




Human Lungs With Diagram
The lungs and respiratory system work together to allow us to breathe fresh air, expel stale air, and even talk. Let's go on a journey learning about the lungs!
Lungs are bag-like organs or body parts that allow you to breathe. They are a part of the respiratory system of the human body. Lungs are found in all animals that have a backbone and breathe air. When an animal inhales (breaths in), oxygen-rich air enters the lungs. Carbon dioxide and water vapour are ejected from the lungs when an animal exhales (breaths out).
Structure and Simple Lungs Diagram
One on each side of the chest, a human body has two lungs. Between the lungs is where the heart is located. The lobes of the right lung are three rounded sections. The left lung is divided into two lobes. The diaphragm is a strong muscle sheet that rests at the base of each lung. The diaphragm and the rib muscles automatically tighten and relax during normal breathing. This movement aids in the filling and emptying of the lungs.
Left and Right Lobes of the Lungs
A series of tubes transport air into and out of the lungs. The trachea, or windpipe, is a large, tough tube that connects the top of the throat to two branching tubes called bronchi. Each of these tubes connects to a different lobe of the lungs. The bronchi are then divided into bronchioles, a web of smaller tubes. The bronchioles branch off into tiny sacs known as alveoli.
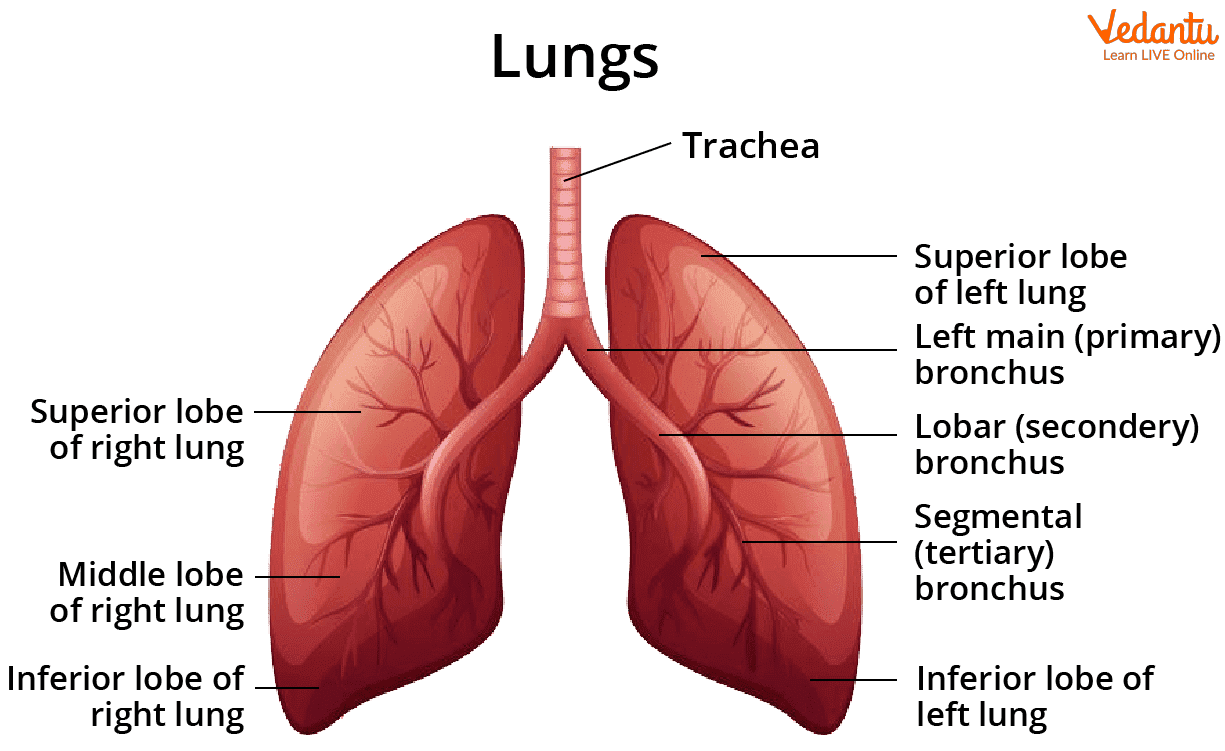
Human Lungs
Lungs for Kids
The lungs weigh roughly 40 grams at birth and double in size after 6 months. The alveoli are small air sacs located at the end of the bronchioles (tiny branches of air tubes in the lungs). The alveoli are the air sac spaces between the lungs and the blood where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged during breathing in and out. Mature pulmonary alveoli begin at 36 weeks of pregnancy and continue to develop until the child is roughly 2 years old. By the age of two, when most of the alveolarisation process has been finished, the total lung weight is around 170 g.
Working of Lungs
When you inhale (breathe in), air enters your lungs and transports oxygen to your blood. Simultaneously, carbon dioxide, a waste gas, travels from your blood to your lungs and is exhaled (breathed out). This process, known as gas exchange, is required for life to exist, which is how the lungs work.
Importance of Lungs
To live, every cell in a body requires oxygen. The air breathed contains oxygen and other gases. When oxygen reaches the lungs, it is carried through the body via the bloodstream. Gas exchange is a necessary process that the lungs and respiratory system carry out on their own.
Lung Infections
Coughing, chest pain, and difficulty breathing are common symptoms of lung problems. Pneumonia and tuberculosis are both serious lung infections. Emphysema and lung cancer are both fatal lung diseases. One of the leading causes of emphysema and lung cancer is smoking.
Interesting Facts About Lungs
The lungs are the most important part of the respiratory system in the human body.
The lungs take in oxygen from the air and expel carbon dioxide.
The lungs transport oxygenated blood (oxygen-rich blood flows from the lungs) to the heart while removing carbon dioxide from the bloodstream.
Humans can vocalise sounds and speak, thanks to their lungs.
The lower respiratory tract includes the human lungs. The nose or nostrils, nasal cavity, mouth, throat (pharynx), and voice box are the major passages and structures of the upper respiratory tract (larynx).
Every 24 hours, an average healthy person will breathe around 2,900 gallons of air.
The lungs have a dome-shaped diaphragm (a thin skeletal muscle) to inhale and expel air.
To create room for the human heart, the left lung is smaller than the right lung.
The upper lobe, middle lobe, and lower lobe are the three lobes of the right lung.
The upper and lower lobes of the left lung are divided into two sections.
The left lung of a female human weighs between 105–515 g, while the right lung weighs between 100–590 g.
The right lung of a human male weighs between 155–720 g on average, whereas the left lung weighs between 110–675 g.
There are approximately 1,500 miles of airways in both human lungs.
Summary
Everybody component requires oxygen from the air a human breathes to survive. The lungs' fragile structure is responsible for breathing and delivering oxygen to the rest of the body. At the same time, it aids in the defence of the body against external threats.
FAQs on Lungs Diagram
1. What is the primary function of the lungs as shown in a diagram of the human respiratory system?
The primary function of the lungs is gas exchange. They take in oxygen from the air you inhale and transfer it into your bloodstream, while removing carbon dioxide, a waste gas, from the blood to be exhaled. This process is essential for cellular respiration and sustaining life.
2. Where are the lungs located in the human body?
The lungs are located within the thoracic cavity, more commonly known as the chest. They are protected by the rib cage and are positioned on either side of the heart. Below the lungs lies a large, dome-shaped muscle called the diaphragm, which plays a crucial role in breathing.
3. What are the key parts to label in a simple lungs diagram for Class 10?
For a standard diagram of the lungs as per the CBSE syllabus, you should be able to label the following key parts:
- Trachea (windpipe)
- Bronchi (the two main branches leading into the lungs)
- Bronchioles (smaller branches off the bronchi)
- Alveoli (tiny air sacs at the end of bronchioles)
- Rib Cage (the protective bony structure)
- Diaphragm (the muscle at the base of the lungs)
- Lobes of the left and right lung
4. What is the main structural difference between the right and left lung?
The main differences are in size and the number of lobes. The right lung is slightly larger and is divided into three lobes (superior, middle, and inferior). The left lung is smaller and has only two lobes (superior and inferior). This size difference accommodates the heart, which is situated slightly to the left side of the chest.
5. How does the diaphragm help in the mechanism of breathing?
The diaphragm is the primary muscle of respiration. During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and flattens, increasing the volume of the chest cavity. This creates lower pressure inside the lungs, causing air to rush in. During exhalation, the diaphragm relaxes and returns to its dome shape, decreasing the chest cavity volume and forcing air out.
6. Why is the left lung smaller than the right lung?
The left lung is smaller to make space for the heart. This anatomical feature is known as the cardiac notch, which is an indentation on the surface of the left lung where the heart sits. This design allows both vital organs to fit efficiently within the confined space of the chest cavity.
7. How is the structure of the alveoli perfectly suited for gas exchange?
The alveoli's structure is optimised for efficient gas exchange in several ways. They are tiny, balloon-like sacs that provide a massive collective surface area (about the size of a tennis court). Their walls are extremely thin—only one cell thick—and are surrounded by a dense network of capillaries. This minimal distance allows for the rapid diffusion of oxygen into the blood and carbon dioxide out of it.
8. What happens to the air as it travels from the trachea to the alveoli?
As air travels through the respiratory tract, it is filtered, warmed, and humidified. The trachea and bronchi are lined with mucus and cilia that trap dust and foreign particles. The air then flows through progressively smaller tubes, the bronchioles, finally reaching the alveoli, where it is at body temperature and saturated with water vapour, ready for efficient gas exchange.
9. Why can't human lungs regenerate after major damage, unlike an organ like the liver?
Human lungs have a very limited capacity for regeneration because of their highly complex and delicate structure. The intricate network of bronchioles and millions of alveoli are too specialised to regrow. While the body can perform minor cellular repairs, it cannot regenerate an entire lobe or large sections of damaged lung tissue, unlike the liver, which has remarkable regenerative capabilities from its simpler structural units.









