




Key Physics Concepts: Understanding Rainfall and Its Importance
A drought is a period of time when a region or area has below-average precipitation. Lack of sufficient precipitation, whether rain or snow, can result in lessened stream flow, crop damage, decreased soil moisture or groundwater, as well as general water scarcity. Droughts are the second most costly weather event after hurricanes.
What Happens If There is No Rainfall?
A drought is a time when the weather is drier than usual and there are issues with the water supply. Although the amount of precipitation in a specific region changes from year to year, on average, it remains stable across time. The average annual precipitation in the Southwest's deserts is less than 3 inches. In comparison, the Northwest receives more than 150 inches of precipitation per year on average.
The soils might dry out and plants can die when there is little or no rain. When rainfall falls below average for several weeks to years, stream flows decrease, lake and reservoir levels drop and the depth of water in wells rises. The dry spell may turn into a drought if dry weather continues, and water supply issues arise.
Potential Effects of Climate Change
Change in Rainfall Pattern: Since the 1950s, a decrease in monsoon rainfall has already been noted. India's summer monsoon will become extremely unpredictable with a 2°C increase in global average temperatures. By the end of the cantury, it is predicted that an exceptionally rainy monsoon, which currently has a probability of happening only once every 100 years, will happen every ten years with a 4°C warming. Wet years are predicted to be wetter, and dry years to be dryer.
Drought: There is evidence that certain regions of South Asia have become drier and more drought-prone since the 1970s. Droughts have serious repercussions. More than half of India's cropland was damaged by droughts in 1987 and 2002–2003, which significantly reduced crop production. In some regions, particularly in north-western India, Jharkhand, Orissa and Chhattisgarh, droughts are anticipated to occur more frequently. By the 2040s, excessive heat is predicted to have a significant negative impact on crop output.
Why doesn’t Drought End When It Rains?
Any type of rain will help with the drought. Even though it will not end the drought, one precipitation could bring about some short-term relief. Light to moderate showers will likely only have a temporary, cosmetic-relieving effect. Most of the rain from thunderstorms will run off into drainage systms and streams rather than soak into the ground because they frequently produce large amounts of precipitation in a short period of time.
Rains that fall heavily are the best treatment for drought. Infiltration of water into the soil recharges groundwater, which in turn maintains vegetation and supplies streams during dry spells. A single soaking rain will end drought conditions for good, but it may take several such storms spread out over several months to end the drought and bring conditions back into the usual range.
Types of Droughts
In general, a drought occurs when there is not enough water available to meet all the demands of both people and the environment. When people think of drought, they frequently picture cracked dirt, dried-up streams, parched crops, or unusually low water levels. Over-extraction of groundwater during droughts severely destroys water access in many vulnerable rural areas.
Meteorological Drought: Meteorological drought is known as the amount of dryness and the length of the dry period.
Hydrological Drought: Hydrological drought is known as the decline in precipitation that impacts groundwater recharge, streamflow, soil moisture and levels in reservoirs and lakes.
Agricultural Drought: Agricultural drought occurs when water supplies are insufficient to meet crop-related water demands, which is the situation that worries farmers the most. Various factors, such as insufficient precipitation, the timing of water availability, restricted access to water supplies or increased water demands from the sector, can cause agricultural droughts.
Socioeconomic Droughts: Socioeconomic droughts assist us in determining the negative social and economic effects of a water resource constraint.
Anthropogenic Drought: Anthropogenic drought has been postulated by scientists based on all types of droughts.
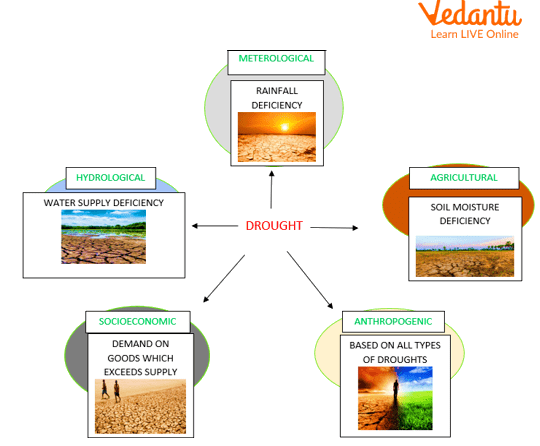
Types of Droughts
Drought Management
Campaigns for education and information.
Urgent conservation initiatives.
Service constraints for water.
Restrictions on water use for non-essential purposes.
Restriction on certain commercial uses.
Emergency pricing for a drought.
Programmes for rationing water.
Augmentation
Interesting Facts
On Venus, and other moons and planets, rain is made of sulfuric acid or methane.
On a planet 5,000 light years away, scientists found raindrops made of iron rather than water.
Antarctica gets only 6.5 inches of rain or snow per year, making it the continent with the lowest annual rainfall by far.
In Africa, the drought affected 150 million people from 1969 to 1980.
Key Features
A lack of precipitation over a lengthy period (often a season or more), resulting in a water deficit, is referred to as a drought.
When rainfall falls below average for several weeks to years, stream flows decrease, lake and reservoir levels drop and the depth of water in wells rises.
The potential effect of climate change can lead to changes in monsoons and drought.
FAQs on What Happens When There’s No Rainfall?
1. What happens in a region if it does not rain for a long time?
If it does not rain for a long period in a region, the area faces a condition known as a drought. The soil becomes dry and hard, making it difficult for plants to grow. The water level in wells, ponds, and lakes goes down, and some may even dry up completely, leading to a severe scarcity of water for drinking, farming, and daily life.
2. How does a lack of rain affect the soil and plants?
A lack of rain has several direct effects on soil and plants:
- Soil: The soil loses its moisture, becomes compacted, and may crack. It becomes infertile as essential nutrients cannot be absorbed by dry roots.
- Plants: Plants begin to wilt and die because they cannot get water through their roots, a process essential for photosynthesis. This leads to the failure of crops and the loss of green vegetation.
3. What are the main consequences of having no rain on animals and human life?
When there is no rain for an extended period, both animals and humans suffer greatly. Animals may die or be forced to migrate in search of water and food. For humans, it leads to crop failure, resulting in food shortages and financial loss for farmers. It also causes a severe scarcity of drinking water, impacting health, sanitation, and industries like power generation that rely on water.
4. How does a prolonged lack of rain affect the level of groundwater?
Groundwater is the water stored beneath the Earth's surface. It is naturally replenished by rainwater that seeps into the ground, a process called infiltration. When there is no rain for a long time, this replenishment stops. At the same time, people draw more groundwater from wells and tube wells to cope with the surface water scarcity. This combination of no new water coming in and increased usage causes the groundwater level to drop significantly.
5. What is the chain of events that leads from no rain to a possible food shortage?
A lack of rain triggers a direct chain reaction that can lead to food shortages. It begins with 1. Scarcity of water for irrigation. This leads to 2. Crop failure, as plants cannot grow without water. The failure of crops results in 3. Reduced food supply in the market. Finally, with less food available and high demand, it can lead to a 4. Food shortage and an increase in food prices.
6. Why is rainwater harvesting an important practice, especially in areas with infrequent rain?
Rainwater harvesting is the simple process of collecting and storing rainwater for later use. It is crucial because it helps counter the problems caused by a lack of rain. By capturing water when it does rain, communities can:
- Increase water availability: Stored water can be used for drinking, irrigation, and other needs during dry periods.
- Recharge groundwater: Directing rainwater into the ground helps raise the depleted groundwater levels.
- Reduce soil erosion: It prevents rainwater from running off and washing away topsoil.
7. Besides farming, what other essential activities are impacted by a severe lack of rain?
While agriculture is the most visibly affected, a severe lack of rain impacts many other essential activities. Hydroelectric power generation often decreases because dams do not have enough water to run turbines. Industries that require large amounts of water for cooling or processing, like manufacturing plants, may have to slow down or halt production. It also affects public health due to a lack of clean water for sanitation and hygiene.





































