




Step-by-Step Guide to Multiplying Two-Digit Numbers
Multiplication is one of the easiest mathematical operations and it is all about combining numbers or other quantities under specific rules to obtain their product. It's a process of repeated addition of a number with respect to the other number. For example, 6X5 means we add 6, 5 times; 6+6+6+6+6=30. This addition process is very complicated and therefore these multiplication methods come in handy.
Before we start, we should at least know the basics of multiplication which are
Multiplicand (the first number) X Multiplier (the second number) = Product
Any number multiplied by 0 makes the product equal to 0. e.g.- 5x0=0
Any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. e.g.- 5x1=5
Three Simple Methods of Double Digit Multiplication
There are 3 main methods of 2-digit by 2-digit multiplication, which are discussed below.
The traditional method
Box/window method
Lattice method
1. Using the Traditional Method
25X42=?
Step 1: Set the problem up. So, we will have to align them according to their place value.
Step 2: Multiplying the number in the one's place and tens place of the multiplier with the entire multiplicand separately.
Note: We need to put 0 before we do the second digit of the multiplier.
Step 3: Add both the values which we got from multiplying separately.
carried = 5
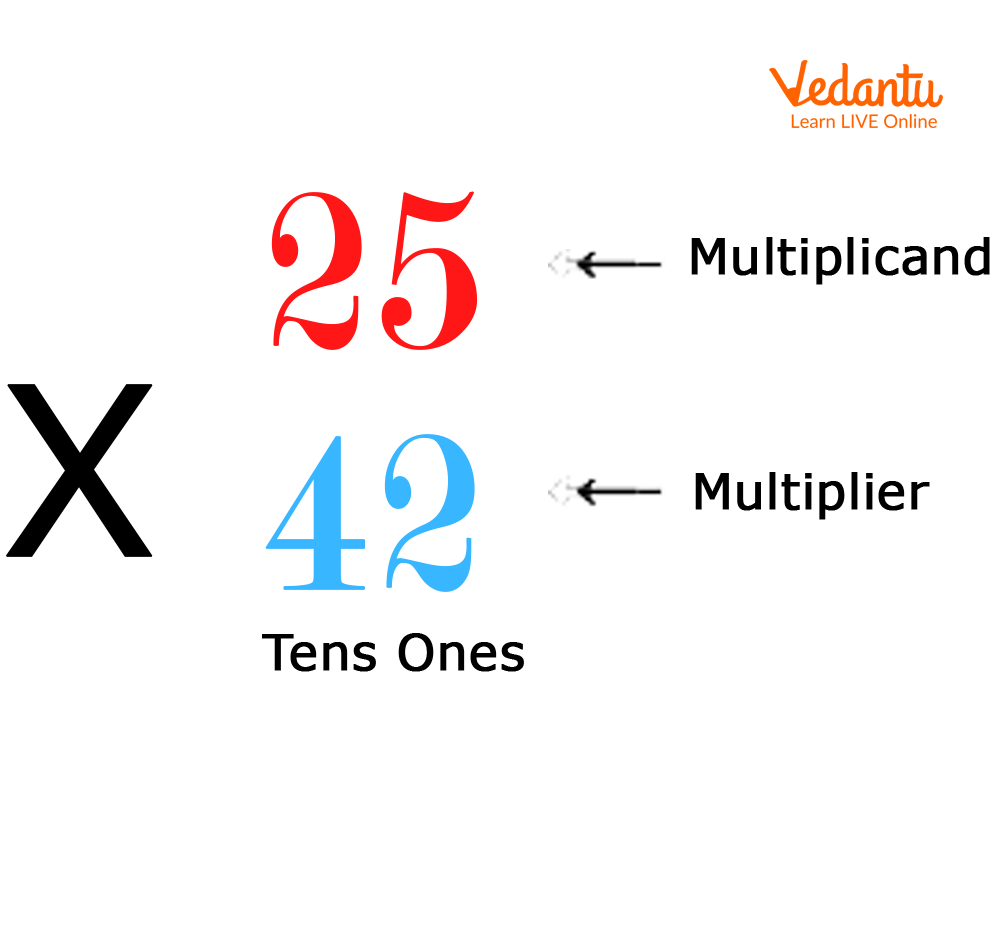
Step 1 of Multiplication
5X2 = 10, 1 will be carried forward to the tens place
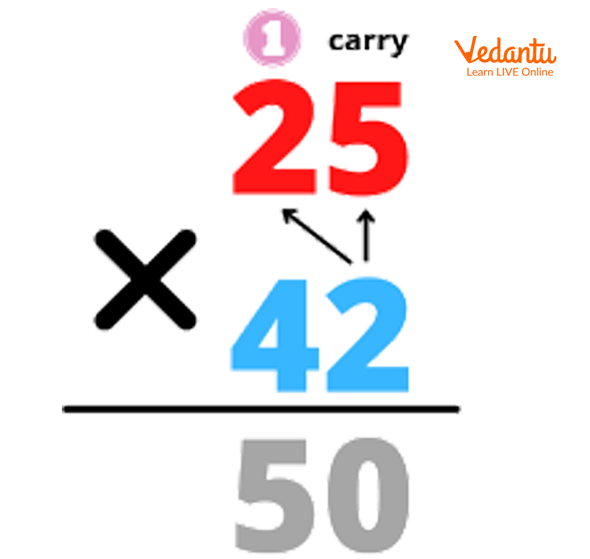
Step 2 of Multiplication
2X2 = 4 and +1 that we
4X5 = 20, 2 carried forward
4X2 = 8 and +2 (carry)= 10. We drop down the 1 as well because there is no further number available to carry.
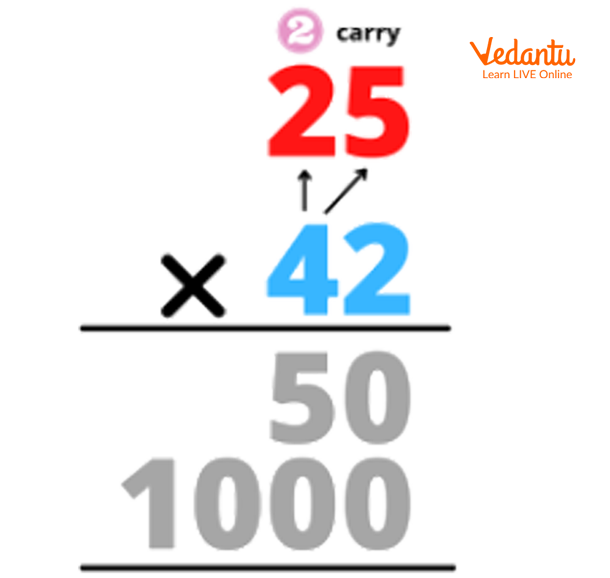
Step 3 of Multiplication
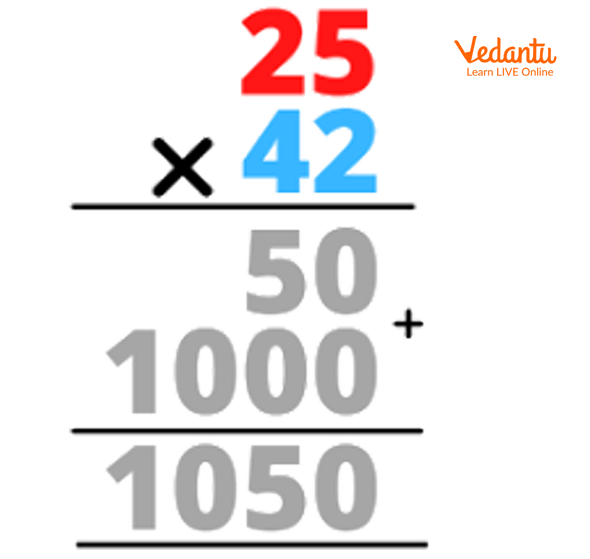
Step 4 of Multiplication
50+1000 we get 1050 which is our final product.
2. Box/Window Method
32X34=?
Step 1: Make a box table or a grid of 2X2 as we are doing a 2-digit multiplication equation.
Step 2: Breaking these factors up into their expanded forms. So, 32 becomes 30 and 2; 34 becomes 30 and 4.
Note: Label the expanded form of the multiplicand on the top and the expanded form of the multiplier on the left-hand side of the grid.
Step 3: We multiply the numbers that meet in each space on the box. Follow the image above.
Step 4: Add all those small products that we got in order to obtain the final product.
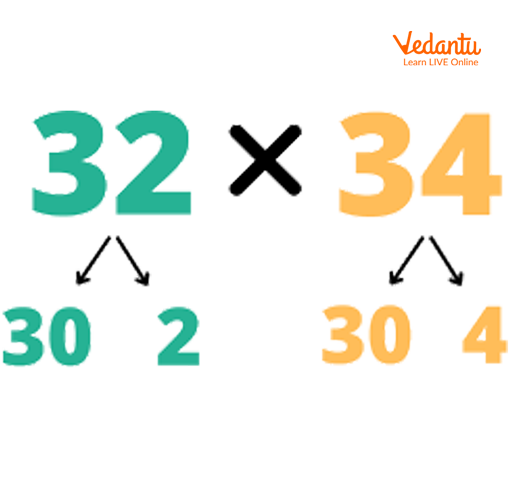
Expanded forms of Factors
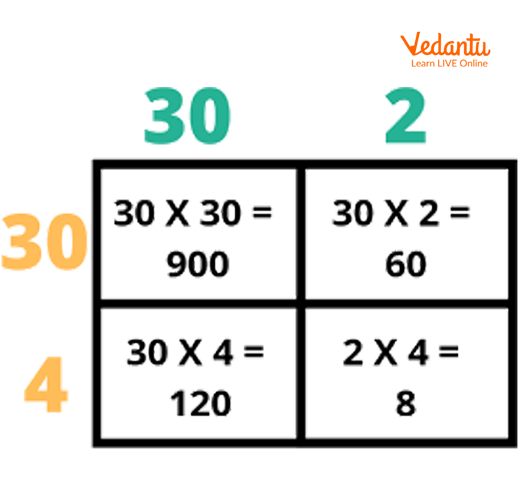
Step 2 of the box Method
900+60+120+8=1088 -> Final Product
3. Lattice Method
25X42=?
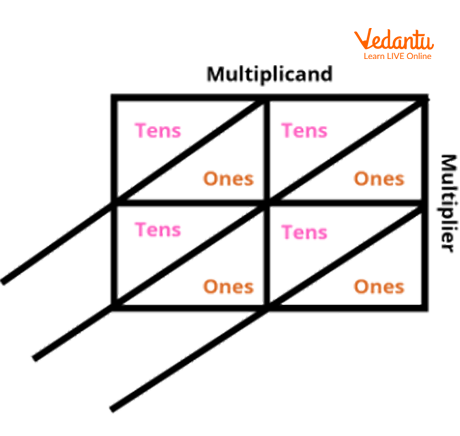
Step 1: Make a grid that matches according to the number of digits required. In this case, we require a 2X2 grid as we are doing 2 digits multiplication.
Note: There is no need to expand the factors so we directly label the multiplicand on top of the grid and the multiplier on the right-hand side of the grid.
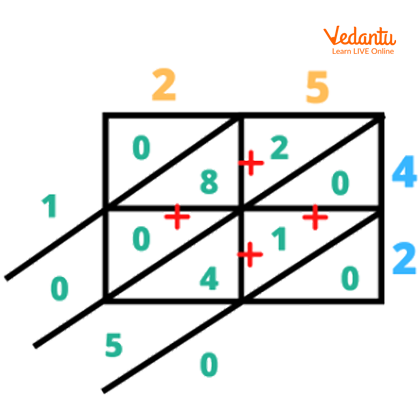
Step 2: Multiply the numbers that meet in each space and write the tens place value of the product on the top of the box and the ones place value of the same on the bottom of the box.
Step 3: Adding the numbers which are in the same lane.
Step 1 of the Lattice Method
5X4=20
2X4=08 (we put 0 in the tens place)
5X2=10
2X2=04
Steps of Lattice Method
We put 0 as it is because there is no other number to add it with.
4+1+0=5
0+8+2=10 (1 has been directly put into the thousands place)
So, our final product is 1050.
Solved Examples
Below are some of the 2-digit by 2-digit multiplication problems:
Q1. 98X66=?
Solution:
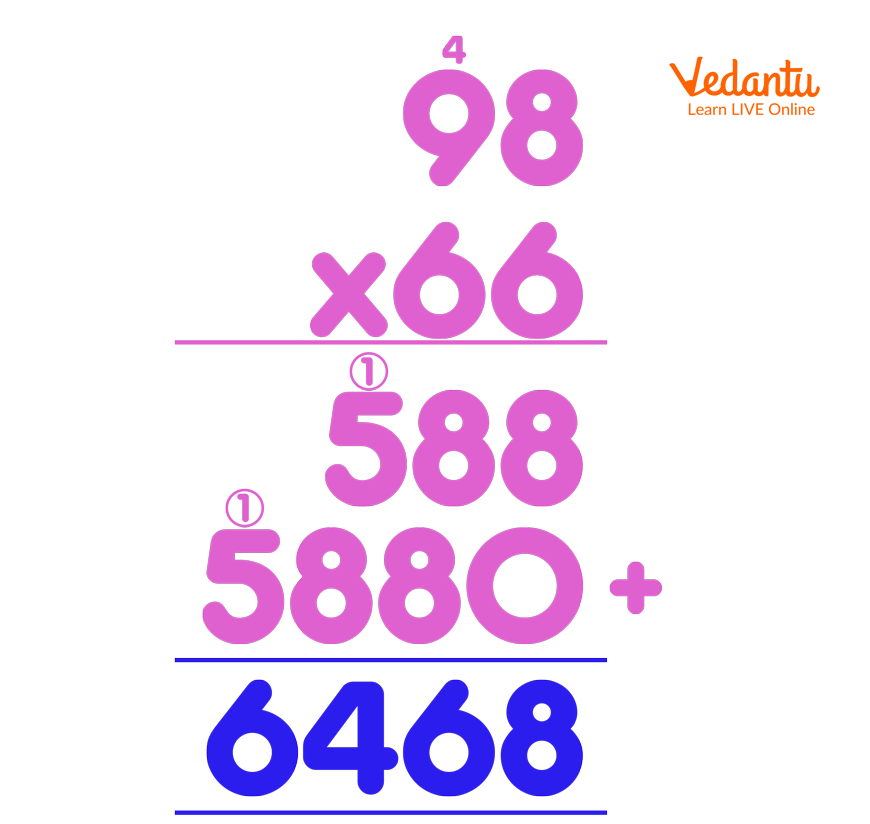
Solution of Q 1
Q2. 75X39=?
Solution:
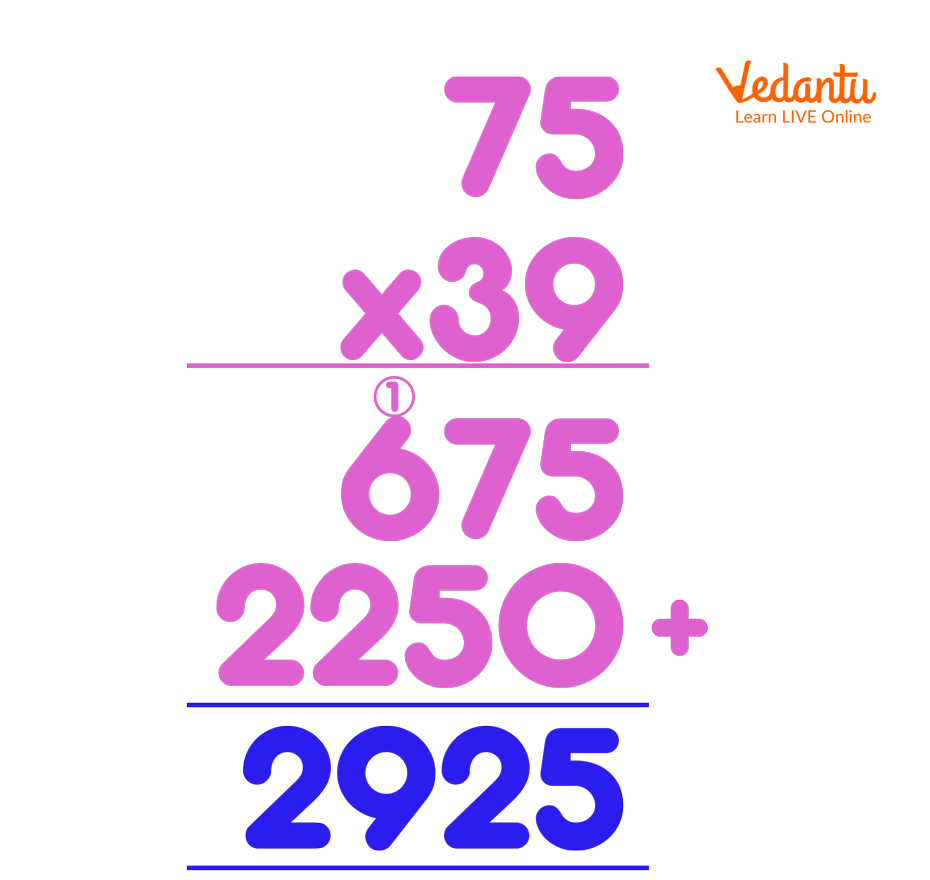
Solution of Q 2
Practice on Your Own
Q1. 62X70=
Ans: 4340
Q2. 49X10=
Ans: 490
Q3. 27X19=
Ans: 513
Summary
In this article, we were able to understand 3 main methods which can be used to multiply numbers which are of 2 digits. If we see, the traditional method is handier and is very easy to multiply numbers that are more than 2 digits as well. We also understood the steps involved in all the 3 methods with the help of images that had the procedures illustrated. You can visit our website to download and practise some multiplication two-digit numbers worksheets for better understanding.
FAQs on 2 Digit Numbers Multiplication Made Simple
1. What does '2-digit number multiplication' mean?
2-digit number multiplication is the process of finding the product of two numbers that both have two digits (i.e., numbers from 10 to 99). For example, multiplying 25 by 42 is an instance of 2-digit multiplication. It is a fundamental arithmetic skill that builds upon single-digit multiplication and an understanding of place value (ones and tens).
2. What is the standard step-by-step method to multiply two 2-digit numbers?
The standard method, also known as long multiplication, involves these steps. Let's multiply 43 by 25:
Step 1: Multiply the ones digit of the bottom number (5) by the top number (43). So, 5 × 3 = 15 (write 5, carry over 1) and 5 × 4 = 20 + 1 (carry-over) = 21. The first partial product is 215.
Step 2: Place a zero in the ones place below your first result. This holds the place value as you are now multiplying by the tens digit.
Step 3: Multiply the tens digit of the bottom number (2) by the top number (43). So, 2 × 3 = 6 and 2 × 4 = 8. The second partial product is 860.
Step 4: Add the two partial products together: 215 + 860 = 1075. The final answer is 1075.
3. Why is understanding place value so important for 2-digit multiplication?
Understanding place value is crucial because it ensures each digit is multiplied by its correct value, not just its face value. For example, in 34 x 12, you are not just multiplying 3 by 1. You are multiplying 30 (3 tens) by 10 (1 ten). Failing to recognise this leads to incorrect partial products and a wrong final answer. When you add a zero in the second step of long multiplication, you are correctly shifting the product to account for multiplying by the 'tens' place, which is a direct application of place value.
4. What is a simple trick to multiply 2-digit numbers mentally?
A simple trick is the 'break-apart' or distributive method. Let's multiply 32 by 15. First, break one number into its tens and ones (e.g., 15 becomes 10 + 5). Now, multiply the other number by each part separately and then add the results:
Multiply 32 by 10, which is easy: 320.
Multiply 32 by 5. You can do this by halving the result of 32 x 10, which gives you 160.
Finally, add the two results: 320 + 160 = 480. This method often makes mental calculation much faster than trying to do long multiplication in your head.
5. How does the box or area model work for 2-digit multiplication?
The box method is a visual way to organise 2-digit multiplication that helps ensure all parts are multiplied correctly. To multiply 53 by 24:
Draw a 2x2 grid (a box with four squares).
Break down each number into its place values and write them on the outside of the box. Write 50 and 3 along the top, and 20 and 4 along the side.
Multiply the numbers for each corresponding row and column to fill the four inner boxes: 50 × 20 = 1000, 3 × 20 = 60, 50 × 4 = 200, and 3 × 4 = 12.
Add all the numbers from the boxes: 1000 + 60 + 200 + 12 = 1272. This method is excellent for visual learners and reinforcing the concept of place value.
6. What is the most common mistake students make in 2-digit multiplication?
The most common mistake is forgetting to add a zero as a placeholder when starting the second line of multiplication. When multiplying the tens digit of the bottom number, the resulting product must start in the tens column. Forgetting the zero causes this product to be misaligned, leading to a significantly smaller and incorrect final answer. Another frequent error is incorrect 'carrying over' when a partial product is 10 or more.
7. Can you provide some real-life examples where 2-digit multiplication is used?
Yes, 2-digit multiplication is used in many everyday situations:
Shopping: Calculating the total cost of buying 12 packets of biscuits if each costs ₹25.
Event Planning: Figuring out how many chairs are needed for an event with 15 rows of 20 chairs each.
Time Calculation: Finding out how many minutes are in 24 hours (24 hours × 60 minutes).
Cooking: Scaling a recipe. If a recipe that serves 12 people needs to be made for 36 people (3 times), you multiply all ingredient quantities by 3.

















