues. It also contains carbohydrate side chains (oligosaccharides) that are linked O-glycosidically to threonine or serine. Mature mucins are composed of two distinct regions:
The amino- and carboxy-terminal regions, which are very lightly glycosylated but are rich in cysteines. The cysteine residues assist in forming disulfide linkages within and among the mucin monomers.
A large central region constitutes multiple tandem repeats of 10 to 80 residue sequences. In these sequences, up to half of the amino acids are serine or threonine. This area is saturated with hundreds of O-linked oligosaccharides. N-linked oligosaccharides are also found on mucins, but in less abundance.
The heavy presence of O-glycosylated in mucin gives it a viscous nature and significant role in oral lubrication. The sugars also help mucins bind to surfaces of mouth to protect them from chemicals, wear and tear, and microbes.
Note:
The salivary glycoproteins involved in the lubrication of the mouth include proline-rich glycoprotein and mucins. Proline-rich glycoproteins, primarily secreted byPA glands, are N-glycosylated. Oligosaccharides make up to $50\%$ of their weight and are responsible for their lubricating properties. Other functions of salivary glycoproteins include binding to oral pathogens and eliminating them from the oral cavity; proline-rich glycoproteins, mucins and salivary agglutinins have an important role in these functions.
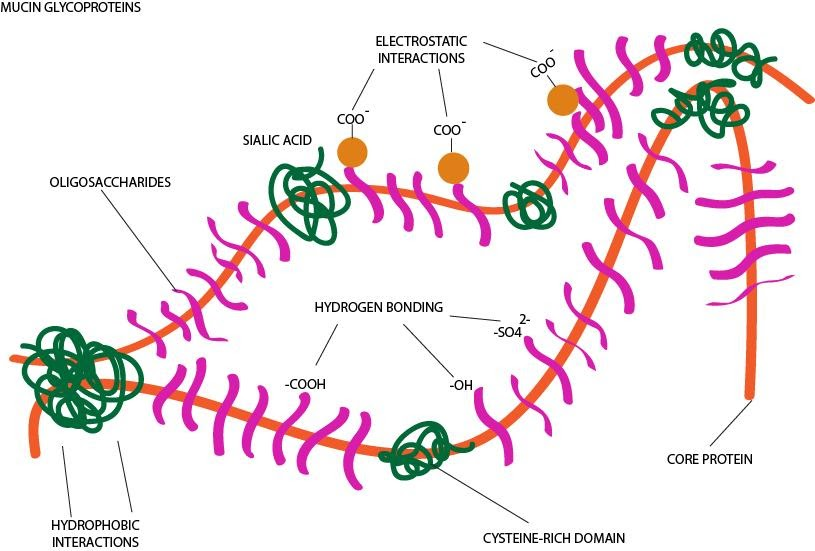
Figure 1: Mucin glycoprotein
Complete Answer:
Glycoproteins are the principal organic constituents of mucus in saliva. Mucus is the slimy, viscoelastic material which envelopes all the mucosal surfaces of the body. Within the mouth, mucins coat the hard and soft tissues and assists in the lubrication and hydration oral structures. Mucins are high-molecular-weight glycoproteins which share some common features. It includes a peptide core (apomucin) enriched in serine, threonine and proline residues. It also contains carbohydrate side chains (oligosaccharides) that are linked O-glycosidically to threonine or serine. Mature mucins are composed of two distinct regions:
The amino- and carboxy-terminal regions, which are very lightly glycosylated but are rich in cysteines. The cysteine residues assist in forming disulfide linkages within and among the mucin monomers.
A large central region constitutes multiple tandem repeats of 10 to 80 residue sequences. In these sequences, up to half of the amino acids are serine or threonine. This area is saturated with hundreds of O-linked oligosaccharides. N-linked oligosaccharides are also found on mucins, but in less abundance.
The heavy presence of O-glycosylated in mucin gives it a viscous nature and significant role in oral lubrication. The sugars also help mucins bind to surfaces of mouth to protect them from chemicals, wear and tear, and microbes.
Note:
The salivary glycoproteins involved in the lubrication of the mouth include proline-rich glycoprotein and mucins. Proline-rich glycoproteins, primarily secreted byPA glands, are N-glycosylated. Oligosaccharides make up to $50\%$ of their weight and are responsible for their lubricating properties. Other functions of salivary glycoproteins include binding to oral pathogens and eliminating them from the oral cavity; proline-rich glycoproteins, mucins and salivary agglutinins have an important role in these functions.

Figure 1: Mucin glycoprotein
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




