




How Do Coefficients Work? Practical Examples Explained
A variable of a single term or the terms of a polynomial is multiplied by a number or an alphabet to produce a coefficient. For instance, the coefficient in the expression \[{\rm{7x}}\] is 7. In the expression \[{\rm{3xy}}\], x's coefficient is \[{\rm{3y}}\].
What is a Coefficient in Math?
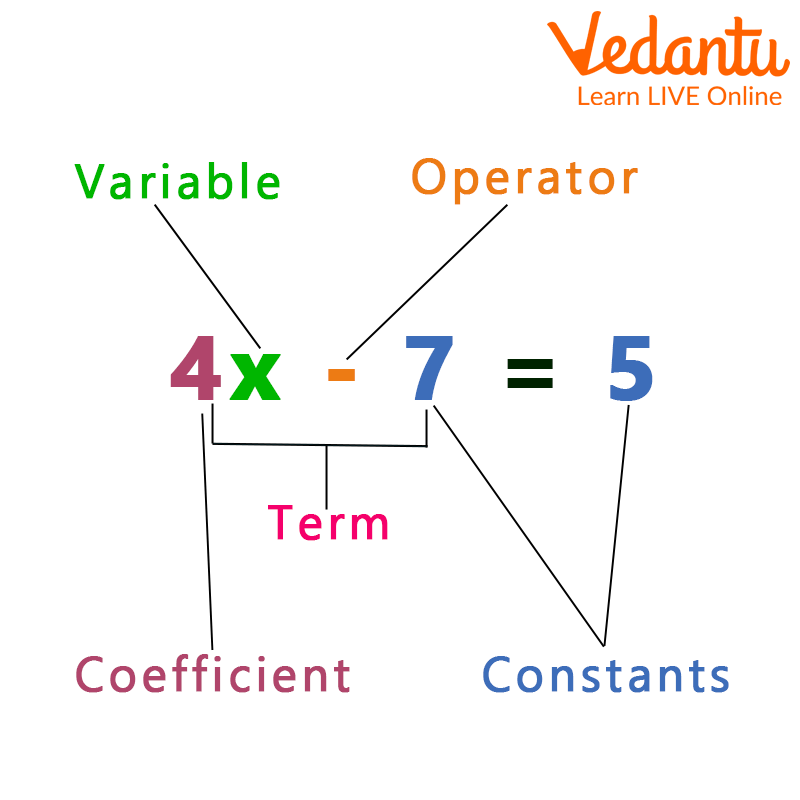
A coefficient in mathematics is a value that is multiplied by the variable in a single term or the terms of a polynomial. It can be a number or any symbol that represents a constant value. It is typically a number, however in other expressions a letter might be used instead. In the formula: \[{\rm{a}}{{\rm{x}}^{\rm{2}}} + {\rm{bx}} + {\rm{c}}\], for instance, x is the variable and a and b are the coefficients.
Coefficient in an Equation
Numerical Coefficient with Example:
A set amount multiplied by a variable is what is referred to as a numerical coefficient. Take into account the supplied monomial \[{\rm{7abc}}\]. 7 is the result for the coefficient of multiplying the fixed integer by the variables \[{\rm{abc}}\]. Therefore, the word "\[{\rm{7abc}}\]" has a numerical coefficient of "7."
Coefficient in Algebra:
A multiplier that multiplies two variables.
As an illustration, \[{\rm{6z}}\] stands for 6 times \[z\]. Since z is a variable, 6 is a coefficient.
For variables without a value, the coefficient is 1.
For instance, \[{\rm{x}}\] is really \[{\rm{1x}}\].
Coefficient of a Term
Follow the instructions below to determine a term's coefficient for a variable:
Step 1: Enclose the variable and its corresponding power, whose coefficient we are determining.
Step 2: Ignore that variable and take into account any other numbers or variables it was used with. The coefficient will then be that.
Coefficient in an Equation
Tips and Tricks on Coefficient:
When using coefficients, keep the following things in mind.
A variable always has a coefficient associated with it.
If a variable's coefficient is 1, then it has no associated value.
Conclusion
In mathematics, a coefficient is the multiplicative factor of an expression, a polynomial term, or a series term. Although it might be any sentence, it typically appears as a number. If the coefficients are variables in and of themselves, they may also be known as parameters.
Coefficient Examples:
Example 1: Find the coefficient of the term \[x^2\] in the formula \[a{x^2} + bx + c\].
Ans: In the statement above, we can see that with \[{{x^2}}\] a is written, thus ‘a’ will be its coefficient.
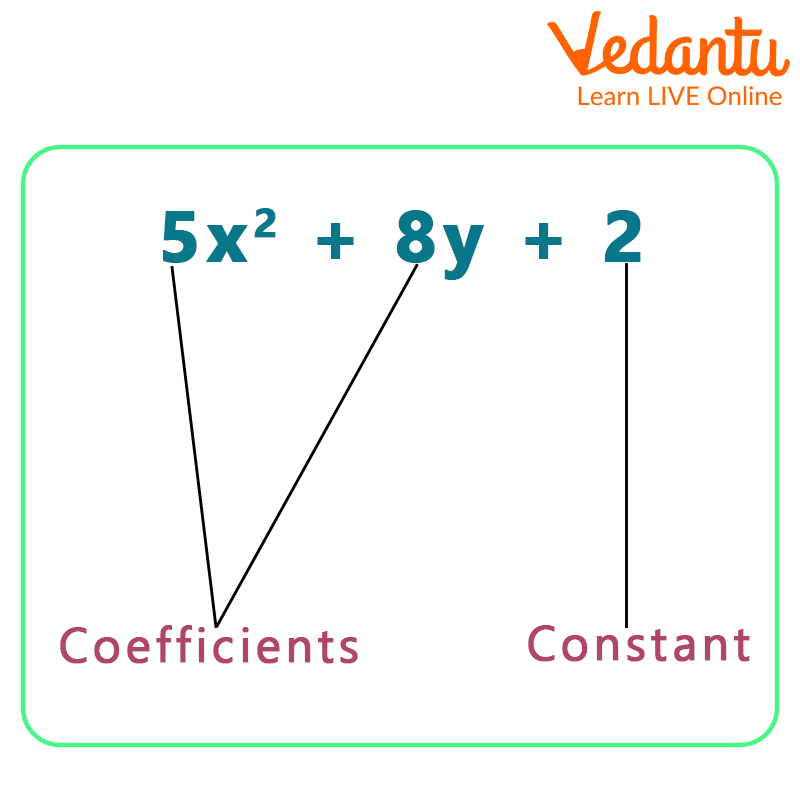
Example 2: Find the numbers that make up the coefficients in the algebraic statement \[3{{\rm{x}}^2} - 2{\rm{y}} + 5\].
Ans: There are three terms in the provided expression. The numerical coefficient in the expression \[{\rm{3}}{{\rm{x}}^{\rm{2}}}\]is 3, the coefficient in the expression \[ - 2{\rm{y}}\] is 2, and 5 is a constant.
Therefore, 3 and -2 are the numerical coefficients.
FAQs on Coefficient Example: Definition, Uses & Solved Questions
1. What is a coefficient in Maths? Explain with an example.
In mathematics, a coefficient is the numerical factor or a constant quantity that is multiplied by a variable in an algebraic term. For example, in the term 7x, the number 7 is the coefficient of the variable x. It essentially tells you 'how many' of the variable you have.
2. How do you find the coefficient of a variable in an expression like 5x² - 9y + 4?
To find the coefficient of a specific variable, identify the term containing that variable and take the number multiplied with it. In the expression 5x² - 9y + 4:
The coefficient of x² is 5.
The coefficient of y is -9 (the sign is always included).
The number 4 is a constant, not a coefficient, as it is not attached to a variable.
3. What is the coefficient when a variable stands alone, such as 'y' or '-y'?
This is a common point of confusion. When a variable appears to stand alone, its coefficient is implicitly 1.
For the term 'y', the coefficient is 1, because y is the same as 1 × y.
For the term '-y', the coefficient is -1, because -y is the same as -1 × y.
4. What is the main difference between a coefficient and a constant?
The key difference lies in their relationship with variables. A coefficient is a multiplicative factor that is always attached to a variable (e.g., the 3 in 3x). A constant is a standalone number in an expression that has a fixed value and is not multiplied by any variable (e.g., the -5 in 3x - 5).
5. Can a coefficient be a variable itself?
Yes, a coefficient can be a variable. This is known as a literal coefficient. In such cases, one variable is considered the main variable, and the other acts as its coefficient. For example, in the term ax², if we are considering the expression in terms of 'x', then 'a' is the literal coefficient of x².
6. Why are coefficients important in real-world applications?
Coefficients are crucial because they represent rates, multipliers, or specific physical properties in formulas that model the real world. For instance:
In Physics, the formula for force (F = ma) uses 'm' (mass) as the coefficient of 'a' (acceleration).
In Finance, in the simple interest formula (I = Prt), 'P' (principal) and 'r' (rate) can be seen as coefficients that determine the amount of interest.
In Chemistry, coefficients are used to balance chemical equations, indicating the ratio of molecules involved in a reaction.
7. In the polynomial 2x³ + x²y - 6y² - 10, what are the numerical coefficients of each term?
To find the numerical coefficients, we look at the number in front of the variables in each term:
The coefficient of the term 2x³ is 2.
The coefficient of the term x²y is 1.
The coefficient of the term -6y² is -6.
The term -10 is the constant of the polynomial.

















